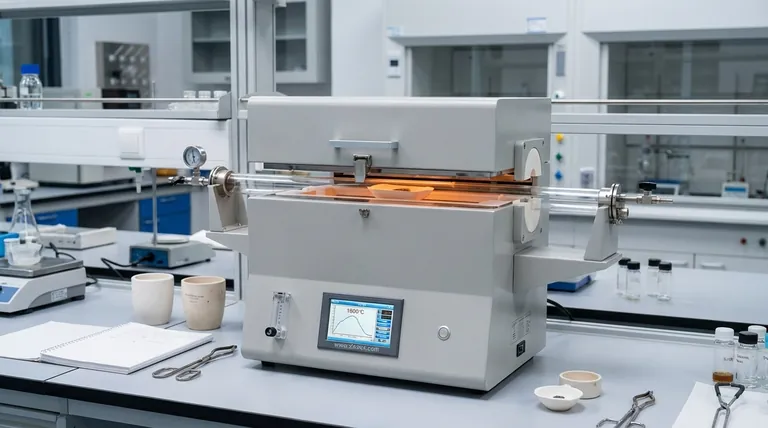
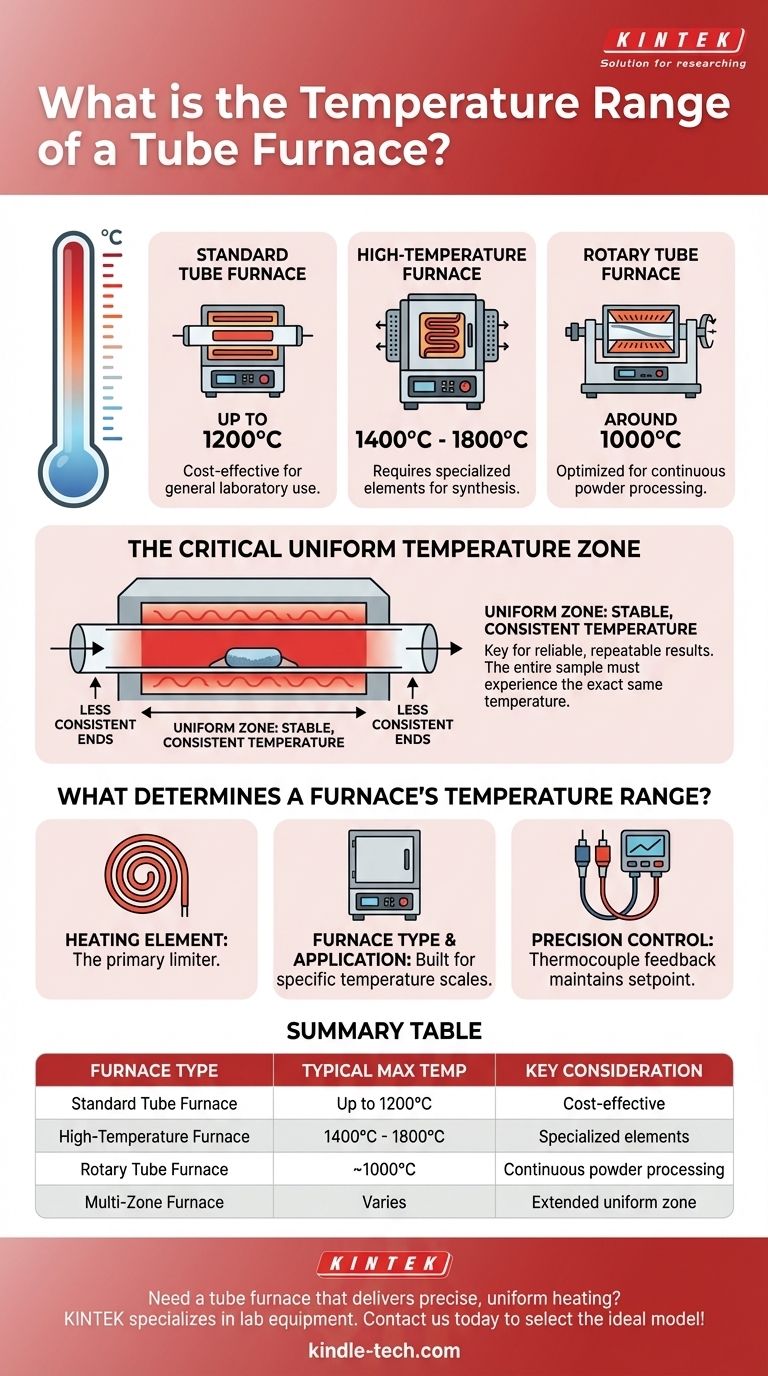
In practice, the operational temperature of a tube furnace varies widely depending on its specific design and intended application. While standard models operate up to 1200°C, high-temperature versions can reliably reach between 1400°C and 1800°C. The specific type, such as a rotary tube furnace, may have a lower maximum temperature, often around 1000°C.
