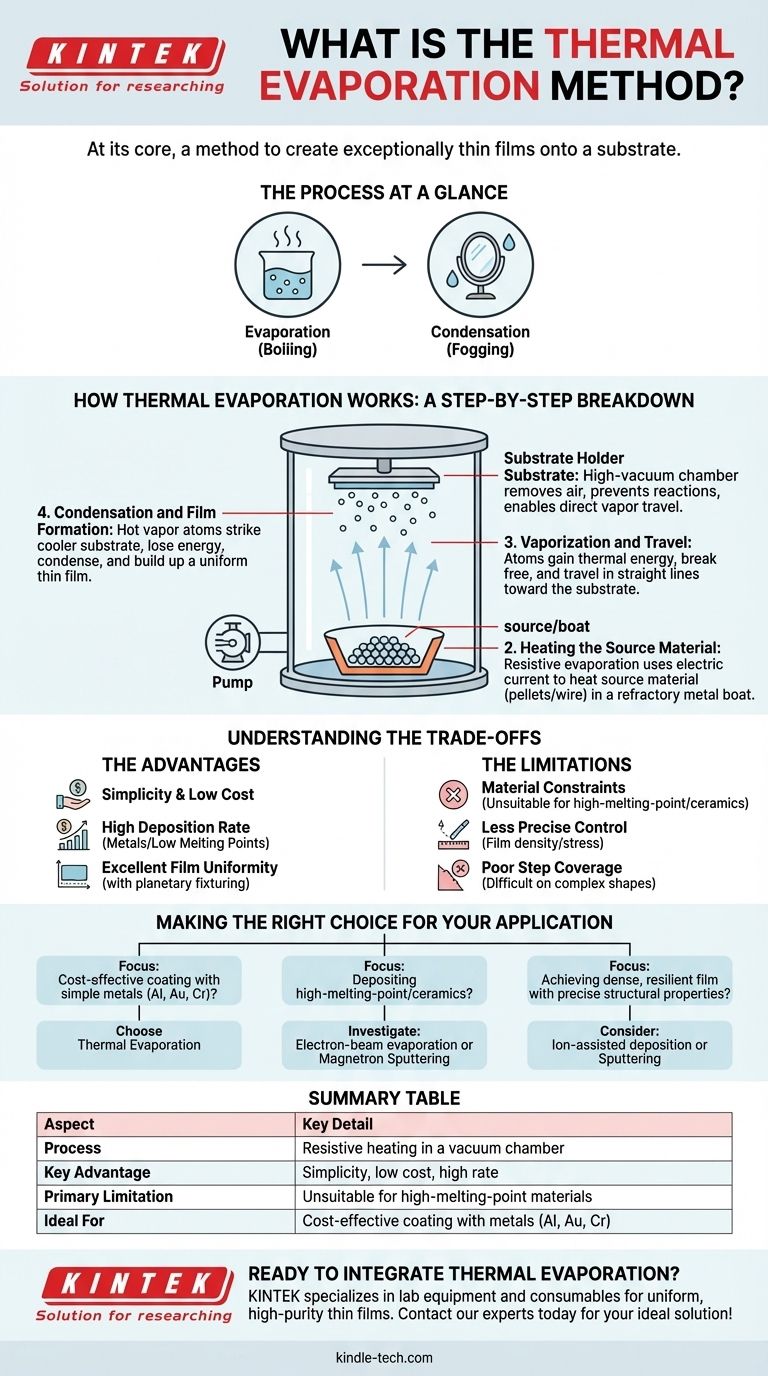
At its core, thermal evaporation is a method used to create exceptionally thin films of a material onto a surface, known as a substrate. The process involves heating a source material inside a high-vacuum chamber until it evaporates, turning into a vapor. This vapor then travels through the vacuum and condenses onto the cooler substrate, forming a uniform thin-film coating.
Thermal evaporation is fundamentally a two-step process of evaporation and condensation, analogous to boiling water to create steam that fogs a cool mirror. It leverages heat and a vacuum to transform a solid material into a vapor that re-solidifies as a thin, pure film on a target surface.
