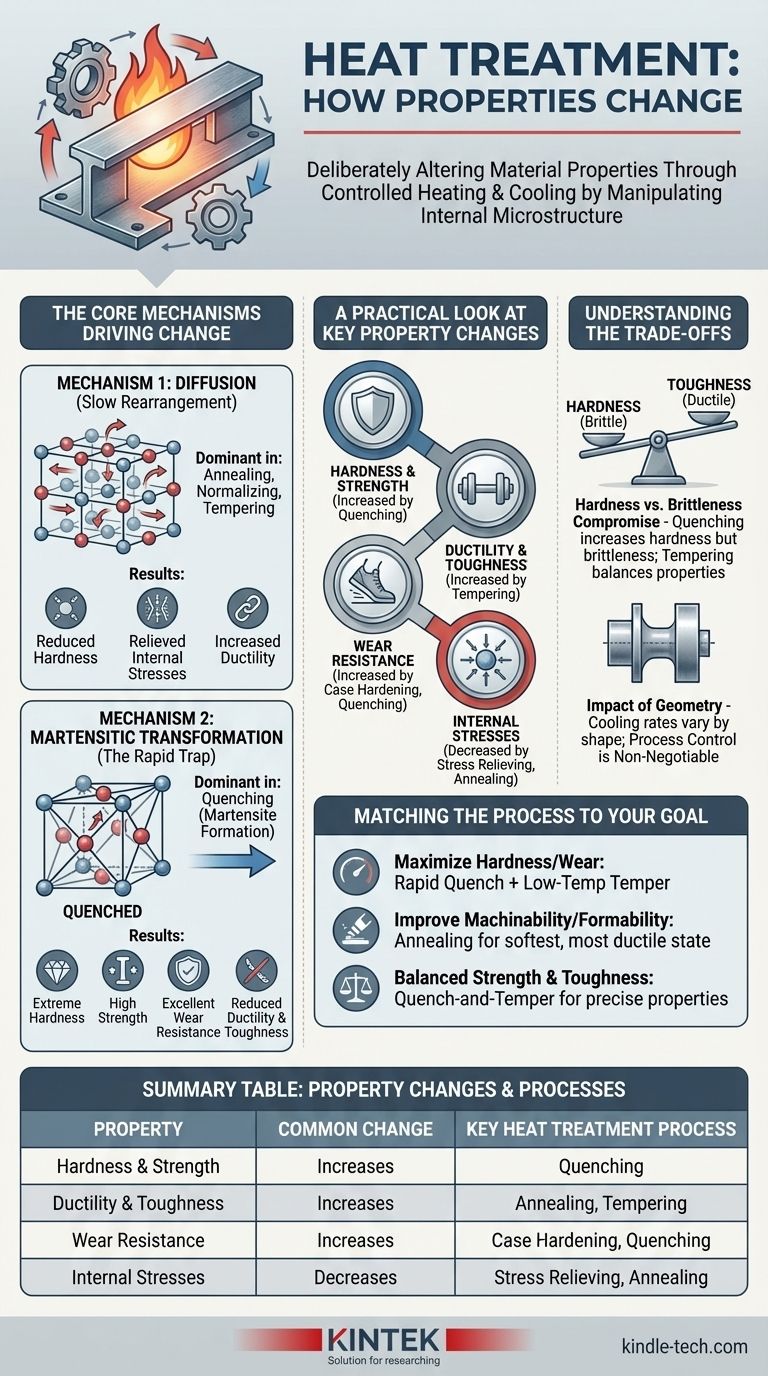
In short, heat treatment is a process used to deliberately alter a material's fundamental mechanical and physical properties. The most common changes are to a metal's hardness, strength, toughness, ductility, and wear resistance. By precisely controlling temperature and cooling rates, you are fundamentally changing the internal crystalline structure of the material to achieve a desired performance characteristic.
The core principle of heat treatment is not just changing properties, but controlling the material's internal microstructure. The way atoms are arranged dictates the final performance, and heat treatment is the primary tool for manipulating that arrangement.

The Core Mechanisms Driving Change
All property changes during the heat treatment of metal alloys are driven by two primary metallurgical mechanisms. Understanding these two processes is key to understanding why the properties change.
Mechanism 1: Diffusion (The Slow Rearrangement)
Diffusion is the process of atoms moving within the material's solid crystal lattice. This movement is highly dependent on both temperature and time.
