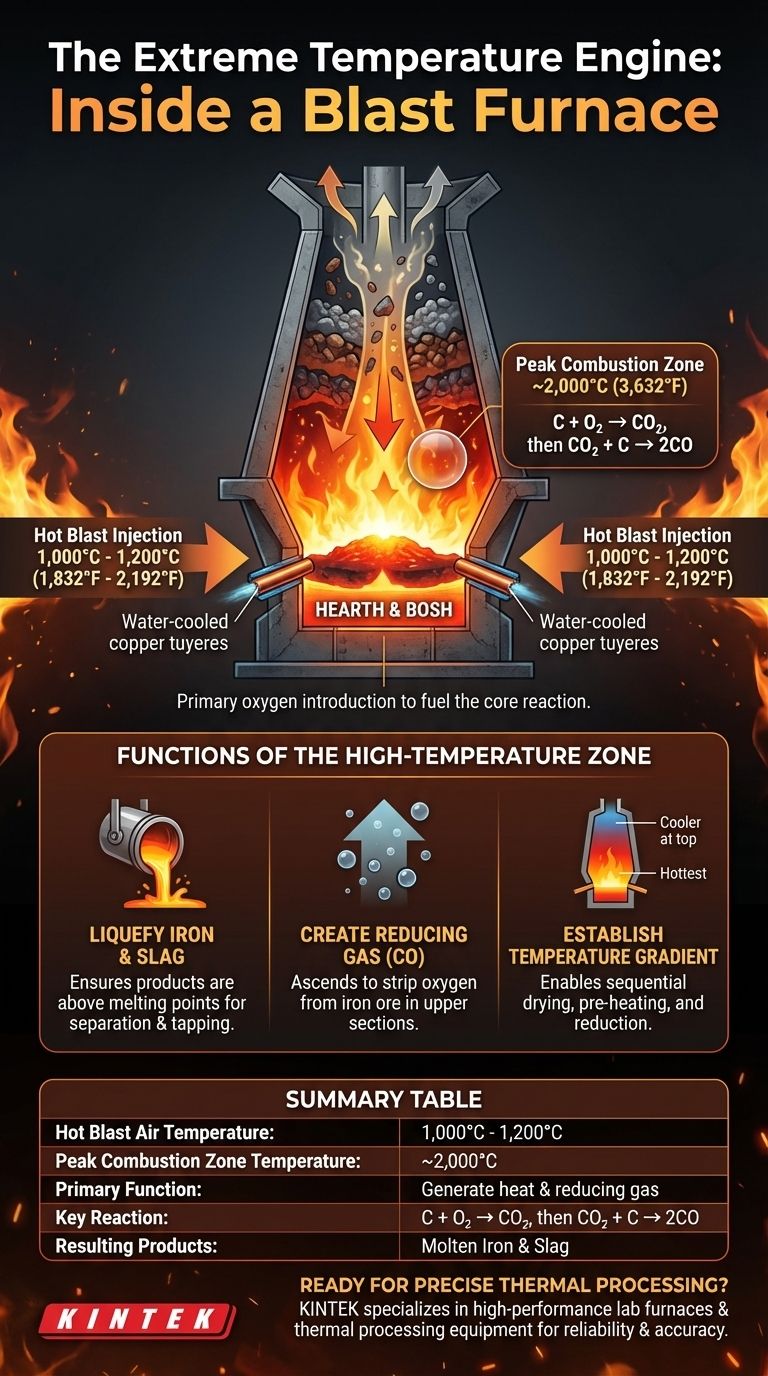
At the very bottom of a blast furnace, the temperature of the hot air being injected is between 1,000°C and 1,200°C (1,832°F to 2,192°F). This injection of superheated air initiates a series of chemical reactions with coke and coal that can drive the localized temperature in this combustion zone even higher, often approaching 2,000°C (3,632°F).
The extreme temperature at the bottom of the furnace is not just for melting materials. Its primary purpose is to initiate the combustion that creates both the intense heat and the crucial reducing gases required to transform iron ore into liquid iron throughout the entire furnace.

The Function of the High-Temperature Zone
The bottom section of a blast furnace, known as the hearth or bosh, is the engine room for the entire iron-making process. The temperature here is the highest in the furnace for very specific reasons.
The Hot Blast Injection
Hot air, pre-heated to between 1,000°C and 1,200°C, is blasted into the furnace through water-cooled copper nozzles called tuyeres. This is the primary introduction of oxygen to fuel the core reaction.
The Primary Combustion Reaction
This blast of hot oxygen immediately reacts with the coke (a high-carbon fuel) and any pulverized coal that has been added. This combustion reaction (C + O₂) is intensely exothermic, releasing a massive amount of energy and heat.
Creating the Reducing Agent
The intense heat from the initial combustion instantly drives a second reaction. The carbon dioxide (CO₂) produced reacts with more hot coke to form carbon monoxide (CO), as described by the equation CO₂ + C → 2CO. This carbon monoxide is the critical reduction gas that travels up the furnace.
Why This Extreme Temperature is Necessary
The heat generated at the bottom serves multiple critical functions that enable the entire operation. It is the foundation upon which the rest of the furnace's chemistry and physics depend.
To Liquefy the Iron and Slag
The temperature must be high enough to ensure that the final products—the molten iron and the liquid impurities known as slag—are well above their melting points. This allows them to trickle down through the coke bed and collect in separate layers in the hearth, ready for tapping.
To Drive the Chemical Process
The column of hot carbon monoxide gas rising from the bottom is what strips the oxygen atoms from the iron ore (iron oxides) in the upper sections of the furnace. Without the intense heat at the bottom to create this gas, the reduction of iron ore to iron simply cannot occur.
To Establish a Temperature Gradient
The furnace operates on a temperature gradient, being hottest at the bottom and progressively cooler towards the top. This gradient allows the raw materials descending from the top to be dried, pre-heated, and chemically reduced in a controlled, sequential manner before they finally reach the melting zone.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the function of this heat is more important than memorizing a single number. The temperature at the bottom is the starting point for everything that happens above it.
- If your primary focus is the energy source: The bottom of the furnace is the primary combustion zone where coke and hot air react, generating the thermal energy for the entire process.
- If your primary focus is the chemistry: This high-temperature zone is where the crucial reducing gas (carbon monoxide) is created, which then travels upward to convert iron ore into iron.
- If your primary focus is the physical process: The intense heat ensures both the final iron and the waste slag become fully liquid, allowing for their effective separation and removal.
Ultimately, viewing the blast furnace not as a simple oven but as a dynamic counter-current chemical reactor is the key to understanding its operation.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Hot Blast Air Temperature | 1,000°C - 1,200°C (1,832°F - 2,192°F) |
| Peak Combustion Zone Temperature | ~2,000°C (3,632°F) |
| Primary Function | Generate heat and reducing gas (CO) |
| Key Reaction | C + O₂ → CO₂, then CO₂ + C → 2CO |
| Resulting Products | Molten Iron and Slag |
Ready to achieve precise thermal processing in your own operations? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and thermal processing equipment designed for reliability and accuracy. Whether your work involves materials testing, metallurgy, or chemical synthesis, our solutions deliver the controlled high-temperature environments you need. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific heating and processing requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance



















