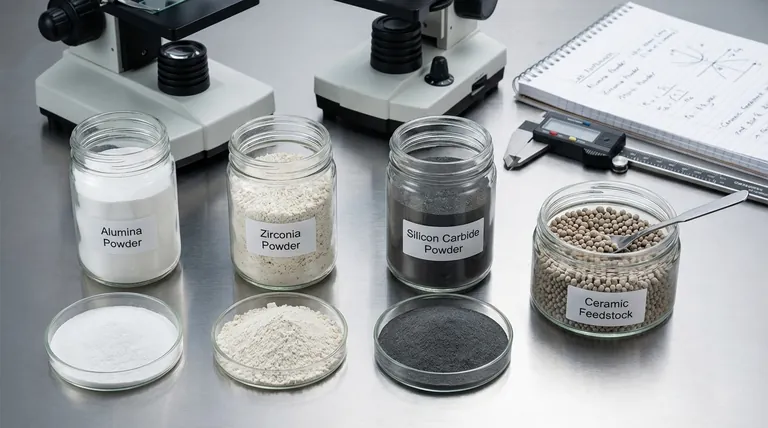
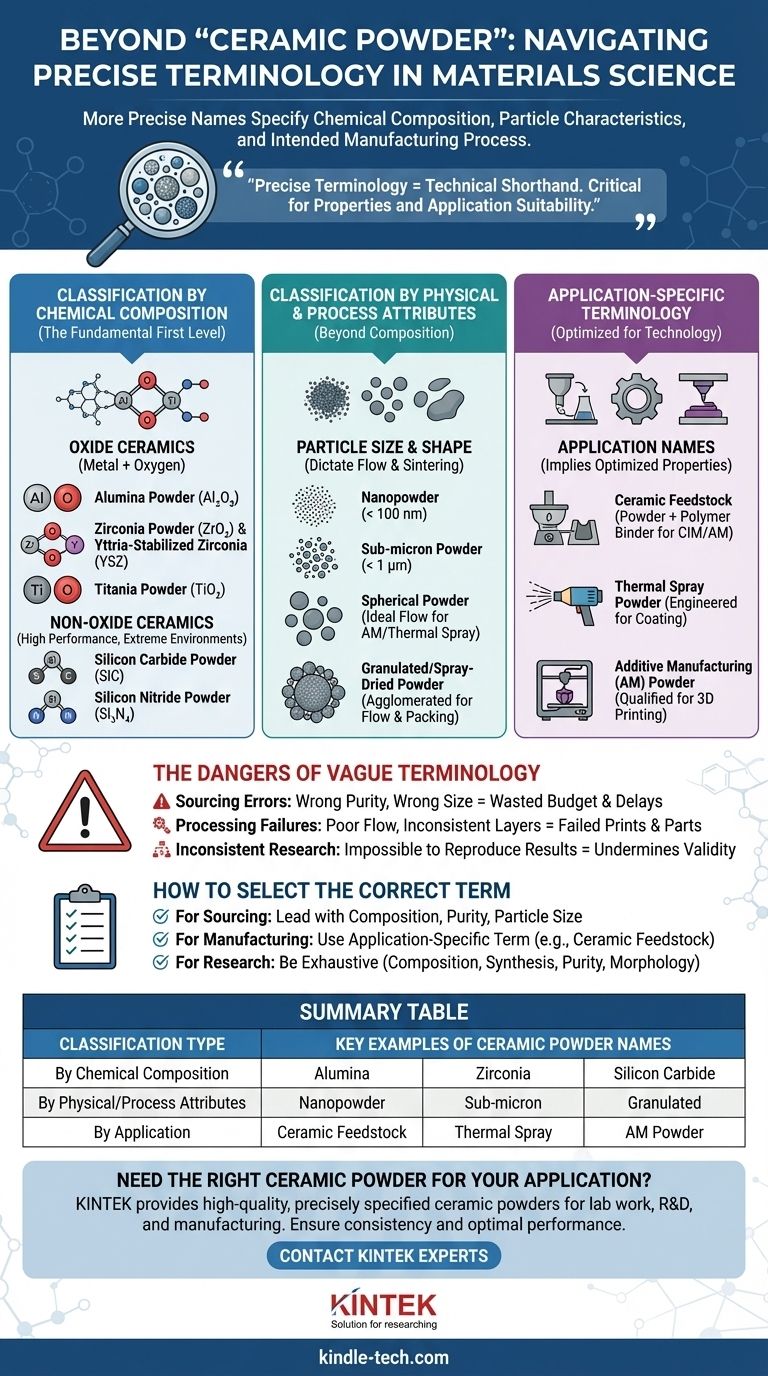
In materials science and manufacturing, the term "ceramic powder" is a general descriptor. More precise names are used to specify the material's exact chemical composition, particle characteristics, or its intended manufacturing process, such as alumina powder, granulated feedstock, or sub-micron zirconia.
The specific name used for a ceramic powder is a form of technical shorthand. It communicates critical details about the material's properties and its suitability for a particular application, moving beyond the generic description of its physical state.

Why Precise Terminology is Critical
In engineering and research, ambiguity leads to errors. Simply calling a material "ceramic powder" is like calling a vehicle "a car" without specifying if it's a sedan, an SUV, or a Formula 1 racer. Each name implies a different function and set of performance characteristics.
Using precise terminology ensures that everyone—from procurement specialists to process engineers—is aligned on the exact material being discussed. This prevents costly mistakes in sourcing, manufacturing, and research.
Classification by Chemical Composition
The most common and fundamental way to name a ceramic powder is by its chemical makeup. This is the first level of specificity required for any technical application.
