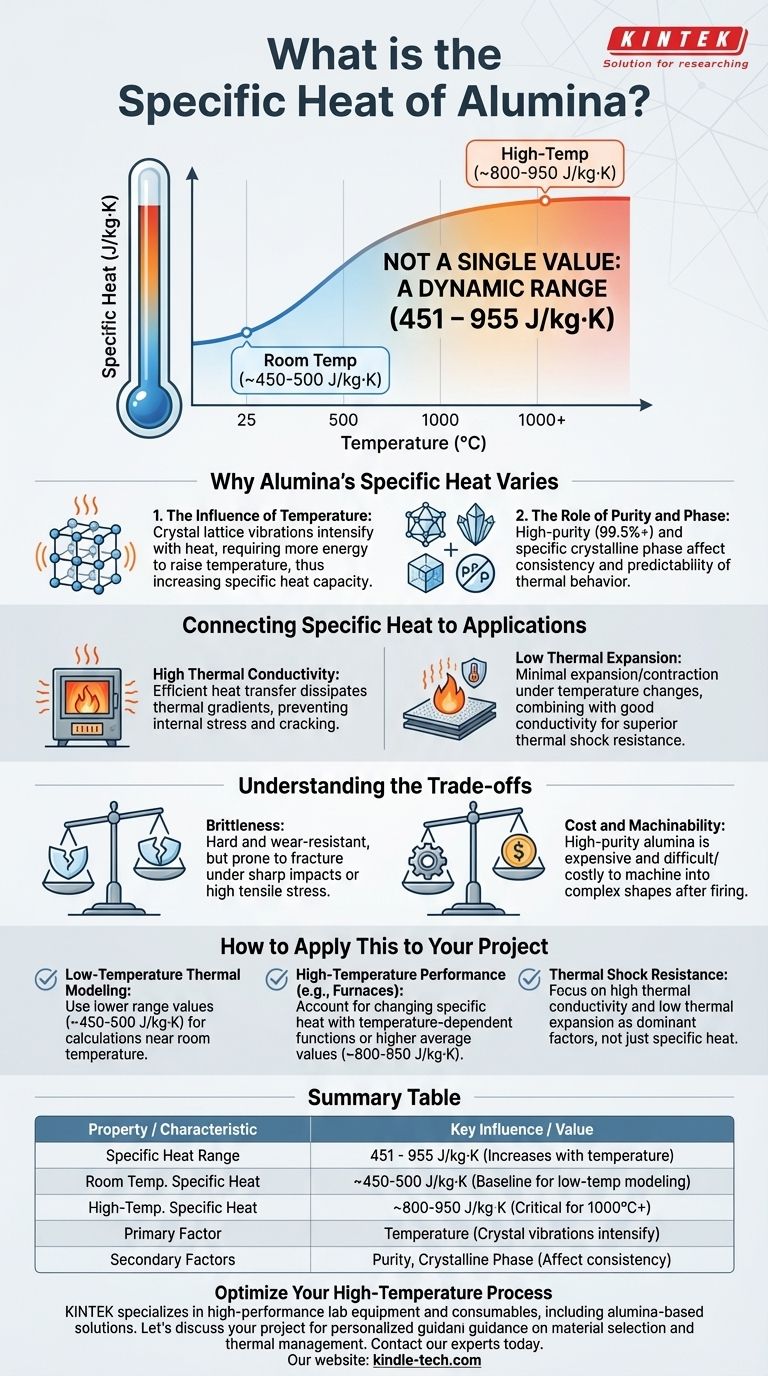
The specific heat of alumina is not a single value but falls within a range, typically between 451 and 955 J/kg·K (Joules per kilogram Kelvin). This variation is primarily because specific heat is dependent on temperature; it increases as the material gets hotter. Purity and the specific crystalline phase of the alumina also play a role.
The core issue isn't finding a single number for specific heat, but understanding that alumina's thermal properties—including its ability to absorb and store heat—change significantly with temperature. This dynamic behavior is what defines its performance in high-temperature applications.

Why Alumina's Specific Heat is a Range
Specific heat capacity measures the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of a material by one degree. For a material like alumina, this is not a static property.
The Influence of Temperature
As alumina heats up, its crystal lattice vibrates more intensely. More energy is required to increase these vibrations further, which translates directly to a higher specific heat capacity.
