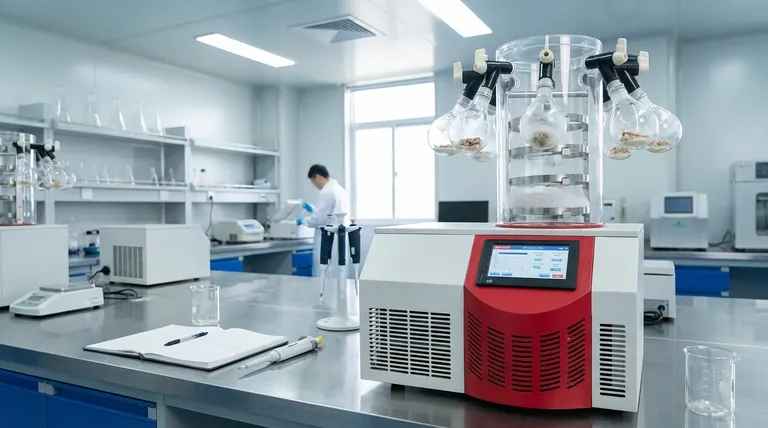
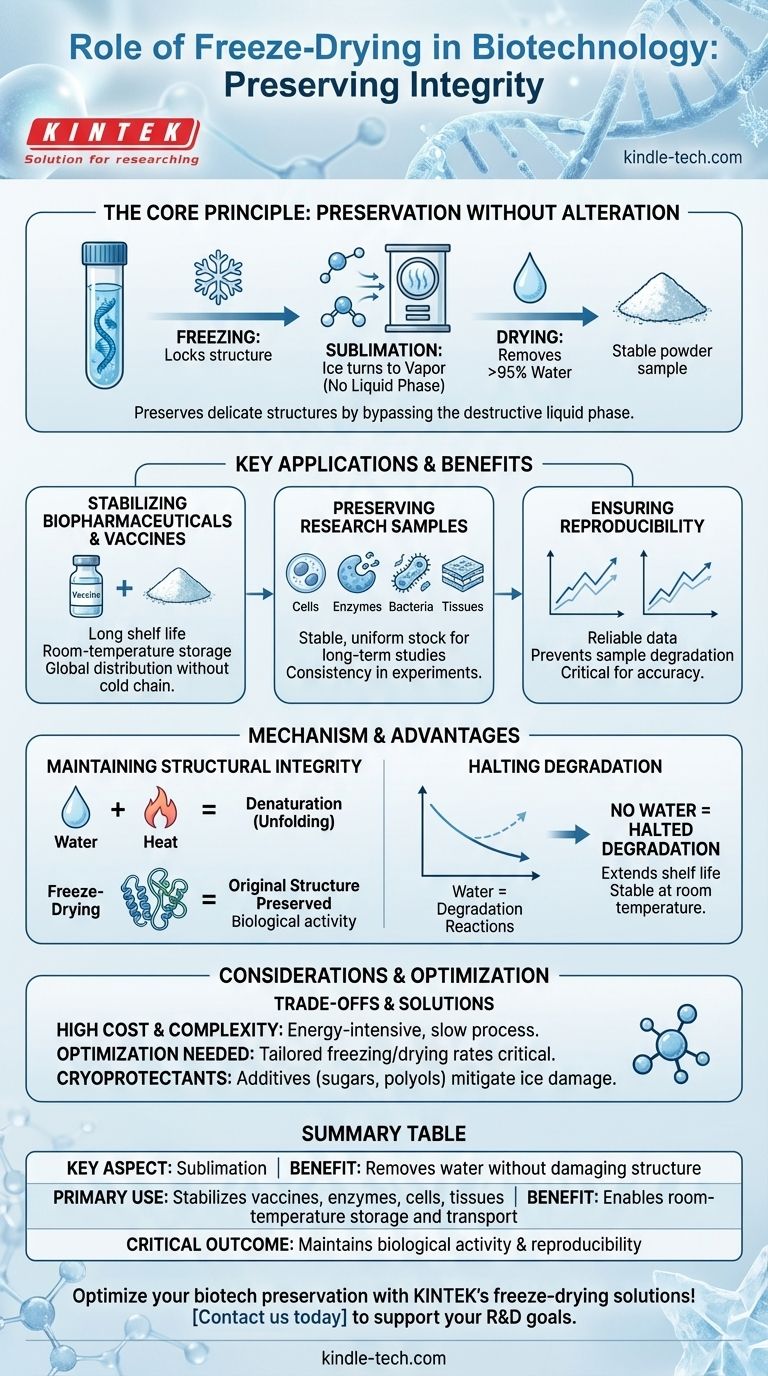
In biotechnology, the essential role of freeze-drying is to stabilize and preserve sensitive biological materials for long-term storage and analysis. This process, also known as lyophilization, removes water from samples like vaccines, enzymes, cells, and tissues without damaging their fundamental structural or chemical composition, ensuring their integrity and viability for future use.
