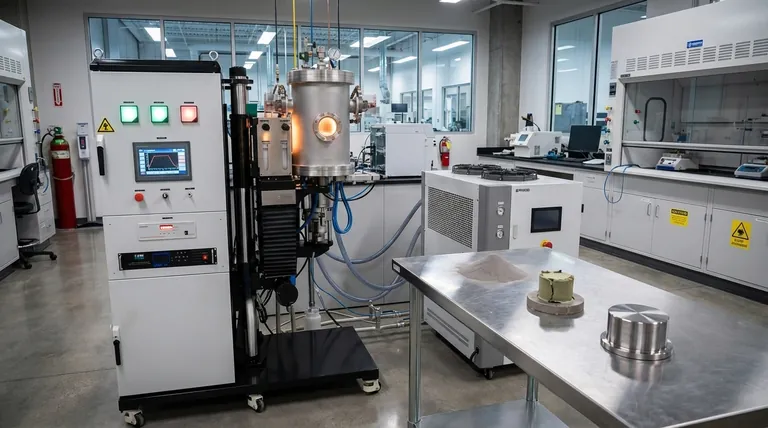
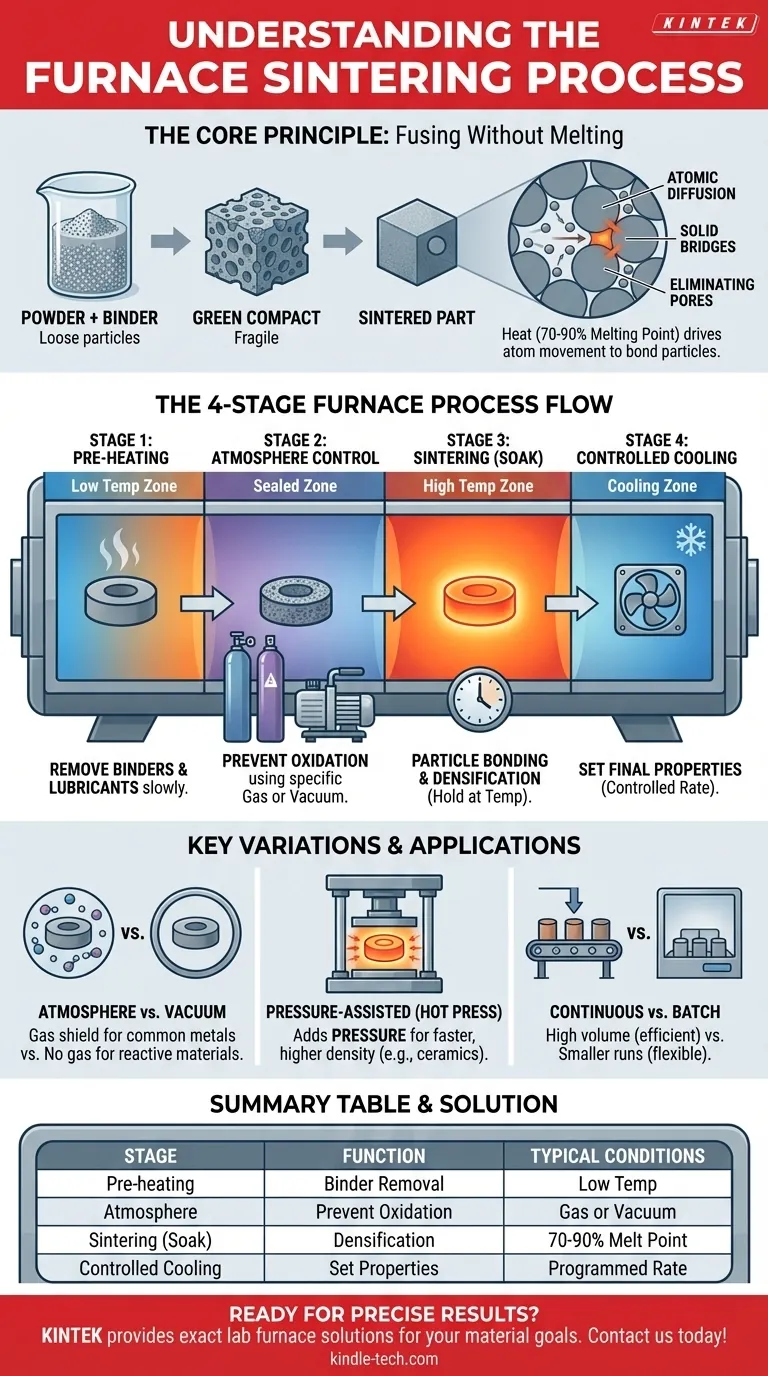
In short, the sintering process uses a furnace to transform a compacted powder into a solid, dense mass by applying heat. Crucially, this is done at a temperature below the material's melting point, causing the particles to fuse together through atomic diffusion rather than by melting and re-solidifying.
