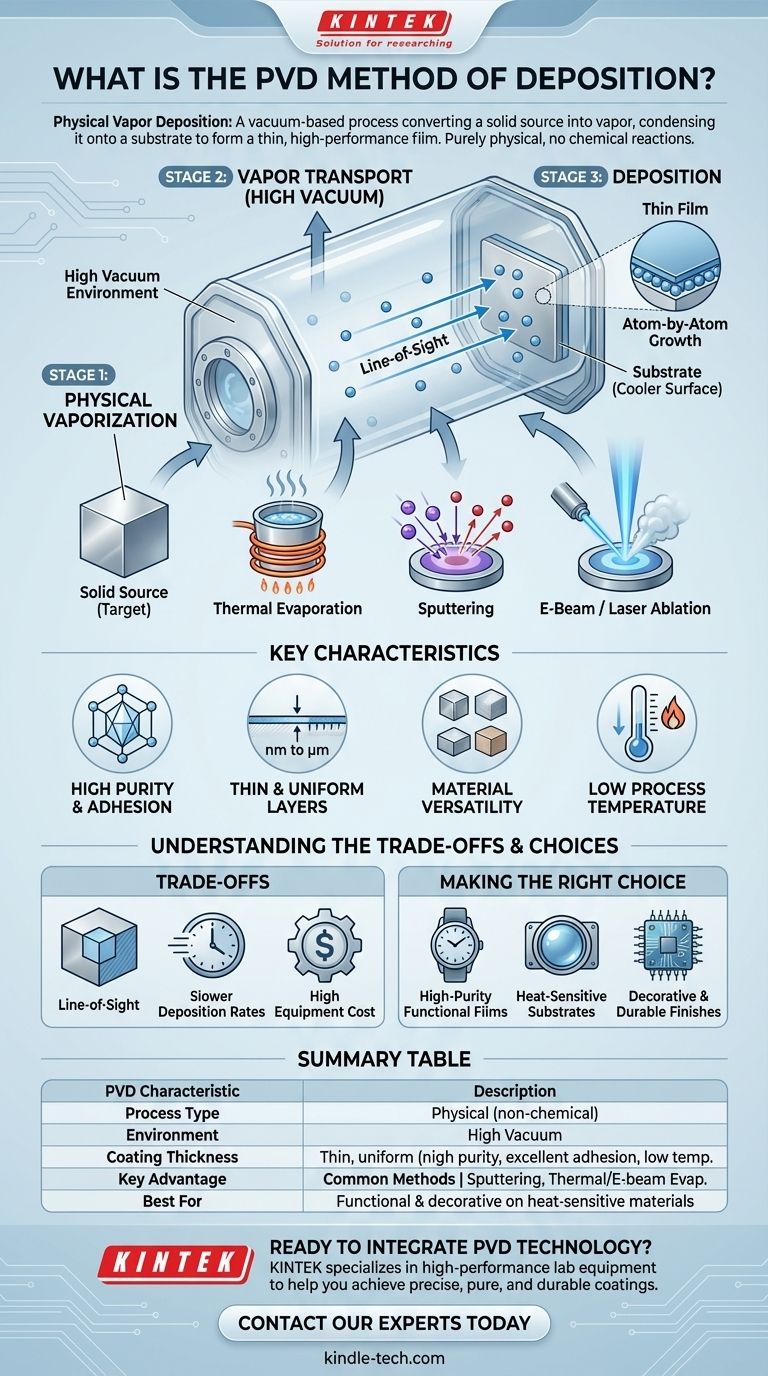
In essence, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a family of vacuum-based coating processes where a solid source material is converted into a vapor, transported through a low-pressure chamber, and then condensed onto a surface (the substrate) to form a thin, high-performance film. The entire process is purely physical; no chemical reactions take place to form the coating.
PVD is best understood as a method of physically transplanting a material from a source to a target. It works atom by atom, offering precise control over the creation of extremely thin, pure, and highly adherent coatings.

Deconstructing the P-V-D Process
The name "Physical Vapor Deposition" perfectly describes its three fundamental stages. Understanding each stage is key to grasping how and why the method works.
Stage 1: Physical Vaporization
The process begins with a solid source material, known as the target. This target is converted into a gaseous vapor phase inside a vacuum chamber. This is the primary distinction between different PVD techniques.
