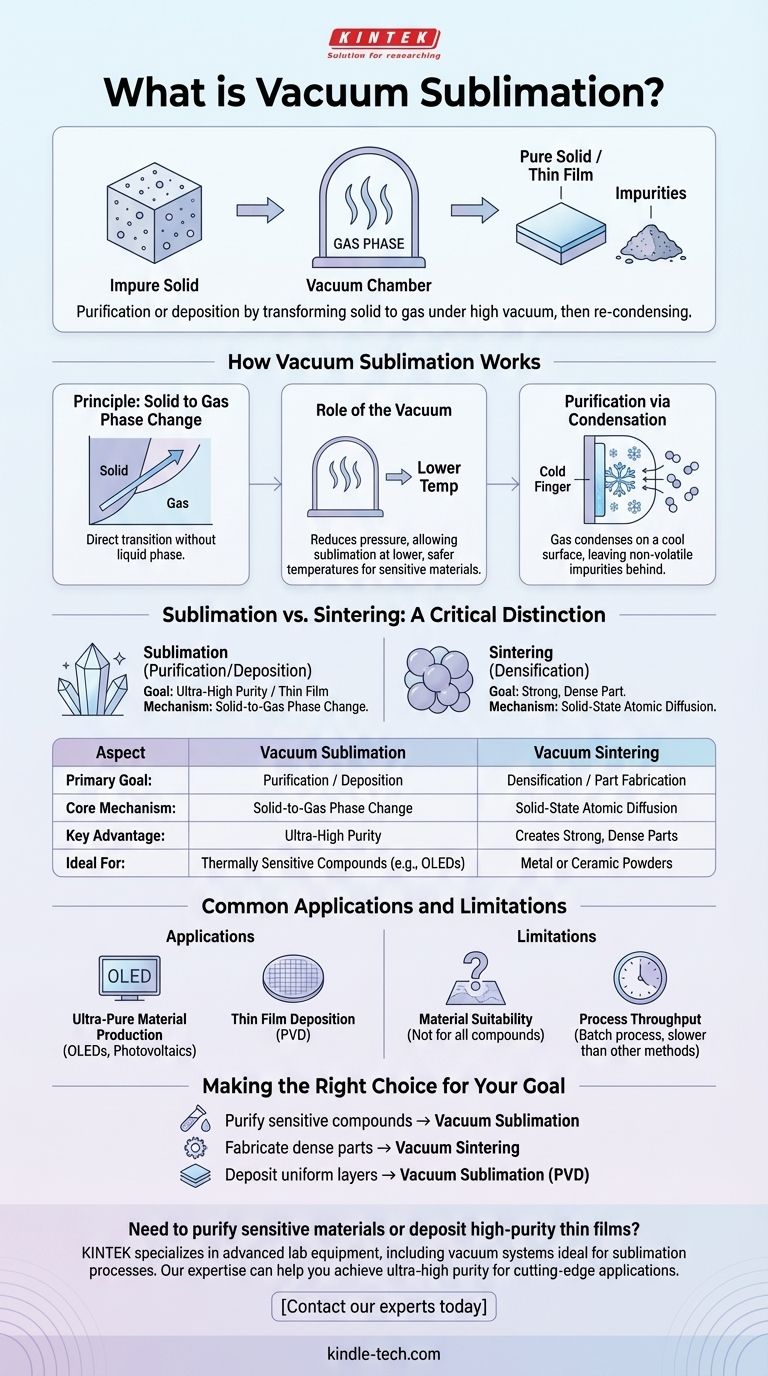
In essence, vacuum sublimation is a purification or deposition technique where a solid material is heated under a high vacuum, causing it to transform directly into a gas without passing through a liquid phase. This gas is then re-condensed into a high-purity solid on a cooler surface, effectively separating it from non-volatile impurities.
The core purpose of vacuum sublimation is not to create a dense, solid part, but to purify a substance or deposit it as a thin film. It leverages a physical phase change (solid-to-gas) under vacuum, which is fundamentally different from processes like sintering that fuse particles together.

