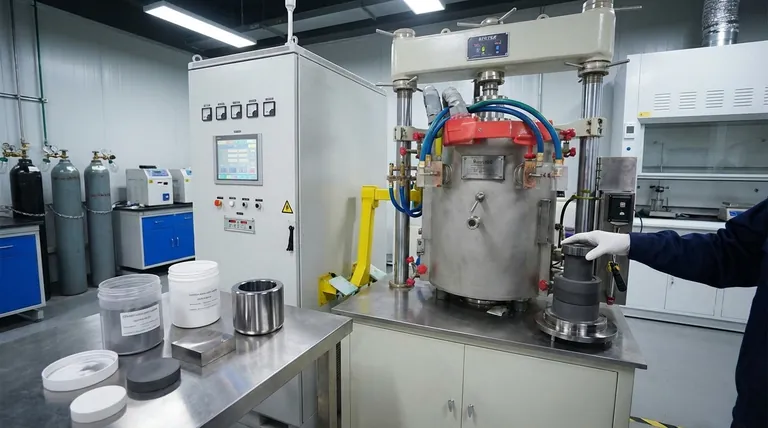
In short, hot pressing is a versatile manufacturing technique that processes a wide range of advanced materials, including technical ceramics, powder metals, and polymers. The critical tooling inside the press, the die that holds this material, is most commonly made from high-purity graphite due to its unique ability to withstand extreme heat and pressure.
The core principle of hot pressing is the simultaneous application of high temperature and pressure. This dictates both the materials you can process (those needing densification) and the materials used for the press tooling (those that can survive the environment).

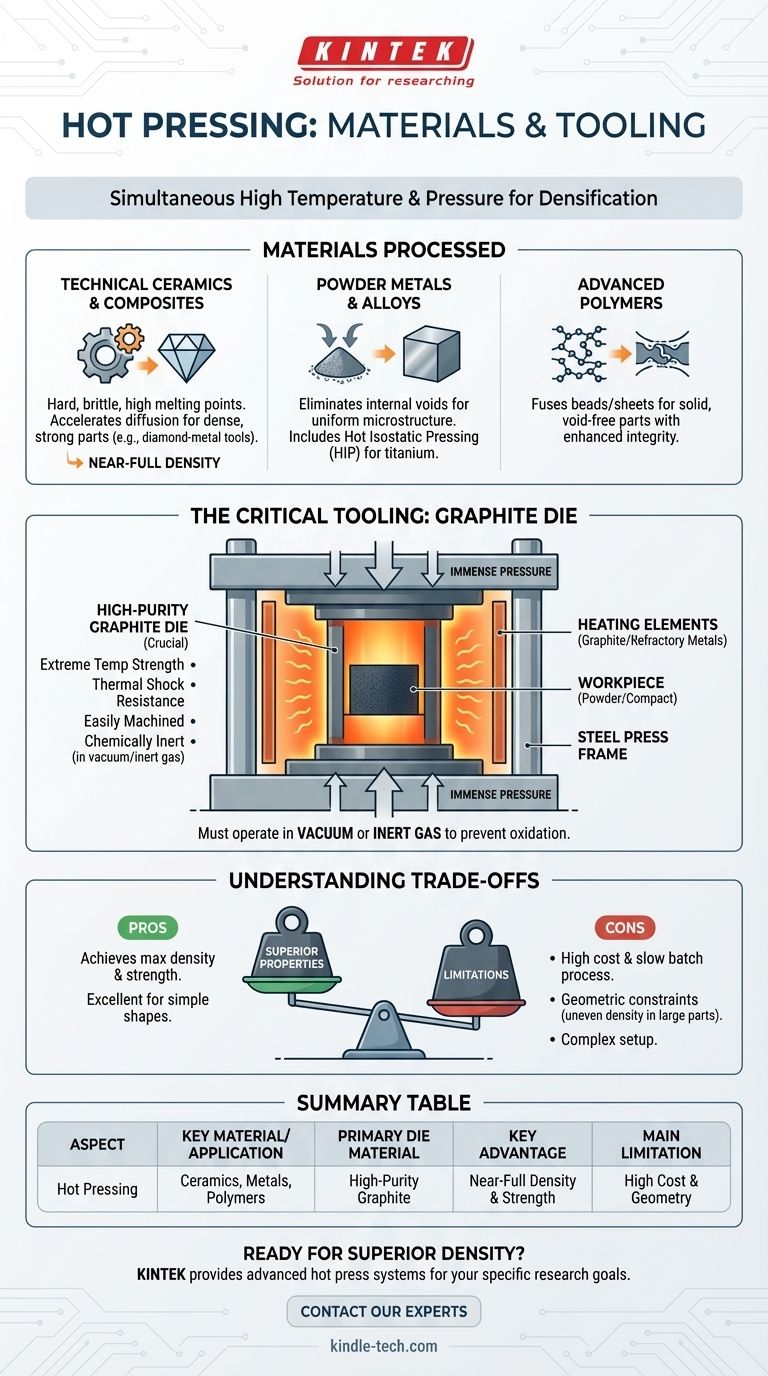
Materials Processed by Hot Pressing
Hot pressing is chosen specifically for materials that are difficult to consolidate using other methods. The goal is to reduce porosity and achieve near-full density, which dramatically improves the material's mechanical properties.