The maximum temperature rating of a furnace is only a starting point. The critical factor for achieving reliable, repeatable results is understanding the size and stability of its uniform temperature zone.

What Determines a Furnace's Temperature Range?
The maximum achievable temperature is not an arbitrary number; it is a direct consequence of the furnace's design, materials, and heating method. Understanding these factors is key to selecting the right instrument.
The Heating Element is a Primary Limiter
The material used for the heating element is the single most important factor defining the furnace's upper temperature limit. Different materials have different maximum operating temperatures before they degrade. Specialized high-temperature furnaces use advanced elements to safely and reliably reach 1800°C or more.
Furnace Type and Application
Different furnace configurations are built for different temperature scales. For example, a rotary tube furnace, designed for continuous processing of powders and granules, is often engineered for temperatures up to 1000°C. In contrast, furnaces designed for static high-temperature synthesis will use a different construction to achieve temperatures of 1800°C.
Precision Control via Thermocouple
Regardless of the range, temperature is actively managed. A thermocouple inside the furnace provides constant temperature feedback to a controller. This allows you to set a precise target temperature, and the system will automatically adjust power to the heating elements to maintain that setpoint accurately.
The Critical Importance of the "Uniform Zone"
The peak temperature at the center of the furnace is often different from the temperature a few inches to the side. This temperature consistency is the most important, and often overlooked, performance metric.
What is a Uniform Temperature Zone?
The uniform temperature zone is the specific length within the furnace tube where the temperature is stable and consistent. Manufacturers often specify this as a length (e.g., +/- 5°C over 150 mm).
Why It Matters for Your Results
For processes like crystal growth, annealing, or catalyst testing, the entire sample must experience the exact same temperature. If part of your sample is outside the uniform zone, your results will be inconsistent and unreliable.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a furnace involves more than just finding the highest temperature for the lowest cost. You must consider the practical realities of its operation.
Rated Temperature vs. Absolute Maximum
Always operate the furnace within its rated temperature. Constantly running a furnace at its absolute maximum temperature, even if possible, will drastically shorten the life of its heating elements and can pose a safety risk. It is not designed for continuous use at its peak limit.
Temperature Uniformity vs. Furnace Length
A longer heated tube does not automatically mean a longer uniform zone. In fact, the temperature naturally drops off near the ends of the tube. Achieving a long, uniform hot zone often requires more advanced designs with multiple, independently controlled heating zones.
How to Select the Right Furnace
Your decision should be driven by the specific requirements of your process, not just a single number on a spec sheet.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heating below 1200°C: A standard, single-zone furnace with a simple controller is typically sufficient and cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature synthesis (1400°C - 1800°C): You must invest in a specialized furnace with the appropriate high-performance heating elements and insulation.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability and accuracy: Prioritize the furnace with the best-specified uniform temperature zone for your sample size, even if its maximum temperature is lower than other models.
Ultimately, choosing the right instrument requires you to match the furnace's documented performance, especially its uniformity, to the precise needs of your work.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Typical Max Temperature | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Tube Furnace | Up to 1200°C | Cost-effective for general use |
| High-Temperature Furnace | 1400°C - 1800°C | Requires specialized heating elements |
| Rotary Tube Furnace | ~1000°C | Optimized for continuous powder processing |
| Multi-Zone Furnace | Varies | Provides extended uniform temperature zone |
Need a tube furnace that delivers precise, uniform heating for your specific application? At KINTEK, we specialize in lab equipment and consumables, offering a range of tube furnaces designed for reliability and accuracy. Whether you require high-temperature synthesis up to 1800°C or consistent heating for sensitive processes, our experts can help you select the ideal model with the right uniform temperature zone for your samples. Contact us today to discuss your requirements and enhance your lab's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a horizontal alumina furnace in Cr-C-Al quenching? Simulating Reactor Thermal Shock
- What role does a steel retort play in the fixed-bed co-pyrolysis process? Optimizing Thermochemical Conversion
- How does a tube calcination furnace contribute to the formation of the Mn-Ce-Mo/LDPC active phase? Expert Insights
- Why is a quartz tube reactor selected for the high-temperature steam reforming of naphthalene? Achieve Precise Results
- What are the low cost catalysts for pyrolysis? Optimize Your Pyrolysis Process with Affordable Catalysts
- Why is a quartz material tube reactor selected for high-temperature steam cracking? Unlock Pure Kinetic Data
- What are the advantages of a tube furnace? Achieve Superior Temperature Uniformity and Control
- What role does a horizontal tube furnace play in TiB2 synthesis? Optimize High-Quality Nanopowder Production



















