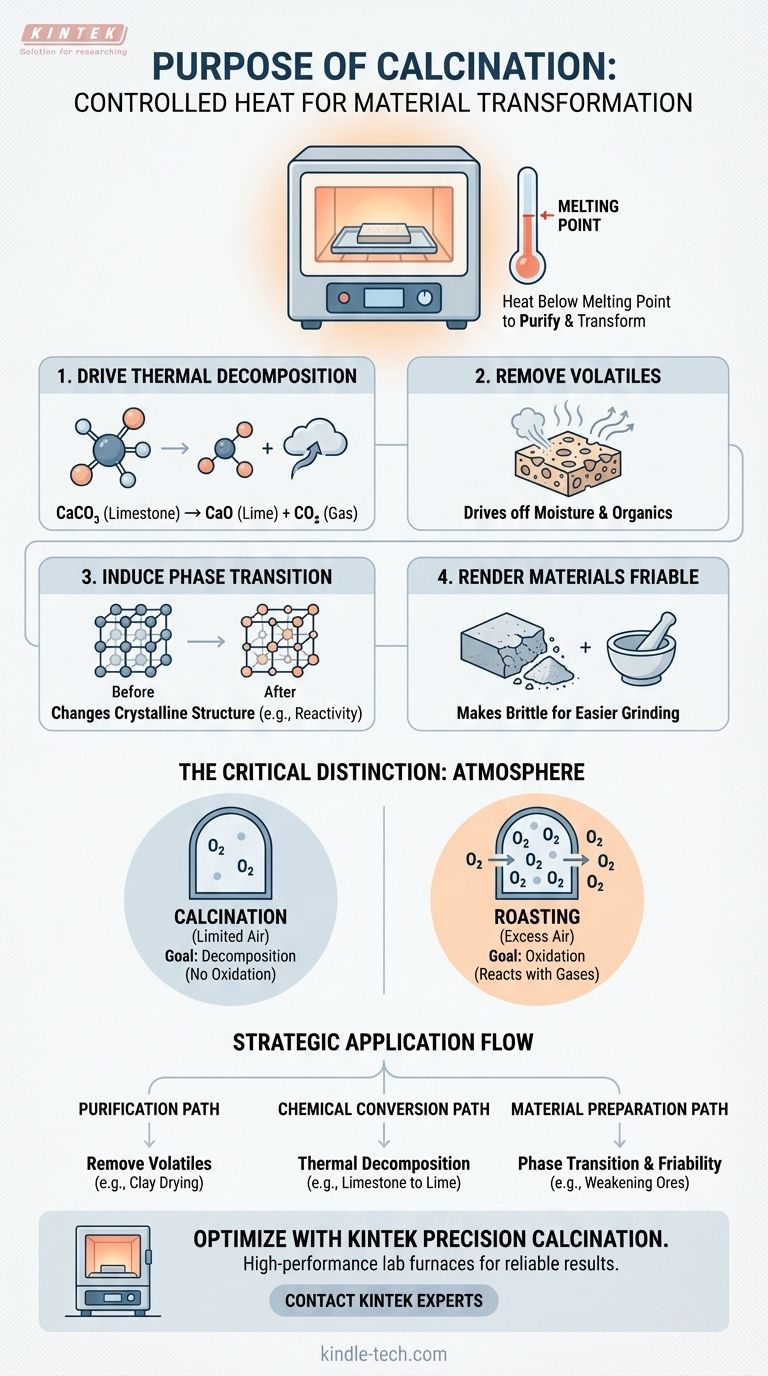
In essence, calcination is a controlled heat treatment process designed to purify and transform solid materials. It involves heating a substance to a high temperature, but crucially, below its melting point, in order to remove volatile components, trigger chemical decomposition, or alter its physical structure.
The core purpose of calcination is not to melt a material, but to fundamentally change its chemical composition or physical state through precise heating, making it suitable for subsequent industrial processes.

The Core Mechanisms of Calcination
To understand the purpose of calcination, it's essential to understand the changes it induces. The process is not a single action but a set of potential transformations driven by heat.
