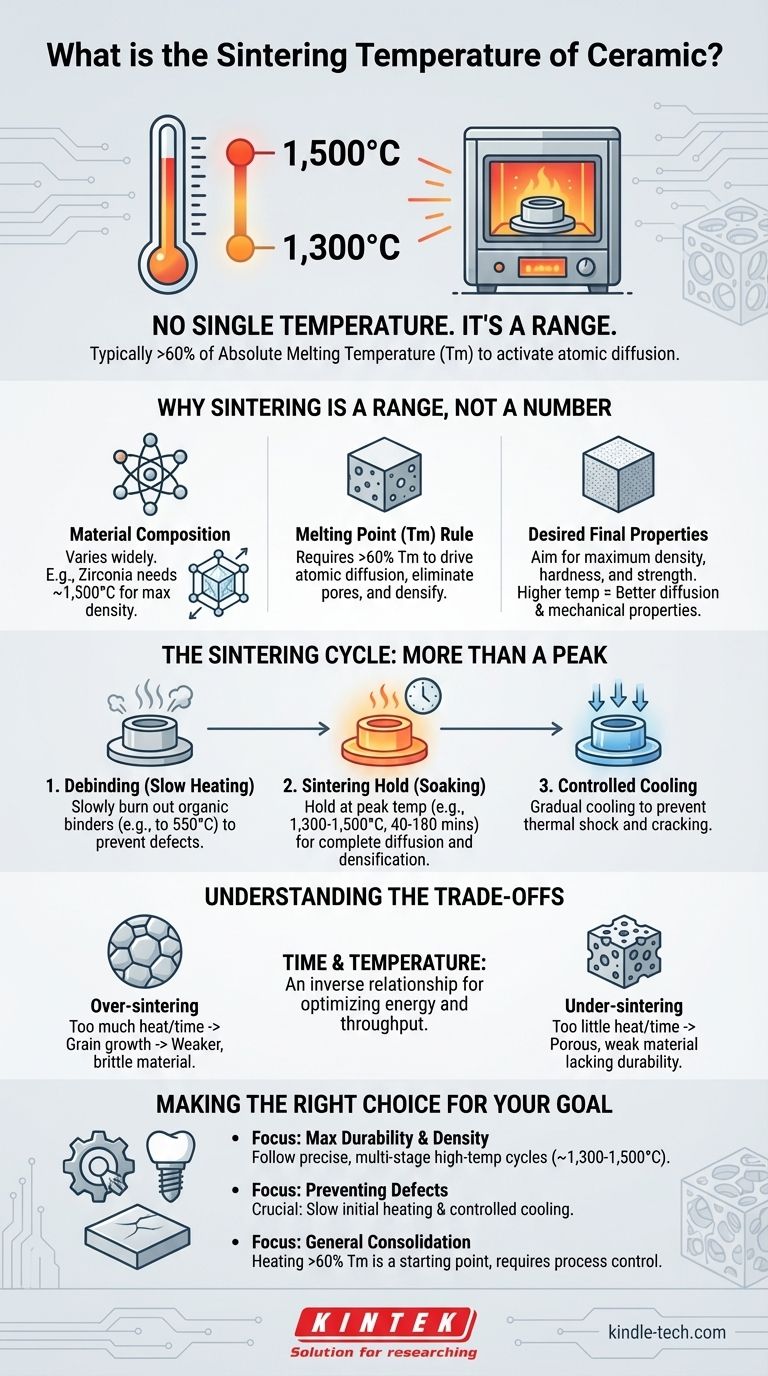
There is no single sintering temperature for ceramic. The correct temperature is entirely dependent on the specific material's composition and the desired final properties, but it generally falls in a high-temperature range, often between 1,300°C and 1,500°C for advanced ceramics like zirconia. Sintering requires a temperature high enough to activate atomic diffusion, which is typically greater than 60% of the material's absolute melting temperature.
The core objective of sintering is not simply to heat ceramic, but to achieve maximum density and strength. Therefore, the "correct" temperature is a carefully engineered variable in a multi-stage process designed to consolidate powder into a durable, solid object.
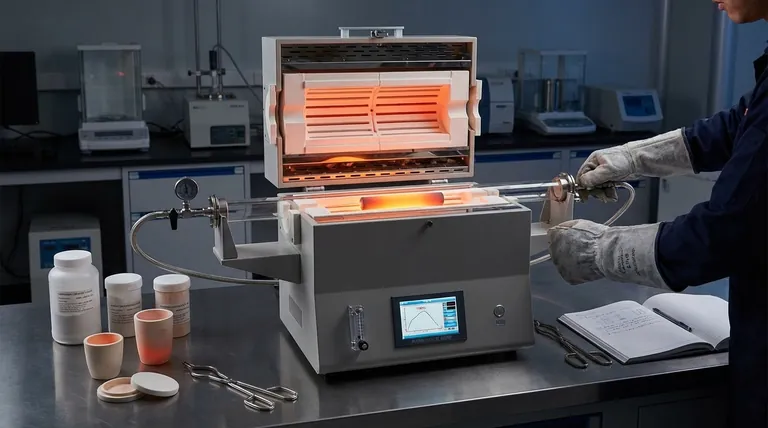

Why Sintering Temperature Is a Range, Not a Number
The term "ceramic" covers a vast family of materials, from common clays to advanced engineering compounds. Each has a unique thermal profile required to achieve proper consolidation.
