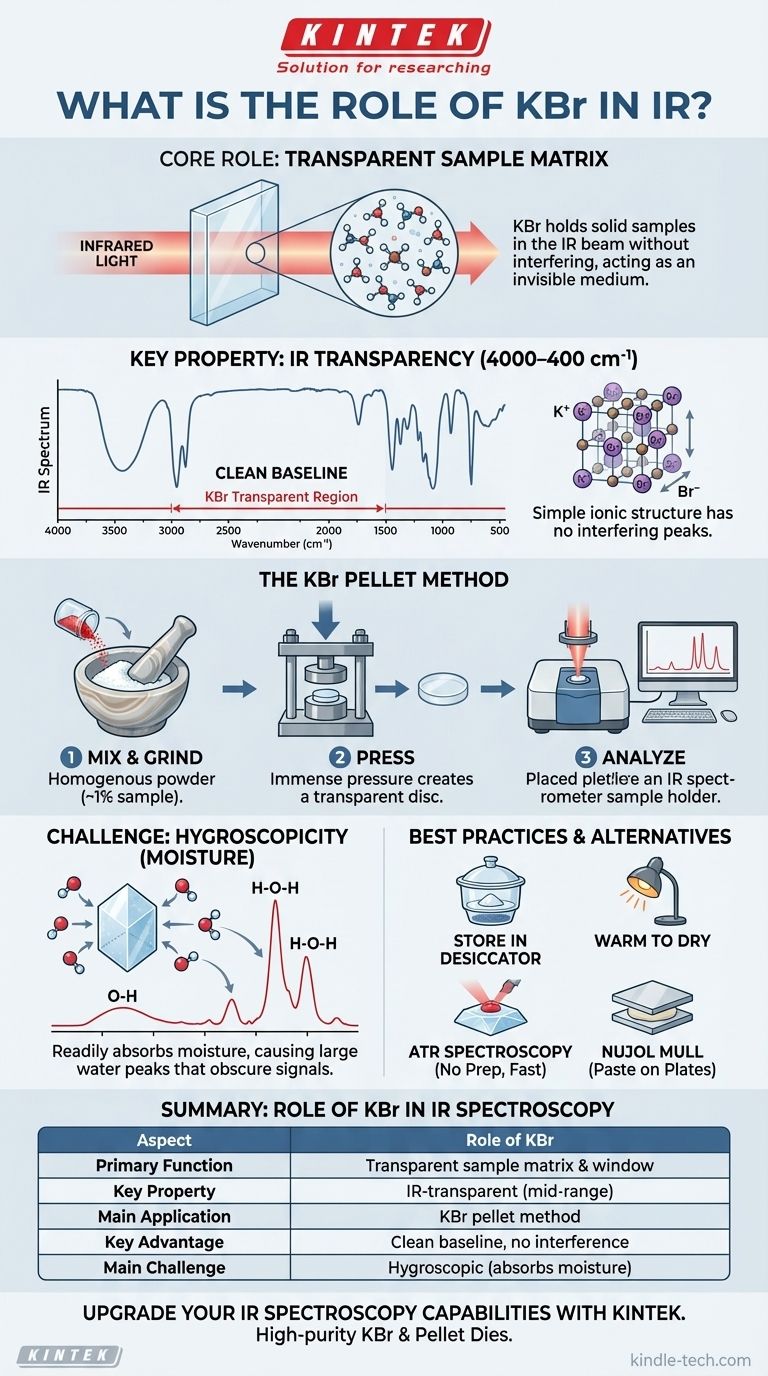
In infrared (IR) spectroscopy, Potassium Bromide (KBr) serves as an ideal sample matrix and window material. Its primary role is to hold a solid sample in the path of the IR beam without interfering with the measurement. Because KBr itself does not absorb light in the most common analytical region of the infrared spectrum, it acts as a transparent medium, allowing the spectrometer to measure the unique absorption of the sample alone.
The core challenge when analyzing solid samples with IR is finding a material to hold them that is invisible to the infrared light. KBr is the industry standard solution because its simple ionic structure is transparent across the mid-infrared range, providing a clear window to observe a sample's molecular vibrations.

Why KBr is the Standard for Solid Samples
The use of KBr is fundamentally tied to a common sample preparation technique known as the KBr pellet method. This method is designed to get a high-quality spectrum from a very small amount of a solid substance.
The Principle of IR Transparency
The single most important property of KBr is its transparency to mid-range infrared radiation (4000–400 cm⁻¹).
Chemical bonds absorb IR light when its frequency matches the bond's natural vibrational frequency. The simple ionic bond between potassium (K⁺) and bromide (Br⁻) in the KBr crystal lattice has a very low vibrational frequency, well below the 400 cm⁻¹ cutoff of most standard instruments.
This means KBr produces no interfering peaks, resulting in a flat, clean baseline against which the sample's true absorption peaks can be accurately measured.