Driving Thermal Decomposition
The most common goal of calcination is thermal decomposition, which means using heat to break down a chemical compound into simpler substances.
A classic example is heating limestone (calcium carbonate, CaCO₃) to produce lime (calcium oxide, CaO) and carbon dioxide (CO₂). The CO₂ is a volatile gas that is driven off, leaving the purified lime behind.
Removing Volatile Substances
Beyond decomposition, calcination is used to remove any unwanted volatile material. This can be as simple as driving off absorbed moisture or as complex as removing chemically bound water or residual organic matter.
This purification step is critical, as these volatiles could otherwise interfere with later chemical reactions or compromise the quality of the final product.
Inducing a Phase Transition
Heat can also be used to change the crystalline structure of a material without changing its chemical formula. This is known as a phase transition.
This change can alter a material's properties, such as its density, hardness, or chemical reactivity, optimizing it for a specific application.
Rendering Materials Friable
A purely physical outcome of calcination is to make a material friable, which means it becomes brittle and easy to crush or grind.
This structural weakening is often a necessary preparatory step, making it easier to handle and process the material in subsequent manufacturing stages.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Distinctions
While powerful, calcination is a specific process that must be distinguished from other thermal treatments to be used correctly.
The Critical Role of Atmosphere
True calcination occurs in the absence or a very limited supply of air (or oxygen). The goal is to break down the material using heat alone, not to react it with gases in the atmosphere.
Calcination vs. Roasting
This is a frequent point of confusion. Roasting is a thermal process performed in an excess of air with the specific goal of oxidizing a material.
For example, roasting is used to convert metal sulfide ores into metal oxides, a completely different chemical goal than the thermal decomposition seen in calcination. Mistaking one for the other would lead to a completely different and undesired product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Calcination is not a one-size-fits-all solution; its application depends entirely on your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is purification: Use calcination to remove water, carbon dioxide, or other volatile impurities from a raw material like clay or bauxite.
- If your primary focus is chemical conversion: Employ calcination to decompose a compound, such as converting a metal carbonate into a more reactive metal oxide for extraction.
- If your primary focus is material preparation: Apply calcination to alter a substance's crystal structure or make it friable for easier downstream processing, such as in catalyst manufacturing.
Ultimately, calcination is a foundational thermal process used to precisely prepare and refine solid materials for their final purpose.
Summary Table:
| Purpose of Calcination | Key Mechanism | Common Example |
|---|---|---|
| Purification | Remove volatile substances (e.g., moisture, CO₂) | Driving off moisture from clay |
| Chemical Conversion | Thermal decomposition of compounds | Converting limestone (CaCO₃) to lime (CaO) |
| Material Preparation | Induce phase transition or make material friable | Weakening ores for easier grinding |
Ready to Optimize Your Material Processing with Precision Calcination?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment, including advanced calcination furnaces, to meet the exacting needs of laboratories and research facilities. Whether you are purifying raw materials, decomposing compounds, or preparing samples for analysis, our solutions deliver the precise temperature control and atmospheric conditions required for reliable results.
Let KINTEK be your partner in achieving superior material transformation. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and discover the ideal calcination solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does a high-temperature calcination furnace contribute to the structural stability of sulfated zirconia catalysts?
- What is the setting of the muffle furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe & Accurate Operation
- What is the advantage and disadvantage of heat treatment? A Guide to Material Enhancement Trade-offs
- What nutrient component is measured by the ash content? The Key to Total Mineral Analysis
- What is the function of a blast drying oven in A356-SiCp composite powder preparation? Ensure Defect-Free Sintering
- What is the purpose of the 400 °C annealing for ceramic green bodies? Ensure Structural Integrity & Prevent Cracking
- What is the necessity of a high-temperature calcination process in the synthesis of CoWO4 nanomaterials? Unlock Purity
- What is the function of a laboratory high-temperature box resistance furnace in the normalizing process? Improve FATT50



















