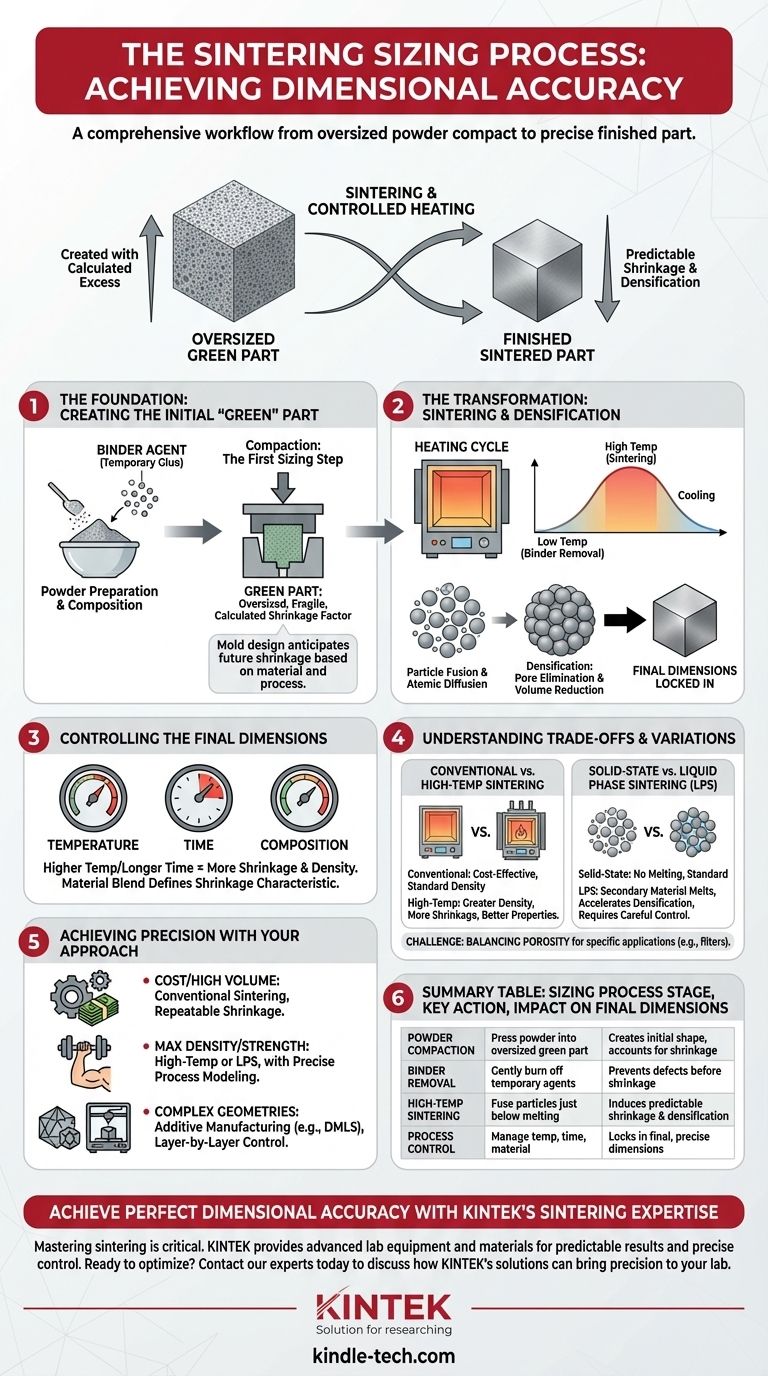
In sintering, the sizing process is not a single action but a comprehensive workflow designed to produce a finished part with precise dimensions. It begins with the mechanical formation of an oversized component from powder and concludes with a controlled heating cycle where the part predictably shrinks into its final, target size. This management of shrinkage is the central challenge and goal of sizing.
The core challenge in sintering is achieving dimensional accuracy. The solution is a two-part strategy: first, create an oversized, preliminary shape called a "green part," and second, use a precisely controlled heating process to induce a predictable amount of shrinkage, consolidating the part to its final, specified dimensions.

The Foundation: Creating the Initial "Green" Part
The journey to a finished sintered component starts with creating a fragile, oversized precursor. The accuracy of this initial stage is fundamental to the accuracy of the final product.
Powder Preparation and Composition
Before any shaping occurs, the primary material powder is mixed. This blend often includes alloying elements to achieve desired mechanical properties and a temporary binding agent.
The binding agent, typically a wax or polymer, acts as a temporary glue. Its sole purpose is to hold the loose powder particles together in a cohesive shape during the initial stages.
Compaction: The First Sizing Step
This is the first critical sizing stage. The prepared powder blend is loaded into a die or mold cavity that reflects the desired shape of the part, but is intentionally oversized.
