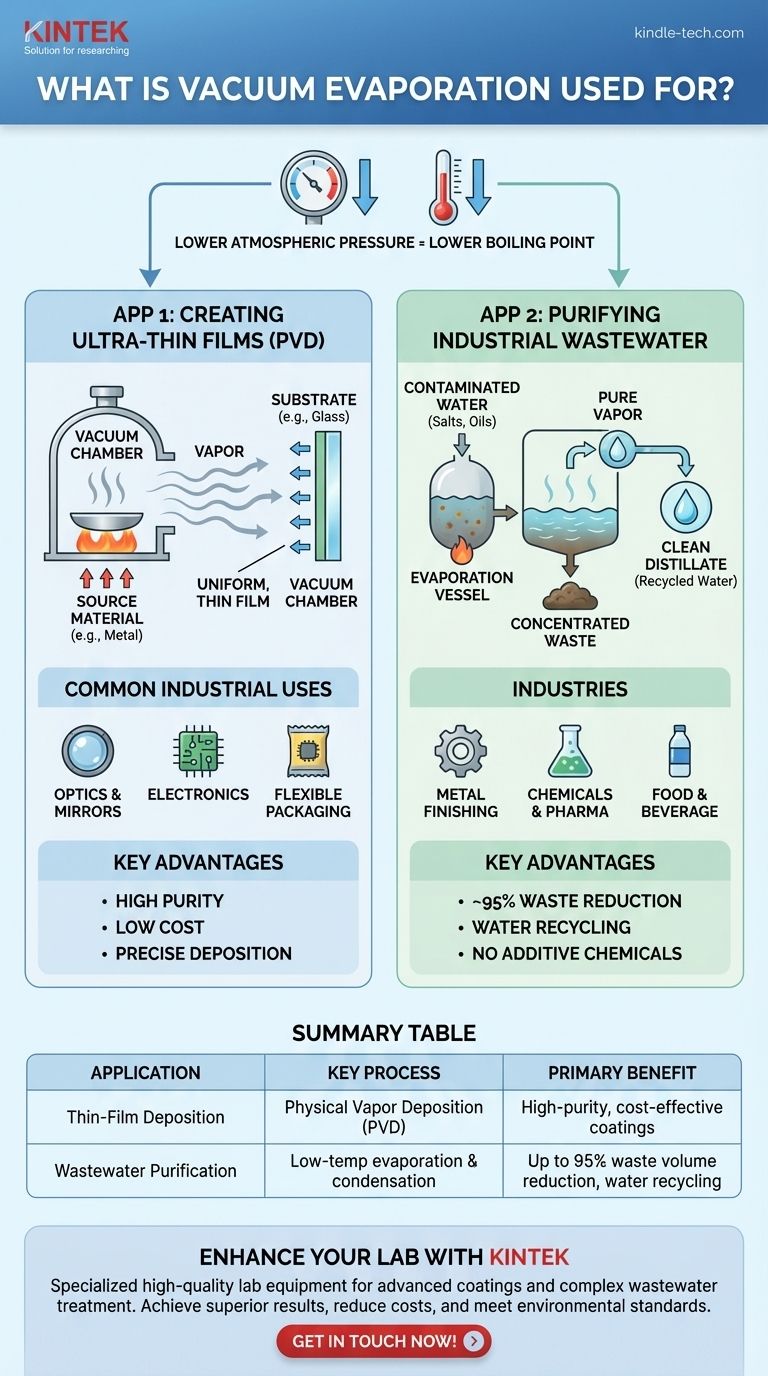
In short, vacuum evaporation is used for two primary and distinct industrial purposes: creating ultra-thin, high-performance coatings on surfaces (a process called thin-film deposition) and purifying industrial wastewater by separating water from contaminants. Both applications leverage the same core principle of lowering pressure to make a substance evaporate more easily.
The central concept behind vacuum evaporation is that reducing atmospheric pressure significantly lowers a substance's boiling point. This single physical principle is exploited in two different ways: either to vaporize metals and other materials for precision coating or to efficiently evaporate water for purification.

The Core Principle: How Vacuum Changes the Game
Evaporation Without High Heat
Under normal atmospheric pressure, water boils at 100°C (212°F). Many metals require thousands of degrees to vaporize.
Creating a vacuum removes most of the air molecules from a chamber. With less atmospheric pressure pushing down on a substance, its molecules can escape into a gaseous state using far less energy.
This means water can be made to boil at room temperature, and hard metals can be vaporized at much lower temperatures than they would otherwise require. This efficiency is the key to both of its major applications.
Application 1: Creating High-Performance Thin Films
One of the most common uses of vacuum evaporation is as a Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) process. It's a method for applying an exceptionally thin and pure layer of material onto a surface, often called a substrate.