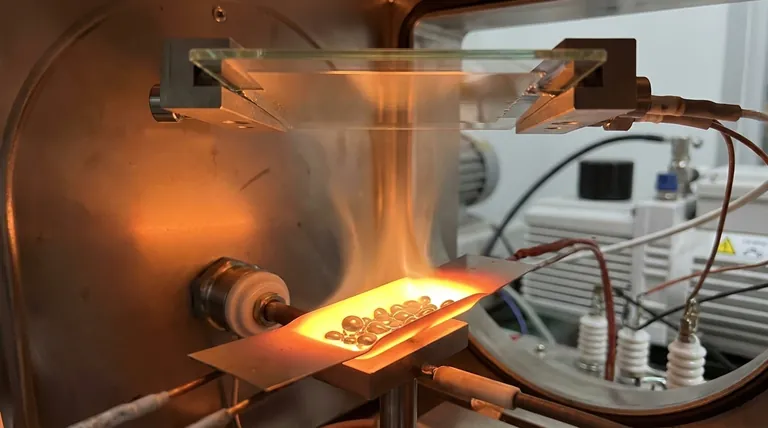

How Thermal Evaporation Works: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
To understand this technique, it's best to break it down into its core stages, which occur in a highly controlled environment.
Creating the Vacuum Environment
The entire process takes place inside a sealed vacuum chamber. High-powered pumps remove air and other gas molecules.
This vacuum is critical for two reasons: it prevents the hot source material from reacting with air, and it allows the vaporized atoms to travel directly to the substrate without colliding with other particles.
Heating the Source Material
The material to be deposited, often in the form of pellets or wire, is placed in a heat-resistant container called a source or boat. This boat is typically made of a refractory metal like tungsten.
An electric current is passed through the source, and its electrical resistance causes it to heat up rapidly. This method is often called resistive evaporation because it uses resistance to generate heat, much like the filament in an incandescent light bulb.
Vaporization and Travel
As the source material heats up, its atoms gain enough thermal energy to break free from the solid state and enter a gaseous state, or vapor.
These vaporized atoms travel in straight, line-of-sight paths from the source toward the substrate, which is typically positioned above it.
Condensation and Film Formation
When the hot vapor atoms strike the cooler surface of the substrate, they rapidly lose energy, cool down, and condense back into a solid state.
This condensation process builds up layer by layer, forming a thin, solid, and often very pure film of the source material across the substrate's surface.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Like any technical process, thermal evaporation has distinct advantages and limitations that make it suitable for specific applications.
The Advantages: Simplicity and Versatility
The primary advantage of thermal evaporation is its relative simplicity and low cost. The equipment is less complex than that for other deposition methods.
It delivers a high deposition rate and is compatible with a wide range of materials, especially metals and compounds with low melting points.
With proper substrate rotation (planetary fixturing), it can achieve excellent film uniformity over large areas.
The Limitations: Material and Control Constraints
The reliance on resistive heating limits the process to materials that can be evaporated at temperatures below the melting point of the heating source itself. This makes it unsuitable for many high-melting-point materials like ceramics.
While simple, the process offers less precise control over film properties like density and stress compared to more energetic methods like sputtering or ion-assisted deposition.
Because the vapor travels in a straight line, it can be difficult to uniformly coat complex, three-dimensional shapes with sharp edges or deep trenches (an issue known as poor "step coverage").
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing a deposition method depends entirely on your material, budget, and desired film characteristics.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective coating with simple metals: Thermal evaporation is an excellent, straightforward choice for materials like aluminum, gold, or chromium.
- If your primary focus is depositing high-melting-point or ceramic materials: You should investigate alternative methods like electron-beam evaporation or magnetron sputtering.
- If your primary focus is achieving a dense, resilient film with precise structural properties: A more energetic process like ion-assisted deposition or sputtering will likely provide better results.
By understanding its simple mechanism and clear trade-offs, you can confidently determine where thermal evaporation fits within your thin-film deposition strategy.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Process | Resistive heating in a vacuum chamber to vaporize a source material. |
| Key Advantage | Simplicity, low cost, and high deposition rate for compatible materials. |
| Primary Limitation | Unsuitable for high-melting-point materials; poor step coverage on complex shapes. |
| Ideal For | Cost-effective coating with metals like aluminum, gold, and chromium. |
Ready to integrate thermal evaporation into your lab's workflow? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable thermal evaporation systems and expert support to help you achieve uniform, high-purity thin films for your research or production needs. Contact our experts today to discuss the ideal solution for your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What is the limitation of sputtering process? Key Drawbacks in Thin Film Deposition
- What is the deposition of thin films? A Guide to Coating Technology for Modern Devices
- What is the pressure for thermal evaporation? Achieve High-Purity Thin Films with Optimal Vacuum
- Why is an alumina boat and Ti3AlC2 powder bed necessary for Ti2AlC sintering? Protect MAX Phase Purity
- What is the evaporation method of physical vapour deposition? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Coating
- Is sputtering better than evaporation purity? A Guide to High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- How is the thickness of a deposited film measured? Master Optical Interference Techniques
- What is the function of electron coating? Boost Your Device's Electrical & Optical Performance



