The lower value in the range (around 450 J/kg·K) corresponds to room temperature, while the upper value (around 950 J/kg·K) is typical for much higher temperatures, approaching 1000°C or more.
The Role of Purity and Phase
The term "alumina" refers to aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃), but its exact properties depend on its purity and crystalline structure (phase).
High-purity alumina (99.5%+) is prized for its thermal stability. While the references don't explicitly link purity to a specific heat value, higher purity generally leads to more predictable and consistent thermal behavior, which is critical for demanding applications.
Connecting Specific Heat to Alumina's Applications
The provided data highlights alumina's use in extreme environments, capable of withstanding temperatures up to 1800°C. Its thermal properties are key to this performance.
High Thermal Conductivity
Alumina exhibits superior thermal conductivity. This means it can transfer heat efficiently rather than holding onto it, which contributes to its excellent thermal shock resistance.
A material that conducts heat well can dissipate thermal gradients quickly, preventing the buildup of internal stress that causes cracking when temperatures change rapidly.
Low Thermal Expansion
Alumina expands and contracts very little with changes in temperature. This low coefficient of thermal expansion is another crucial factor in its ability to resist thermal shock.
When combined with good thermal conductivity, it means the material experiences minimal physical stress even under rapid heating or cooling cycles.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While alumina's properties are exceptional, it's important to recognize its operational context. Its strengths in one area are balanced by its characteristics in another.
Brittleness
Like most ceramics, alumina is hard and wear-resistant but also brittle. It has very high compressive strength but can fracture under sharp impacts or high tensile stress.
This means that while it can handle extreme heat and chemical attack, mechanical shock is a primary failure mode that must be managed in any design.
Cost and Machinability
High-purity alumina is more expensive than many metals and polymers. Due to its extreme hardness, it is also very difficult and costly to machine into complex shapes after it has been fired.
Components are often formed into their final or near-final shape before the final high-temperature sintering process.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your interpretation of alumina's specific heat should depend entirely on your engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is thermal modeling at low temperatures: Use a value near the lower end of the range, approximately 450-500 J/kg·K, for calculations around room temperature.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature performance (e.g., furnace linings, insulators): You must account for the changing specific heat. Use a temperature-dependent function or an average value closer to 800-950 J/kg·K for high-temperature calculations.
- If your primary focus is thermal shock resistance: Remember that specific heat is only part of the equation; high thermal conductivity and low thermal expansion are the more dominant properties ensuring alumina's survival.
Ultimately, understanding that specific heat is a dynamic variable is the key to correctly predicting alumina's behavior in any thermal system.
Summary Table:
| Property | Value / Characteristic | Key Influence |
|---|---|---|
| Specific Heat Range | 451 - 955 J/kg·K | Increases significantly with temperature |
| Room Temp. Specific Heat | ~450-500 J/kg·K | Baseline for low-temperature modeling |
| High-Temp. Specific Heat | ~800-950 J/kg·K | Critical for applications near 1000°C+ |
| Primary Factor | Temperature | Crystal lattice vibrations intensify with heat |
| Secondary Factors | Purity, Crystalline Phase | Affect consistency and predictability |
Optimize Your High-Temperature Process with the Right Materials
Understanding the dynamic thermal properties of materials like alumina is crucial for the success and safety of your high-temperature applications, whether you're designing furnace linings, insulators, or custom components.
KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including alumina-based solutions, to meet the demanding needs of laboratories and industrial settings. We can help you select the right materials based on your specific temperature requirements and operational goals.
Let's discuss your project: Contact our experts today for personalized guidance on material selection and thermal management solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Purity Alumina Granulated Powder for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Lab Internal Rubber Mixer Rubber Kneader Machine for Mixing and Kneading
People Also Ask
- What are the classification of ceramic powder? A Guide to Selecting the Right Material for Your Application
- What are other names for ceramic powder? Classify by Composition, Size & Application
- What are the high temperature properties of alumina? Discover Its Stability, Strength, and Limits
- What is the temperature range of alumina tube? A Guide to Maximizing Performance and Lifespan
- What are the examples of ceramic powder? A Guide to Oxide and Non-Oxide Materials



