The Deposition Process Explained
A source material, such as a metal like aluminum, is placed inside a vacuum chamber. This source is heated until it evaporates, releasing a vapor of its atoms.
These atoms travel in a straight line through the vacuum until they strike the cooler substrate (e.g., a piece of glass or plastic). Upon contact, they condense back into a solid, forming a uniform, thin film.
Common Industrial Uses
This process is essential for manufacturing a wide range of products:
- Mirror and Optical Coatings: Applying reflective layers on glass for mirrors or anti-reflective coatings on lenses.
- Electronics: Creating electrically conductive films for circuits and components.
- Flexible Packaging: Depositing a thin barrier film (like aluminum) on materials like potato chip bags to keep out oxygen and moisture.
- Decorative Finishes: Giving plastics a metallic, chrome-like appearance.
- Protective Coatings: Adding a durable layer to protect surfaces from corrosion.
Key Advantages for Coatings
As a PVD method, vacuum evaporation is valued for its high purity, as the vacuum environment minimizes contamination. It is also the least expensive PVD process, making it highly economical for many applications.
The line-of-sight trajectory of the vapor allows for precise deposition, though it can also be a limitation for complex shapes.
Application 2: Purifying Industrial Wastewater
The same principle of lowering the boiling point is also a highly effective method for water treatment, especially for waste streams with dissolved, non-volatile contaminants.
The Separation Process Explained
Contaminated water is pumped into a low-pressure vessel. The vacuum allows the water to evaporate at a low temperature, which consumes less energy than boiling it at atmospheric pressure.
The water vapor is pure, leaving behind the contaminants (salts, heavy metals, oils) that have much higher boiling points. This vapor is then channeled away and condensed back into clean water, known as the distillate.
The leftover pollutants form a much smaller volume of highly concentrated waste, known as the concentrate.
Industries That Rely on It
This method is crucial for industries that produce difficult-to-treat wastewater, including:
- Metal Forming & Finishing
- Pharmaceuticals and Chemicals
- Food & Beverage Processing
Key Advantages for Treatment
The primary benefit is a massive reduction in wastewater volume, often by up to 95%. This dramatically lowers disposal costs.
The process allows for the recycling of clean water back into industrial processes and does not require expensive additive chemicals.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
For Thin-Film Deposition
The "line-of-sight" nature means it is excellent for coating flat surfaces but struggles to evenly coat complex, three-dimensional objects with hidden surfaces.
While it is the most cost-effective PVD process, other methods may be chosen if properties like film density or surface adhesion are more critical than cost.
For Wastewater Treatment
Vacuum evaporation is ideal for removing contaminants with high boiling points, like salts and metals. However, it is not effective for separating contaminants that evaporate easily with the water, such as volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
While its energy consumption is low compared to traditional boiling, it is still an energy-intensive process compared to other filtration methods like reverse osmosis, with which it is often paired.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
- If your primary focus is creating precise surface coatings: Vacuum evaporation is an excellent choice for cost-effective, high-purity films on relatively simple geometries, such as lenses, packaging films, and decorative parts.
- If your primary focus is treating challenging industrial wastewater: This method is a powerful solution for separating water from dissolved, non-volatile contaminants, especially when the goal is significant waste volume reduction and water recycling.
Ultimately, vacuum evaporation is a testament to how controlling a single environmental variable—pressure—can solve two fundamentally different and critical industrial challenges.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Process | Main Industries | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thin-Film Deposition | Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) | Electronics, Optics, Packaging | High-purity, cost-effective coatings |
| Wastewater Purification | Low-temperature evaporation & condensation | Metal Finishing, Chemicals, Food & Beverage | Up to 95% waste volume reduction, water recycling |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with vacuum evaporation technology?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific needs. Whether you're developing advanced coatings or treating complex wastewater streams, our vacuum evaporation solutions offer precision, efficiency, and reliability.
We help you:
- Achieve superior thin-film deposition for your R&D or production.
- Implement effective wastewater purification to meet environmental standards.
- Reduce operational costs with energy-efficient and durable equipment.
Contact us today to discuss how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success. Let's find the perfect solution for your application. Get in touch now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Conductive Boron Nitride Crucible BN Crucible
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of vacuum evaporation? Purify Water or Create High-Purity Coatings
- What is evaporation material? The Key to Precision Thin-Film Deposition
- How does a molybdenum evaporation source function in H2S for MoS2 synthesis? Master Reactive Film Deposition
- How is deposition time calculated? Mastering the Clock for Strategic Legal Advantage
- What is the thermal evaporation technique? A Guide to Thin-Film Deposition for Your Lab



