Technical Ceramics and Composites
These materials are the primary application for hot pressing. Because they are inherently hard and brittle with very high melting points, they do not densify easily through simple sintering.
Hot pressing applies pressure during the heating cycle, which forces the powder particles together, accelerating diffusion and resulting in a dense, strong final part. Examples include diamond-metal composite cutting tools, boron carbide, and silicon nitride.
Powder Metals and Alloys
While many metal powders can be cold-pressed, hot pressing is used for high-performance alloys that benefit from a fully dense, uniform microstructure.
The process helps eliminate internal voids that can become failure points. Hot isostatic pressing (HIP), a related method, is frequently used for critical components made from titanium and other advanced alloys by applying pressure from all directions.
Advanced Polymers
Hot pressing is also used to mold and consolidate high-performance polymers and polymer composites.
The combination of heat and pressure ensures that polymer beads or sheets fuse completely, creating a solid, void-free part with enhanced structural integrity.
Materials Used in Hot Press Tooling
The equipment itself must be made of materials that can endure the severe operating conditions without failing or contaminating the workpiece.
The Central Role of Graphite
The die assembly—the mold that contains the powder and the punches that apply pressure—is almost always machined from graphite.
Graphite is chosen for several critical reasons: it maintains its strength at extreme temperatures, has excellent resistance to thermal shock, is easily machined into complex die shapes, and is chemically inert in the required vacuum or inert gas atmospheres.
The Press Frame and Heating System
The main body of the press is a robust steel frame designed to handle immense loads.
The heating elements surrounding the graphite die are specialized materials capable of reaching very high temperatures. These can be additional graphite elements, or refractory metals like molybdenum or tungsten, depending on the required temperature and atmosphere.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, hot pressing is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Shape and Geometric Constraints
The process is excellent for producing parts with relatively simple geometries like discs, blocks, and tubes. The reference notes that thin-walled or complex shapes can be made due to the good fluidity of the powder at temperature.
However, the reliance on a rigid die makes it difficult to produce highly intricate parts. Furthermore, very long or large parts can suffer from uneven density due to friction against the die walls, a significant limitation.
Process Time and Cost
Hot pressing is a batch process, not a continuous one. Each cycle of loading, heating, pressing, and cooling can take several hours.
This makes it significantly slower and more expensive per part compared to mass-production techniques like injection molding or cold pressing and sintering. It is reserved for applications where the material's final properties are the absolute priority.
Atmospheric Control
To prevent the graphite die and the material being processed from oxidizing (burning up) at high temperatures, the entire process must be conducted in a vacuum or an inert gas environment. This adds significant complexity and cost to the equipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your material and desired outcome will determine if hot pressing is the correct approach.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density and strength in ceramics or hard composites: Hot pressing is the industry-standard solution for eliminating porosity.
- If your primary focus is consolidating high-performance metal powders into critical components: Hot pressing or the related hot isostatic pressing (HIP) is necessary to achieve a fully dense, reliable microstructure.
- If your primary focus is producing simple, high-quality polymer specimens or parts: Hot pressing provides an effective way to create fully consolidated, void-free polymer components.
Ultimately, hot pressing is a specialized tool for creating superior materials when performance justifies the investment in time and cost.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Material/Application |
|---|---|
| Primary Die Material | High-Purity Graphite |
| Commonly Processed Materials | Technical Ceramics, Powder Metals, Advanced Polymers |
| Key Advantage | Achieves Near-Full Density & Superior Strength |
| Main Limitation | High Cost & Geometric Constraints |
Ready to achieve superior material density and performance?
KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables, like hot press systems, that are essential for processing technical ceramics, metals, and polymers. Our expertise ensures you get the right solution to meet your specific research and production goals, maximizing the strength and reliability of your materials.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our hot press solutions can benefit your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot press for CuCr50? Achieve Superior Density & Purity in Alloy Production
- Why is precise temperature control necessary for SiC/Cu Vacuum Hot Pressing? Mastering the Cu9Si Interface Phase
- What advantages does hot pressing sintering equipment provide for NASICON? Achieve 100% Dense Solid Electrolyte Plates
- What are the primary advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Maximize Density in B4C-CeB6 Ceramics
- Why is a vacuum essential for sintering metal-ceramic composites? Achieve Pure, High-Density Results



















