The short answer is there is no single machine for brazing; the term refers to several different types of equipment. The most common machines include torch, furnace, induction, and resistance brazing systems, each using a different method to apply heat and join materials together with a filler metal.
The specific "machine" used for brazing is determined by the method of heating. The core challenge is not finding a single machine, but rather selecting the right heating technology for your specific material, production volume, and joint complexity.
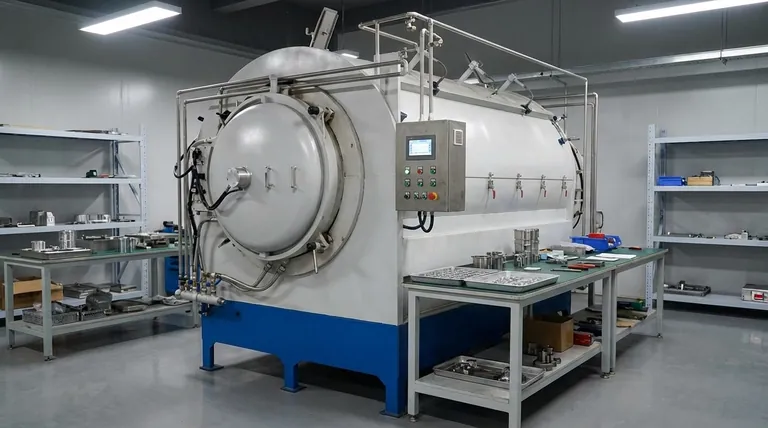

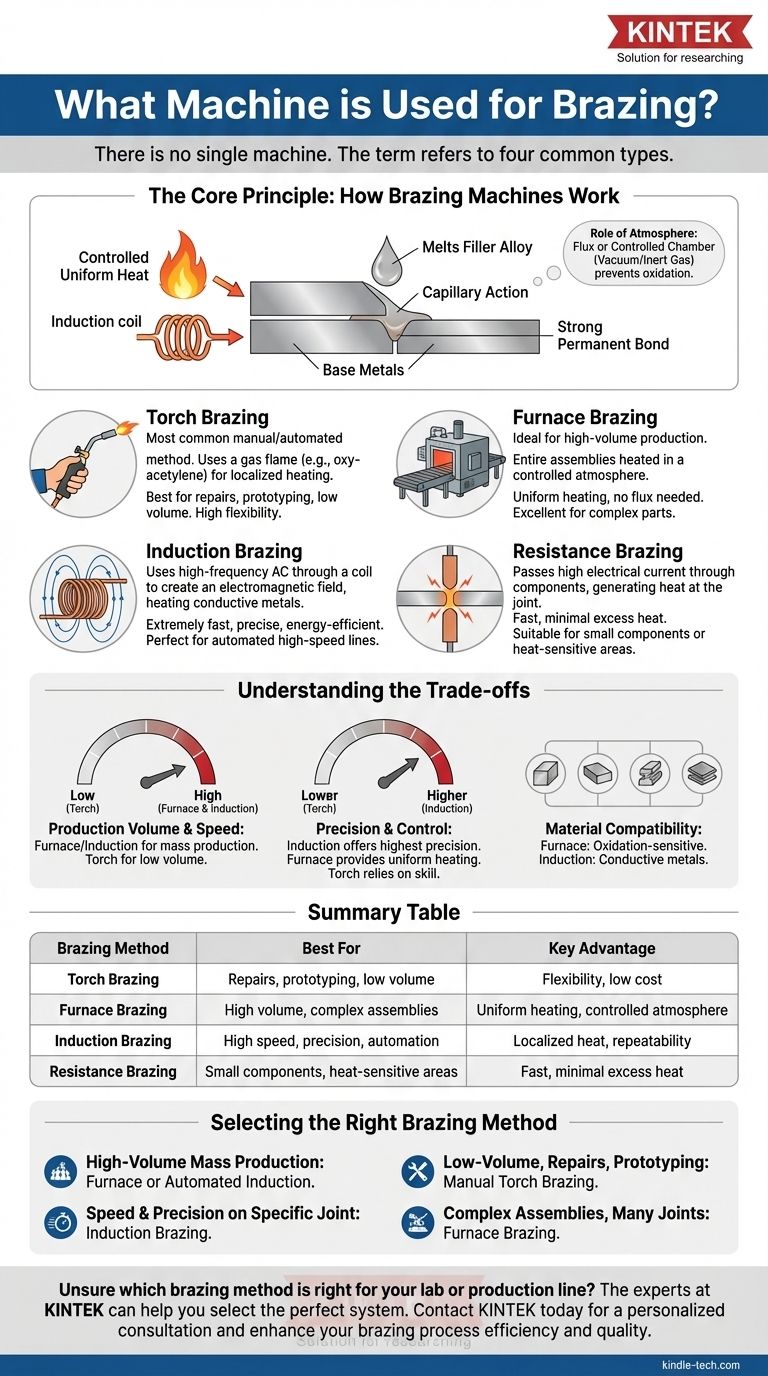
The Core Principle: How Brazing Machines Work
Every brazing machine, regardless of its type, is designed to accomplish one fundamental task: to heat the base metals to a temperature high enough to melt a filler alloy, which then flows into the joint via capillary action.