High pressure is then applied, compacting the powder into a solid, albeit fragile, form. This compressed component is known as the "green part." It has the basic shape but lacks the strength and density of the final product.
The Role of the Oversized Design
The mold for the green part is engineered to account for the shrinkage that will occur later. Calculating this shrinkage factor is a key aspect of sintering design, relying on the specific material composition and process parameters.
The Transformation: Sintering and Densification
The green part is then moved to a sintering furnace, where heat transforms it from a fragile compact into a dense, unified solid. This is where the final dimensions are locked in.
The Heating Cycle: From Green to Solid
The process begins with a low-temperature stage to slowly burn off or evaporate the binding agent used during compaction. This must be done carefully to prevent defects in the part.
After the binder is removed, the temperature is raised to just below the melting point of the primary material. This high heat is maintained for a specific duration.
The Mechanism of Shrinkage and Densification
At this elevated temperature, the individual powder particles begin to fuse at their contact points. This atomic diffusion across particle boundaries closes the microscopic gaps, or porosity, between them.
As these pores are eliminated, the part undergoes densification, becoming more solid. This reduction in internal volume causes the entire component to shrink in a controlled and predictable manner.
Controlling the Final Dimensions
The final size of the component is determined by three main factors: temperature, time, and composition. Higher temperatures or longer times in the furnace generally lead to more shrinkage and higher density. The material blend itself also has a predefined shrinkage characteristic.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Variations
Not all sintering processes are the same. The chosen technique directly impacts shrinkage, density, and the final properties of the component, presenting a series of engineering trade-offs.
Conventional vs. High-Temperature Sintering
Conventional sintering is a cost-effective and widely used method. However, high-temperature sintering can achieve greater density and superior mechanical properties by further reducing porosity. The trade-off is that it typically causes more shrinkage, which must be precisely managed.
Solid-State vs. Liquid Phase Sintering (LPS)
In standard solid-state sintering, particles fuse without melting. In Liquid Phase Sintering (LPS), a secondary material with a lower melting point is included in the powder mix. This material melts and flows into the gaps between the solid primary particles, dramatically accelerating densification.
While LPS can produce very dense parts quickly, it can also alter the final material properties and requires careful control to manage the liquid flow and potential part distortion.
The Challenge of Porosity
While the goal is often to minimize porosity, some applications, like self-lubricating bearings or filters, intentionally leave a certain amount of controlled porosity. In these cases, the sizing process is balanced to achieve the target dimensions while maintaining the required pore network.
Achieving Precision in Your Sintering Process
Your approach to sizing will depend entirely on the final goal for your component. The key is to match the process to the desired outcome of cost, performance, or geometric complexity.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness and high volume: Rely on conventional sintering with a well-characterized powder mix to ensure repeatable and predictable shrinkage.
- If your primary focus is maximum density and mechanical strength: Consider high-temperature or liquid phase sintering, but invest in the process modeling required to precisely account for the increased shrinkage.
- If your primary focus is creating highly complex geometries: Explore additive manufacturing methods like Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS), where sizing is controlled layer-by-layer during the printing process itself.
Mastering the sizing process is about understanding that shrinkage is not a flaw, but a fundamental and controllable mechanism of sintering.
Summary Table:
| Sizing Process Stage | Key Action | Impact on Final Dimensions |
|---|---|---|
| Powder Compaction | Press powder into an oversized 'green part' | Creates the initial shape, accounting for future shrinkage |
| Binder Removal | Gently burn off temporary binding agents | Prevents defects before shrinkage begins |
| High-Temp Sintering | Fuse particles just below melting point | Induces predictable shrinkage and densification |
| Process Control | Manage temperature, time, and material composition | Locks in the final, precise dimensions of the part |
Achieve Perfect Dimensional Accuracy with KINTEK's Sintering Expertise
Mastering the sintering sizing process is critical for producing high-performance, precision components. Whether your goal is cost-effective mass production or achieving maximum part density, the right equipment and consumables are essential for predictable results.
KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and materials your laboratory needs to excel. We supply reliable sintering furnaces, high-quality powder blends, and the technical support to help you perfectly control shrinkage and achieve your target dimensions every time.
Ready to optimize your sintering process? Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can bring precision and reliability to your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the sintering temperature of zirconium? A Guide to the 1400°C-1600°C Range for Dental Labs
- What is the temperature of sintering zirconia? Mastering the Protocol for Perfect Dental Restorations
- What is the sintering time for zirconia? A Guide to Precise Firing for Optimal Results
- What is one of the newest applications for dental ceramics? Monolithic Zirconia for Full-Arch Bridges
- What are the white spots on zirconia after sintering? A Guide to Diagnosing and Preventing Defects



















