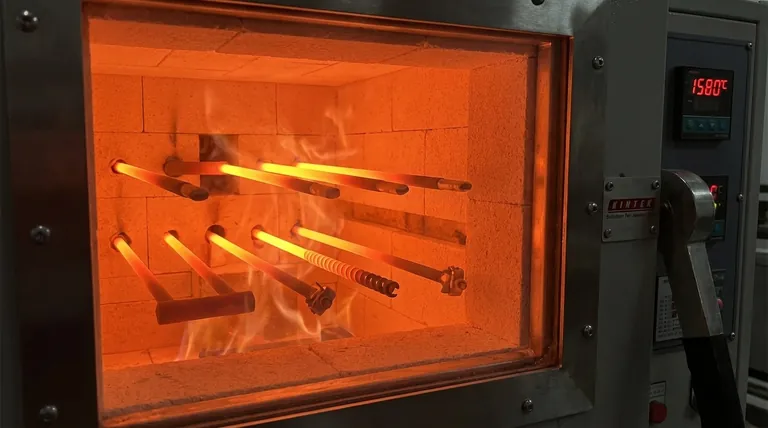
The temperature limit of silicon carbide (SiC) is not a single value but a series of thresholds that depend on the operating environment and the specific application. While its theoretical melting point is extremely high at approximately 2830°C, its practical limit in air is much lower, typically between 1500°C and 1600°C, due to oxidation. In inert atmospheres, its upper stability limit is closer to 2500°C.
The most critical factor determining silicon carbide's useful temperature range is its environment. In most real-world applications involving air, the practical limit is defined by the onset of rapid oxidation around 1600°C, not by its much higher melting point.
Deconstructing SiC's Temperature Limits
To use silicon carbide effectively, you must understand the difference between its absolute melting point, its stability limit, and its practical operating temperature in air.
The Absolute Limit: Melting Point (~2830°C)
This is the temperature at which solid silicon carbide transitions to a liquid state. This value represents the absolute theoretical maximum temperature the material can endure before complete structural failure.
The Structural Limit: Decomposition (~2500°C)
Before it melts, SiC can begin to decompose into its constituent elements, silicon and carbon. Its upper stability limit is therefore considered to be around 2500°C, making this a more realistic boundary for applications in inert or vacuum environments where oxidation is not a concern.
The Practical Limit: Oxidation in Air (~1600°C)
For most common applications, such as furnace heating elements operating in air, the limiting factor is oxidation. Above 1600°C, the silicon in SiC reacts with atmospheric oxygen, forming a layer of silicon dioxide (SiO₂).
While this oxide layer can be protective at lower temperatures, the rate of oxidation accelerates significantly above 1600°C, degrading the material and limiting its service life. This is why many SiC resistors are rated for use only up to about 1500°C.
Why SiC Excels at High Temperatures
Silicon carbide’s value extends beyond its heat tolerance. Several other properties make it a uniquely capable material for high-temperature and high-performance applications.
Exceptional Thermal Conductivity
SiC possesses a thermal conductivity comparable to that of some metals like copper. This unique trait for a ceramic allows it to dissipate heat quickly and evenly, preventing the formation of destructive hot spots and making it an ideal material for heating elements.
Excellent Thermal Shock Resistance
The material has a very low coefficient of thermal expansion. This means it expands and contracts very little when heated and cooled, giving it an outstanding ability to withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking or failing.
High Chemical Stability
Silicon carbide is extremely resistant to chemical attack, particularly from strong acids. This chemical inertness allows it to perform reliably in harsh environments where other materials would quickly corrode and fail.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect. To properly engineer a solution with SiC, you must be aware of its practical limitations.
Brittleness is a Key Constraint
Like many other hard ceramics, SiC is brittle. While it is exceptionally hard and resistant to wear, it can fracture under sudden mechanical shock or impact. Designs must account for this by minimizing tensile stress and avoiding impact loads.
Aging of Heating Elements
When used as heating elements, SiC components experience a gradual increase in electrical resistance over time due to slow oxidation and changes in their crystalline structure. This "aging" process is a critical design consideration.
High-end systems often require a variable power source, such as an auto-transformer with multiple taps, to compensate for this resistance increase and maintain consistent power output throughout the element's lifespan.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by the specific demands of your project.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature in an inert atmosphere: You can engineer your system to operate near SiC's stability limit of ~2500°C, but material integrity becomes the primary concern.
- If your primary focus is long-term stability in air: Plan for a maximum continuous operating temperature between 1500°C and 1600°C to prevent rapid oxidative failure.
- If your primary focus is thermal cycling and shock resistance: SiC is an excellent choice due to its low thermal expansion, but your mechanical design must protect it from physical impact due to its brittle nature.
Understanding these distinct environmental and application-driven limits is the key to successfully harnessing the power of silicon carbide.
Summary Table:
| Environment | Practical Temperature Limit | Key Limiting Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Air / Oxidizing | 1500°C - 1600°C | Rapid Oxidation |
| Inert / Vacuum | Up to ~2500°C | Decomposition |
| Absolute Maximum | ~2830°C | Melting Point |
Need a high-temperature solution for your lab?
Silicon carbide's exceptional properties—like high thermal conductivity and shock resistance—make it ideal for demanding applications. Choosing the right grade and design is critical for performance and longevity.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables. Our experts can help you select the perfect silicon carbide components for your furnaces or high-temperature processes, ensuring reliability and efficiency.
Contact our technical team today to discuss your specific requirements and optimize your high-temperature operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Custom-Made Alumina Zirconia Special-Shaped Ceramic Plates for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Processing
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Non-Standard Insulator Customization
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Ball Valve Seat
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Hydrothermal Synthesis Reactor Polytetrafluoroethylene Carbon Paper and Carbon Cloth Nano-growth
People Also Ask
- What are the uses of silicon carbide rod? The Ultimate Heating Solution for Extreme Temperatures
- What is the maximum temperature for a SiC heating element? Unlock the Key to Longevity and Performance
- What kind of metal is used in heating elements? A Guide to Materials for Every Temperature & Atmosphere
- What are silicon carbide heating elements used for? Reliable High-Temp Heating for Industrial Processes
- What is a silicon carbide heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat for Industrial Processes



