The Fundamental Principle: The Role of Melting Point
Sintering works by using thermal energy to drive atomic diffusion between particles. This process reduces the surface area of the powder, eliminates pores, and densifies the material.
A reliable rule of thumb is that the sintering temperature must be greater than 60% of the material's melting temperature (Tm). This provides enough energy for atoms to move and bond across particle boundaries without fully melting the object.
Material Composition Is Key
Different ceramics require vastly different temperatures. For example, zirconia undergoes a crystalline change around 1,100°C to 1,200°C.
However, to achieve its renowned hardness and near-total density (~99%), it is typically sintered at a much higher temperature, closer to 1,500°C. This higher temperature maximizes the diffusion process, resulting in the superior mechanical properties the material is known for.
The Goal: Achieving Final Properties
The ultimate purpose of sintering is to produce a dense, non-porous material. It is this density that imparts the exceptional qualities of sintered ceramic.
These properties include extreme hardness, resistance to scratches and high temperatures, and an imperviousness to water, stains, and UV rays. An incorrect sintering temperature will fail to achieve the density needed for these characteristics.
The Sintering Cycle: More Than a Peak Temperature
Effective sintering is not about reaching a single temperature but about controlling a complete thermal profile. This cycle is a carefully planned journey of heating and cooling.
Stage 1: Initial Heating and Debinding
Before reaching the peak sintering temperature, the part is heated slowly. A typical cycle might involve heating to 225°C and then to 550°C for an extended period.
This initial phase, known as debinding, is critical for burning out organic binders mixed with the ceramic powder. Rushing this stage can trap gases and cause cracks or defects in the final part.
Stage 2: The Sintering Hold (Soaking)
Once at the peak temperature (e.g., 1,300°C), the part is held there for a specific duration, often from 40 to 180 minutes.
This "soaking" period is as important as the temperature itself. It allows time for the diffusion process to complete, pores to close, and the material to reach its target density.
Stage 3: Controlled Cooling
Finally, the part is cooled at a controlled rate. Rapid cooling can induce thermal shock, creating internal stresses that lead to catastrophic cracking.
A programmed cooling phase, such as stepping down to 600°C before a final furnace cool, ensures the part remains stable and achieves its full potential strength.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right sintering profile involves balancing competing factors to avoid common pitfalls.
Over-sintering: The Risk of Too Much Heat
If the temperature is too high or the hold time is too long, a phenomenon called grain growth can occur. While the part becomes dense, the excessively large crystalline grains can actually weaken the final material, making it more brittle.
Under-sintering: The Cost of Too Little Heat
If the temperature is too low or the hold time is too short, the part will not reach full density. It will remain porous, weak, and will lack the durability, water resistance, and strength that sintered ceramics are valued for.
The Time-Temperature Balance
There is an inverse relationship between time and temperature in sintering. A process can sometimes achieve similar density by using a slightly lower temperature for a significantly longer hold time. This balance is a key consideration in industrial production to optimize for energy costs and furnace throughput.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal sintering profile is dictated entirely by your material and your performance requirements.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and density (e.g., for engineering or dental parts): You must follow the material manufacturer's precise, multi-stage thermal cycle, which often involves peak temperatures between 1,300°C and 1,500°C.
- If your primary focus is preventing defects: You must pay critical attention to the slow initial heating for debinding and the controlled cooling phase to prevent cracking from thermal shock.
- If your primary focus is general consolidation (e.g., non-structural components): The principle of heating above 60% of the material's melting point is a valid starting point, but achieving optimal properties still requires careful process control.
Ultimately, mastering sintering is about controlling a complete thermal journey to engineer the final properties of your ceramic material.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Influence on Sintering Temperature |
|---|---|
| Material Composition | Different ceramics (e.g., zirconia) have unique melting points, dictating the required heat. |
| Melting Point (Tm) | Sintering typically requires a temperature >60% of the material's absolute melting temperature. |
| Desired Final Properties | Maximum density and strength (e.g., for dental parts) demand precise, high-temperature cycles (~1,300°C - 1,500°C). |
| Sintering Cycle Stages | The complete profile (debinding, soaking, cooling) is as critical as the peak temperature itself. |
Achieve precise, high-temperature sintering for your ceramic materials with KINTEK.
Our advanced lab furnaces are engineered for the exacting control required in multi-stage sintering cycles, from careful debinding to high-temperature soaking and controlled cooling. Whether you are developing advanced engineering components, dental ceramics, or other high-performance materials, KINTEK's equipment helps you achieve maximum density, strength, and durability while preventing defects like cracking and grain growth.
Contact us today to discuss your specific ceramic sintering needs and how our solutions can enhance your process efficiency and final product quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- What is the function of a corundum furnace tube in chlorine corrosion tests? Ensure Purity in High-Heat Experiments
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control



