Common methods for vaporization include:
- Thermal Evaporation: The simplest method, where the target material is heated until it evaporates, much like water boiling into steam.
- Sputtering: The target is bombarded with high-energy ions (typically from a gas like argon), which act like a subatomic sandblaster, knocking atoms off the target surface.
- Electron-Beam or Laser Ablation: A highly focused beam of electrons or a high-power laser strikes the target, providing intense, localized energy to vaporize the material.
Stage 2: Vapor Transport
Once the material is in a vapor state, it travels from the source to the substrate. This journey happens in a high vacuum (very low-pressure) environment.
The vacuum is critical because it removes other gas molecules from the chamber. This ensures the vaporized atoms can travel in a straight, unimpeded line to the substrate without colliding with or reacting with air or other contaminants. This is often called a line-of-sight process.
Stage 3: Deposition
When the vapor atoms reach the cooler substrate, they condense back into a solid state. This condensation builds up on the surface one atom at a time, forming a thin, dense, and highly controlled film.
Because the film grows atom by atom, the process allows for exceptional control over the coating's thickness, structure, and density.
Key Characteristics of PVD Coatings
The unique nature of the PVD process imparts specific, desirable characteristics to the resulting films.
High Purity and Adhesion
Because the process occurs in a vacuum and involves no chemical reactions, the deposited film is exceptionally pure, matching the composition of the source material. The energy of the depositing atoms also contributes to excellent adhesion to the substrate.
Thin and Uniform Layers
PVD is renowned for its ability to produce extremely thin films, often just a few microns or even nanometers thick. The line-of-sight nature, often combined with substrate rotation, allows for a very uniform and consistent coating thickness.
Material Versatility
PVD is not limited by a material's chemistry, only by whether it can be vaporized. This makes it an excellent choice for depositing a wide range of materials, including metals, alloys, ceramics, and other compounds, even those with very high melting points.
Low Process Temperature
While the source is vaporized at high energy, the substrate itself can remain at a relatively low temperature. This makes PVD suitable for coating materials, like certain plastics or pre-hardened steels, that cannot withstand the high heat of other processes like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
Understanding the Trade-offs
No process is perfect. Objectivity requires acknowledging PVD's limitations.
The Line-of-Sight Problem
PVD's greatest strength is also a weakness. Since the vapor travels in a straight line, it is difficult to evenly coat complex, three-dimensional shapes with internal surfaces or deep recesses. Exposed surfaces get coated, but "shadowed" areas do not.
Deposition Rates
Compared to wet chemical processes like electroplating, PVD can have slower deposition rates. This can make it less economical for applications that require very thick coatings or have extremely high throughput demands.
Equipment and Cost
PVD systems, which require high-vacuum chambers and sophisticated energy sources, represent a significant capital investment. The complexity of the equipment makes it a high-cost, high-value process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
PVD is a powerful tool when applied correctly. Use these points to guide your decision.
- If your primary focus is high-purity functional films: PVD is an excellent choice for creating layers for optical, electronic, or wear-resistance applications where chemical purity is paramount.
- If you are coating complex 3D shapes: You must account for PVD's line-of-sight nature and determine if substrate rotation is sufficient or if an alternative, more conformal method is required.
- If your substrate is heat-sensitive: PVD's low-temperature operation gives it a distinct advantage over high-temperature chemical processes.
- If your goal is a decorative yet durable finish: PVD is widely used to apply brilliant, hard-wearing metallic finishes on everything from watches to plumbing fixtures.
Ultimately, selecting PVD is a strategic choice for applications demanding precise, pure, and high-performance thin films on a substrate's surface.
Summary Table:
| PVD Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Process Type | Physical (non-chemical) |
| Environment | High Vacuum |
| Coating Thickness | Thin, uniform (nanometers to microns) |
| Key Advantage | High purity, excellent adhesion, low substrate temperature |
| Common Methods | Sputtering, Thermal Evaporation, E-beam Evaporation |
| Best For | Functional & decorative coatings on heat-sensitive materials |
Ready to integrate PVD technology into your R&D or production line?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including PVD systems, to help you achieve precise, pure, and durable coatings for your materials. Whether you're developing new electronics, optical components, or wear-resistant surfaces, our expertise and solutions are tailored to meet your laboratory's specific needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our PVD equipment can advance your projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