Oxide Ceramics
Oxide ceramics are compounds of a metal and oxygen. They are the most widely used group due to their stability and availability.
- Alumina Powder (Al₂O₃): Also known as aluminum oxide powder. It is extremely common due to its high hardness and thermal stability.
- Zirconia Powder (ZrO₂): Or zirconium dioxide. Often specified as Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia (YSZ) powder when yttrium is added to improve its toughness.
- Titania Powder (TiO₂): Also called titanium dioxide. Widely used for its photocatalytic and dielectric properties.
Non-Oxide Ceramics
These materials lack oxygen and are known for exceptional performance in extreme environments, such as high temperatures or abrasive conditions.
- Silicon Carbide Powder (SiC): Valued for its extreme hardness, high thermal conductivity, and resistance to chemical corrosion.
- Silicon Nitride Powder (Si₃N₄): Known for outstanding thermal shock resistance and high fracture toughness.
- Boron Nitride Powder (BN): Sometimes called "white graphite" due to its similar structure and lubricating properties.
Classification by Physical & Process-Related Attributes
Beyond composition, names can describe the powder's physical form or how it has been prepared for a specific manufacturing process.
Particle Size and Shape
The size and shape (morphology) of the powder particles dictate how they pack together, flow, and sinter into a dense final part.
- Nanopowder / Nanocrystalline Powder: Refers to powders with particle sizes below 100 nanometers. This extremely small size increases surface area, which can aid in sintering at lower temperatures.
- Sub-micron Powder: Indicates particles that are smaller than one micron (1,000 nanometers) but larger than nanoparticles.
- Spherical Powder: This describes the ideal particle shape for processes that require good flowability, such as additive manufacturing and thermal spray. The name often includes the process, e.g., plasma-spheroidized powder.
- Granulated Powder / Spray-Dried Powder: This refers to fine powders that have been intentionally agglomerated into larger, spherical granules. This process dramatically improves the flowability and packing density, making it suitable for pressing operations.
Application-Specific Terminology
Often, the powder is named after the process it is designed for. This implies that its properties have been optimized for that technology.
- Ceramic Feedstock: This is a crucial term, especially in injection molding (CIM) and additive manufacturing. It refers to a ready-to-use mixture of ceramic powder and a polymer binder. It is not a pure powder.
- Thermal Spray Powder: A powder engineered with a specific particle size distribution and morphology for use in thermal or plasma spray coating processes.
- Additive Manufacturing (AM) Powder: A general term for powders qualified for 3D printing processes like binder jetting or selective laser sintering (SLS).
The Dangers of Vague Terminology
Using an imprecise term like "ceramic powder" in a technical context introduces significant risk. The consequences often manifest in sourcing, processing, and quality control.
Sourcing and Procurement Errors
If a purchase order simply specifies "zirconia powder," you could receive a coarse, low-purity material instead of the high-purity, sub-micron YSZ powder required for a medical implant. This leads to wasted budget and project delays.
Processing Failures
A powder's flowability is critical. Trying to use a fine, non-spherical powder in a binder jetting 3D printer designed for granulated feedstock will result in poor bed density, inconsistent layers, and failed prints.
Inconsistent Research Results
In academic or R&D settings, failing to specify the exact powder characteristics (e.g., manufacturer, particle size distribution, morphology, purity) makes experimental results impossible to reproduce, undermining the validity of the work.
How to Select the Correct Term
Choosing the right name depends entirely on your objective. Use the most specific term possible to communicate your exact requirements.
- If your primary focus is sourcing or material specification: Lead with the chemical composition, purity, and particle size (e.g., "99.8% pure, sub-micron alumina powder with a D50 of 0.5 µm").
- If your primary focus is manufacturing or processing: Use the application-specific term, as it implies the necessary physical properties (e.g., "ceramic feedstock for injection molding" or "spherical Ti-6Al-4V powder for AM").
- If your primary focus is research and development: Be exhaustive in your description, detailing the chemical name, synthesis method, purity, particle size distribution, and morphology to ensure absolute clarity and reproducibility.
Ultimately, using precise terminology for ceramic powders is the foundation for predictable and successful materials engineering.
Summary Table:
| Classification Type | Key Examples of Ceramic Powder Names |
|---|---|
| By Chemical Composition | Alumina Powder (Al₂O₃), Zirconia Powder (ZrO₂), Silicon Carbide Powder (SiC) |
| By Physical/Process Attributes | Nanopowder, Sub-micron Powder, Granulated/Spray-Dried Powder |
| By Application | Ceramic Feedstock (for CIM), Thermal Spray Powder, Additive Manufacturing (AM) Powder |
Need the Right Ceramic Powder for Your Application?
Using the correct, high-purity ceramic powder is critical for the success of your lab work, R&D, or manufacturing process. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including a wide range of precisely specified ceramic powders.
We can help you source the exact material you need—from alumina and zirconia to specialized feedstocks for additive manufacturing—ensuring consistency, reproducibility, and optimal performance in your projects.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and let KINTEK be your trusted partner in materials science.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Purity Alumina Granulated Powder for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Advanced Engineering Fine Ceramics Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Parts
- Boron Nitride (BN) Crucible for Phosphorous Powder Sintered
- High Purity Zinc Foil for Battery Lab Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the function of high-purity alumina powder in pack cementation? Ensure Uniform Aerospace Blade Coatings
- What is the maximum temperature for alumina tube? Unlock Its Full Potential with High Purity
- What should be done if scratches on an electrode cannot be removed with 1.0um alumina powder? Expert Repair Tips
- What are the examples of ceramic powder? A Guide to Oxide and Non-Oxide Materials
- What are the high temperature properties of alumina? Discover Its Stability, Strength, and Limits


