Higher temperatures give atoms more energy, allowing them to move from their fixed positions and rearrange into more stable, lower-energy states. This is the dominant mechanism in processes like annealing, normalizing, and tempering.
By allowing atoms to diffuse and rearrange, you can achieve a more uniform and stable microstructure. This typically results in reduced hardness, relieved internal stresses, and increased ductility (the ability to deform without fracturing).
Mechanism 2: Martensitic Transformation (The Rapid Trap)
In contrast to diffusion, some transformations happen almost instantly and without the long-range movement of atoms. The most important of these is the formation of martensite.
This occurs when certain alloys (like steel) are heated and then cooled so rapidly (quenched) that the atoms don't have time to rearrange into their normal low-temperature structure.
Instead, they become trapped in a highly strained, distorted crystal structure called martensite. This internal strain is what gives the material its properties: extreme hardness, high strength, and excellent wear resistance, but at the cost of significantly reduced ductility and toughness, making it brittle.
A Practical Look at Key Property Changes
While the underlying mechanisms are atomic, the results are tangible changes to properties that directly impact engineering performance.
Hardness and Strength
These two properties are closely related and are often the primary targets of heat treatment. Processes like quenching dramatically increase hardness and tensile strength by creating a martensitic structure.
Ductility and Toughness
Ductility (ability to deform) and toughness (ability to absorb energy) are often inversely related to hardness. A very hard material is often brittle. Processes like annealing increase ductility and toughness by creating a softer, more uniform microstructure.
Wear Resistance
Resistance to abrasion and wear is directly linked to surface hardness. Treatments like case hardening or quenching are used specifically to create a hard, wear-resistant surface on a component.
Internal Stresses
Manufacturing processes like welding, forming, and machining can introduce significant internal stresses. A slow heating and cooling cycle, like annealing or stress relieving, allows the microstructure to relax, significantly reducing these internal stresses and improving dimensional stability.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a heat treatment process is never about maximizing one property in isolation. It is always a strategic compromise based on the application's needs.
The Hardness vs. Brittleness Compromise
This is the most fundamental trade-off. A fully quenched, martensitic steel part is exceptionally hard but may be too brittle for practical use, as it could shatter under impact. This is why tempering is performed after quenching—it slightly reduces hardness to gain a significant improvement in toughness.
The Impact of Geometry
A component's size and shape critically affect the outcome. A thick section will cool much more slowly than a thin one during a quench, potentially resulting in a hard exterior but a softer, weaker core. This can lead to non-uniform properties throughout the part.
Process Control is Non-Negotiable
Heat treatment is not a blunt instrument. Minor variations in temperature, soak time, or cooling rate can lead to dramatically different microstructures and, therefore, different properties. Achieving consistent, reliable results requires precise process control.
Matching the Process to Your Goal
Your choice of heat treatment should be driven entirely by the final performance you require from the component.
- If your primary focus is maximizing hardness and wear resistance: A rapid quench to form martensite is the goal, often followed by a low-temperature temper to relieve some brittleness.
- If your primary focus is improving machinability or formability: Annealing is the correct choice to create the softest, most ductile state possible and eliminate internal stresses.
- If your primary focus is a balanced combination of strength and toughness: A quench-and-temper process is ideal, as it allows you to precisely dial in the final properties by adjusting the tempering temperature.
Ultimately, heat treatment gives you direct control over a material's internal structure, allowing you to tailor its properties to the precise demands of your application.
Summary Table:
| Property | Common Change | Key Heat Treatment Process |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness & Strength | Increases | Quenching, Martensitic Transformation |
| Ductility & Toughness | Increases | Annealing, Tempering |
| Wear Resistance | Increases | Case Hardening, Quenching |
| Internal Stresses | Decreases | Stress Relieving, Annealing |
Ready to achieve precise material properties for your lab applications? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including advanced heat treatment solutions. Whether you need to enhance hardness, improve toughness, or ensure uniform material performance, our expertise can help you optimize your processes. Contact us today to discuss how KINTEK can support your laboratory's specific needs with reliable, precision-engineered equipment.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why do you heat treat in a vacuum? Achieve Perfect Surface Finish and Material Integrity
- What are the parts of a vacuum furnace? A Guide to the 5 Core Systems
- How does heat treatment process work? Tailor Material Properties for Your Application
- What is the process of vacuum quenching? Achieve Superior Hardness with a Pristine Surface Finish
- What are the four types of heat treating processes? Master Annealing, Normalizing, Hardening, and Tempering



