The core principle of sintering is not to melt the material, but to give its atoms enough energy to move across particle boundaries. This migration eliminates the pores between particles, creating a strong, unified component from a powder.

The Core Principle: Fusing Without Melting
To truly understand sintering, you must grasp its fundamental mechanism. It's a process of solid-state transformation driven by heat and, in some cases, pressure.
From Powder to Solid
The starting point is always a material in powdered form. This powder is often mixed with a binding agent and compressed into a desired shape, known as a "green compact" or "green part." This initial part is fragile and highly porous.
The Role of Heat
Heat is the primary catalyst in sintering. The furnace raises the temperature of the green compact to a precise point, typically 70-90% of its absolute melting temperature.
The Mechanism of Atomic Diffusion
At this elevated temperature, the atoms within the material become highly agitated. They gain enough energy to migrate, or diffuse, across the contact points where individual powder particles touch. This movement of atoms effectively builds "bridges" between particles.
The Goal: Densification
As these bridges form and widen, the particles pull closer together. This process eliminates the empty space, or pores, between the particles. The result is a significant increase in the part's density and strength, often accompanied by a predictable amount of shrinkage.
The Key Stages of Sintering in a Furnace
While specific parameters vary by material, the process within a furnace follows a clear, multi-stage path. Many modern industrial furnaces are designed with different zones to perform these stages continuously.
Stage 1: Pre-heating and Binder Removal
The first heating phase is a low-temperature step. Its purpose is to slowly burn off any lubricants or organic binding agents used during the initial compaction stage. Doing this too quickly can damage the part.
Stage 2: Atmosphere Control
As the temperature rises, controlling the furnace's internal atmosphere becomes critical. A specific gas (like nitrogen or argon) or a vacuum is used to prevent the material from oxidizing or having other unwanted chemical reactions at high temperatures. This ensures the material's chemical purity.
Stage 3: Sintering (Holding at Temperature)
This is the main event. The furnace holds the material at the precise sintering temperature for a set period. During this "soak time," atomic diffusion is most active, causing the particles to bond, the pores to shrink, and the part to densify into a solid mass.
Stage 4: Controlled Cooling
Finally, the part is cooled in a highly controlled manner. The cooling rate can be just as important as the heating temperature for determining the final metallurgical properties, such as hardness and strength, of the finished component.
Understanding the Key Variations
Not all sintering processes are identical. The equipment and parameters are adapted based on the material and the desired outcome.
Atmosphere vs. Vacuum Sintering
An atmosphere furnace surrounds the part with a specific, non-reactive gas to protect it. A vacuum furnace removes all gases, which is critical for highly reactive metals that could be contaminated by even trace amounts of atmospheric gases.
Pressure-Assisted Sintering
Some processes, like hot press sintering, apply high external pressure to the part while it is being heated. This pressure mechanically forces the particles together, which can significantly speed up densification, allow for lower sintering temperatures, and achieve near-perfect density, especially in advanced ceramics.
Continuous vs. Batch Furnaces
For high-volume production, continuous furnaces are common. Parts move on a conveyor belt through different zones, each set to a specific temperature and atmosphere to correspond with a stage of the sintering process. Batch furnaces process one load at a time, which is more suitable for smaller runs or complex heating profiles.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal sintering approach is dictated entirely by the material you are working with and the final properties your component requires.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of common metal parts: A continuous atmosphere furnace provides the most efficient and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density in advanced ceramics: Hot press sintering, which combines high heat and pressure, is the necessary approach.
- If your primary focus is processing highly reactive or specialty metals: A vacuum furnace is essential to prevent oxidation and ensure material purity.
Ultimately, sintering is a precise thermal process that enables the creation of strong, complex, and net-shape parts from simple powders.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Stage | Key Function | Typical Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-heating | Binder/Lubricant Removal | Low Temperature |
| Atmosphere Control | Prevent Oxidation/Contamination | Specific Gas or Vacuum |
| Sintering (Soak) | Particle Bonding & Densification | 70-90% of Melting Point |
| Controlled Cooling | Set Final Material Properties | Programmed Cooling Rate |
Ready to achieve precise, high-quality results with your powder materials? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing the exact furnace technology—from atmosphere to vacuum and hot press systems—that your laboratory needs for successful sintering. Let our experts help you select the right solution for your material and production goals. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- Does sintering use diffusion? The Atomic Mechanism for Building Stronger Materials
- Why is a high vacuum environment necessary in sintering equipment for TiAl alloys? Ensure High-Purity Metal Bonding
- Why must green bodies produced via binder jetting undergo treatment in a vacuum sintering furnace?
- What are the factors influencing shrinkage during sintering? Control Dimensional Changes for Precision Parts
- How does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace facilitate the post-treatment of Zirconia coatings?



