How Vacuum Sublimation Works
The process is governed by the principles of phase transitions and the unique environment created by a vacuum. It is a multi-step technique used extensively in chemistry and materials science.
The Principle: Solid to Gas Phase Change
All materials have a phase diagram that maps their state (solid, liquid, gas) at different temperatures and pressures. Sublimation is the direct transition from the solid phase to the gas phase.
For many substances, this requires very high temperatures at normal atmospheric pressure.
The Role of the Vacuum
Placing a material in a vacuum chamber drastically reduces the ambient pressure. This lowers the temperature required for sublimation to occur, similar to how water boils at a lower temperature at high altitudes.
This is crucial for thermally sensitive materials (like many organic compounds) that would decompose or burn if heated to their sublimation point at atmospheric pressure.
The Final Step: Purification via Condensation
Once the target material becomes a gas, it travels through the vacuum chamber. Non-volatile impurities are left behind as a solid residue.
The chamber contains a cooled surface, often called a "cold finger." When the gaseous material contacts this surface, it rapidly cools and condenses back into a highly pure solid, completing the purification cycle.
Sublimation vs. Sintering: A Critical Distinction
The process you referenced, vacuum sintering, is often confused with sublimation because both occur in a vacuum furnace. However, their goals and mechanisms are completely different.
The Goal: Purification vs. Densification
The goal of sublimation is purification or deposition. You start with an impure solid and end with a pure solid (or a thin film) and leftover contaminants.
The goal of sintering is densification. You start with a pressed powder (a "green body") and use heat and pressure to fuse the particles into a strong, dense, solid object.
The Mechanism: Phase Change vs. Atomic Diffusion
Sublimation is a phase change process. The bulk material turns into a gas and is then redeposited elsewhere.
Sintering is a solid-state process. The material never becomes a liquid or gas. Instead, atoms diffuse across the boundaries of the powder particles, bonding them together and reducing the empty space between them.
Common Applications and Limitations
Understanding where vacuum sublimation excels—and where it doesn't—is key to using it effectively. It is a powerful but specific tool.
Application: Ultra-Pure Material Production
Vacuum sublimation is the gold standard for purifying materials used in high-tech applications, such as organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) and organic photovoltaics. Even small impurities can ruin the performance of these devices.
Application: Thin Film Deposition
By carefully controlling the condensation step, sublimation can be used to deposit uniform, high-purity thin films onto a substrate. This process is a form of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD).
Limitation: Material Suitability
The primary limitation is that not all materials can be sublimated. The substance must be able to transition to a gas phase at a temperature below its decomposition point. Many ceramics and high-melting-point metals are not suitable.
Limitation: Process Throughput
Sublimation is typically a batch process and can be slower than other industrial purification methods like crystallization or distillation, making it less suitable for producing large bulk quantities.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct vacuum thermal process, you must first define your objective.
- If your primary focus is purifying a thermally sensitive organic or inorganic compound: Vacuum sublimation is the ideal method for achieving the highest levels of purity.
- If your primary focus is fabricating a dense, strong mechanical part from a powder: Vacuum sintering is the correct industrial process.
- If your primary focus is depositing a uniform, high-purity layer of material onto a surface: Vacuum sublimation (as a form of PVD) is a leading technique.
Ultimately, choosing the right method depends entirely on whether your goal is to change a material's form or to refine its chemical purity.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Vacuum Sublimation | Vacuum Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Purification / Thin Film Deposition | Densification / Part Fabrication |
| Core Mechanism | Solid-to-Gas Phase Change (Sublimation) | Solid-State Atomic Diffusion |
| Key Advantage | Achieves Ultra-High Purity | Creates Strong, Dense Parts |
| Ideal For | Thermally Sensitive Compounds (e.g., OLED materials) | Metal or Ceramic Powders |
Need to purify sensitive materials or deposit high-purity thin films?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including vacuum systems ideal for sublimation processes. Our expertise can help you achieve the ultra-high purity required for cutting-edge applications in OLEDs, photovoltaics, and more.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can meet your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
People Also Ask
- What are the uses of PECVD? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin-Film Deposition
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma activated chemical vapor deposition? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
