The KBr Pellet Method
This technique involves intimately mixing a small amount of a solid sample (typically ~1% by weight) with high-purity KBr powder.
First, the sample and KBr are ground together to a very fine, homogenous powder using an agate mortar and pestle. This step ensures the sample particles are small enough to prevent scattering of the IR light.
The mixture is then placed into a special die and compressed under immense pressure (several tons). The pressure causes the soft KBr powder to flow and fuse into a thin, semi-transparent or transparent solid disc, known as a pellet. The sample is now trapped and evenly dispersed within this solid KBr matrix, ready for analysis.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
While KBr is an excellent material, it is not without its challenges. Proper handling is essential for acquiring a high-quality spectrum.
The Problem of Moisture (Hygroscopicity)
KBr's most significant drawback is that it is hygroscopic, meaning it readily absorbs moisture from the air.
Water (H₂O) has very strong IR absorption bands—a broad peak for the O-H stretch around 3400 cm⁻¹ and a sharp H-O-H bending peak near 1640 cm⁻¹. If your KBr is "wet," these large water peaks can obscure important signals from your sample in those regions.
Best Practices for Handling KBr
To avoid moisture contamination, spectroscopy-grade KBr must be stored in a desiccator or a drying oven when not in use.
When preparing a pellet, it is best to work quickly. Some labs gently warm the KBr powder under a heat lamp just before use to drive off any adsorbed water.
Alternatives to the KBr Pellet
The challenges associated with KBr pellets have led to the development of other methods.
Nujol mulls involve grinding the solid sample with a drop of mineral oil (Nujol) to create a paste, which is then smeared between two salt plates (often made of KBr or NaCl). This is faster but adds the complication of Nujol's own C-H absorption peaks appearing in the spectrum.
Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR) is a modern, popular alternative that requires almost no sample preparation. The solid is simply pressed against a crystal (like diamond or ZnSe), and the IR beam interacts with the surface. ATR is fast, easy, and avoids all moisture issues related to KBr.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The best sample preparation technique depends on your sample, equipment, and analytical needs.
- If your primary focus is obtaining the highest possible spectral resolution for a stable solid: The KBr pellet method, when performed carefully to exclude all moisture, remains a gold standard for transmission spectroscopy.
- If your primary focus is a fast, routine analysis with minimal sample preparation: Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR) is almost always the superior and more convenient choice in modern laboratories.
- If your sample is sensitive to high pressure or might react with the ionic KBr matrix: A Nujol mull or ATR are safer and more appropriate methods.
Understanding the properties and limitations of your matrix material is the first step toward acquiring a clean, reliable, and interpretable IR spectrum.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Role of KBr in IR Spectroscopy |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Acts as a transparent sample matrix and window material |
| Key Property | IR-transparent in mid-range (4000–400 cm⁻¹) |
| Main Application | KBr pellet method for solid sample analysis |
| Key Advantage | Provides a clean baseline with no interfering peaks |
| Main Challenge | Hygroscopic - requires careful handling to avoid moisture |
| Common Alternatives | ATR spectroscopy, Nujol mulls |
Upgrade Your IR Spectroscopy Capabilities with KINTEK
Struggling with sample preparation for IR analysis? KINTEK specializes in high-purity laboratory equipment and consumables, including spectroscopy-grade Potassium Bromide (KBr) and pellet dies designed for reliable, high-resolution results.
Our products help you:
- Achieve superior spectral clarity with moisture-controlled KBr
- Streamline your solid sample analysis workflow
- Maintain consistent laboratory performance
Whether you're working with traditional transmission spectroscopy or modern ATR techniques, we have the solutions to meet your laboratory's specific needs.
Ready to enhance your IR spectroscopy results? Contact our experts today to discuss your application requirements and discover how KINTEK can support your research and quality control processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Grinding Mill Mortar Grinder for Sample Preparation
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
People Also Ask
- What role do laboratory hydraulic presses play in the post-processing of iron-based aerogels? Expert Compaction Guide
- What are the advantages of a hydraulic press machine? Unmatched Power, Precision & Cost-Effectiveness
- How does an industrial-grade hydraulic press ensure the accuracy of electromagnetic shielding tests? Precision Molding
- What is the role of a laboratory hydraulic press in LLZO pellet preparation? Enhance Ionic Conductivity via Cold Pressing
- Why KBr disc is used in IR spectroscopy? Achieve High-Resolution Analysis of Solid Samples
- What is the purpose of using rolling equipment or hydraulic presses for aluminum welds? Enhance Joint Strength Now
- How are XRF samples prepared? Master the Pressed Pellet vs. Fusion Bead Methods
- What should the mortar and pestle be cleaned with before preparing a KBr pellet for IR? Ensure Accurate IR Spectroscopy Results