The Role of Heat and Atmosphere
The equipment must provide controlled, uniform heat to the parts being joined without melting them. The process must also manage surface oxidation.
This is achieved either with a chemical flux, which cleans the surface, or by performing the brazing inside a chamber with a controlled atmosphere, such as a vacuum or inert gas. This ensures the molten filler alloy can "wet" the base metals and form a strong, permanent bond.
Common Types of Brazing Equipment Explained
The primary difference between brazing machines is how they generate and apply heat. Each method is suited for different applications.
Torch Brazing
Torch brazing is the most common manual or automated method. It uses a gas flame (like oxy-acetylene) to heat a localized area of the parts being joined.
This method offers high flexibility and is excellent for repairs, one-off jobs, and low-volume production where precision is controlled by a skilled operator.
Furnace Brazing
Furnace brazing is ideal for high-volume production. Entire assemblies are placed in a furnace, often on a conveyor belt, and heated in a controlled atmosphere.
This approach ensures that all joints on a complex part are heated uniformly and simultaneously. The controlled atmosphere (like vacuum or hydrogen) eliminates the need for flux, resulting in very clean joints.
Induction Brazing
Induction brazing uses a high-frequency alternating current passed through a copper coil. This creates an electromagnetic field that heats the conductive metal parts placed within it.
This method is extremely fast, precise, and energy-efficient. It delivers localized heat only to the joint area, making it perfect for automated, high-speed production lines where quality and repeatability are critical.
Resistance Brazing
This method passes a high electrical current through the components, generating heat at the joint due to electrical resistance. The parts themselves become part of the electrical circuit.
Resistance brazing is fast and produces very little excess heat, making it suitable for joining small components or parts located near heat-sensitive materials.
Automated Brazing Systems
An "automatic brazing machine" is not a heating type itself but rather a system that integrates one of the heating methods (like induction or torch) into a robotic or automated process.
These systems are used for mass production to achieve high speeds, precise tolerances, and consistent quality for materials like steel, copper, and aluminum.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right equipment requires balancing production needs with cost and material constraints.
Production Volume and Speed
Furnace and automated induction systems are built for mass production, capable of producing thousands of parts per hour. Manual torch brazing is significantly slower and reserved for low-volume applications.
Precision and Control
Induction brazing offers the highest degree of precision, as the heating is localized, controllable, and extremely repeatable. Furnace brazing provides excellent thermal uniformity across an entire large part, while torch brazing relies heavily on operator skill.
Material Compatibility
While nearly any metal or ceramic can be brazed, the equipment choice matters. Furnace brazing is excellent for materials sensitive to oxidation, while induction is best for conductive metals.
Initial Cost and Complexity
Manual torch brazing has a very low entry cost and is simple to set up. In contrast, furnace and automated induction systems represent a significant capital investment requiring specialized integration and programming.
Selecting the Right Brazing Method
Your final choice depends entirely on your project's goals.
- If your primary focus is high-volume mass production: Furnace brazing or a fully automated induction system is your most efficient solution.
- If your primary focus is speed and precision on a specific joint: Induction brazing provides unmatched control, speed, and repeatability.
- If your primary focus is low-volume work, repairs, or prototyping: Manual torch brazing offers the most flexibility and the lowest initial investment.
- If you are joining complex assemblies with many joints at once: Furnace brazing ensures uniform heating and consistent quality across the entire component.
Ultimately, the best brazing machine is the one that aligns with your specific application, budget, and quality requirements.
Summary Table:
| Brazing Method | Best For | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Torch Brazing | Repairs, prototyping, low volume | Flexibility, low cost |
| Furnace Brazing | High volume, complex assemblies | Uniform heating, controlled atmosphere |
| Induction Brazing | High speed, precision, automation | Localized heat, repeatability |
| Resistance Brazing | Small components, heat-sensitive areas | Fast, minimal excess heat |
Unsure which brazing method is right for your lab or production line? The experts at KINTEK specialize in lab equipment and consumables, including brazing solutions. We can help you select the perfect system to achieve strong, clean joints while optimizing for your production volume, material compatibility, and precision requirements.
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and let us help you enhance your brazing process efficiency and quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does annealing equipment affect the functional characteristics of Ti-22Nb alloys? Optimize Superelasticity Now
- What energy transfer happens in a furnace? Master Convection, Conduction & Radiation for Your Process
- What are the methods of sintering? Choose the Right Technique for Your Materials
- What is an example of sintering? From Ancient Pottery to Modern 3D Printing
- What is the temperature of a kiln? It Depends on Your Process and Kiln Type
- What is physical vapor deposition process? A Guide to High-Performance Vacuum Coating
- What is a calciner in chemistry? A Guide to High-Temperature Material Transformation
- What are the advantages of vacuum firing? Achieve Ultimate Material Purity and Performance



