The core value of freeze-drying isn't just preservation; it's preservation with near-perfect fidelity. By removing water while the material is frozen solid, it bypasses the destructive liquid phase, effectively pausing biological activity without altering the very structure that makes the material work.

The Core Principle: Preservation Without Alteration
Freeze-drying is the gold standard for stabilizing biologics because it is uniquely designed to maintain the integrity of delicate molecular structures. The entire process is built around avoiding damage.
The Mechanism of Sublimation
The process begins by freezing the material, locking its molecular structure in place. A strong vacuum is then applied, allowing the frozen water to turn directly into vapor without ever becoming a liquid—a process called sublimation.
This is the critical step. By avoiding the liquid phase, freeze-drying prevents the chemical reactions and physical stresses that would otherwise degrade the sample.
Maintaining Structural Integrity
For materials like enzymes, antibodies, and vaccines, their function is entirely dependent on their precise three-dimensional shape. The presence of water and heat can cause these proteins to unfold, or denature, rendering them useless.
Freeze-drying meticulously preserves this original structure, ensuring the material retains its biological activity when it is eventually rehydrated.
Halting Biological and Chemical Degradation
Water is the medium for most biological and chemical reactions that lead to decay. By removing approximately 95% to 99% of the water, freeze-drying effectively halts these degradation pathways.
This creates a product with a vastly extended shelf life that is stable even at room temperature, which is a major advantage over materials requiring constant, energy-intensive refrigeration.
Key Applications in Biotechnology and Pharma R&D
Freeze-drying is not a niche technique; it is a foundational technology enabling some of the most critical work in modern biotechnology and pharmaceutical development.
Stabilizing Vaccines and Biopharmaceuticals
Many modern vaccines and therapeutic proteins are incredibly unstable in their liquid form. Freeze-drying converts them into a stable powder that can be stored for years and easily transported without a complex "cold chain."
This technology is crucial for distributing life-saving medicines globally, especially to remote areas.
Preserving Research Samples
In research, consistency is everything. Scientists use freeze-drying to preserve a wide array of samples, including cells, tissues, bacteria, and viruses.
This creates a stable, uniform stock of materials that can be used over the course of long-term studies, ensuring that experimental conditions remain consistent.
Ensuring Experimental Reproducibility
The reliability of scientific data depends on the quality of the starting materials. If an enzyme or reagent degrades between experiments, the results will be inconsistent and unreliable.
By providing a method to create stable, storable batches of these materials, freeze-drying underpins scientific accuracy and reproducibility.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, freeze-drying is not a universal solution and comes with its own set of challenges that must be managed.
High Cost and Complexity
Freeze-dryers are sophisticated pieces of equipment, and the process itself is slow and energy-intensive. This makes it a more expensive preservation method compared to simple freezing or refrigeration.
The Need for Optimization
The freezing and drying rates must be carefully optimized for each specific material. If freezing occurs too slowly, large ice crystals can form and physically damage cell membranes or delicate protein structures.
Developing a successful lyophilization cycle often requires significant research and development.
Use of Cryoprotectants
To mitigate the damage caused by ice crystal formation, special stabilizing agents known as cryoprotectants (like sugars or polyols) are often added to the formulation before freezing.
The selection and concentration of these agents are critical variables that must be tailored to the specific biological material being preserved.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, the decision to use freeze-drying depends entirely on the need to preserve the precise biological function of a sensitive material.
- If your primary focus is the long-term storage of research reagents: Freeze-drying is the best method for creating stable, baseline samples that ensure experimental reproducibility over time.
- If your primary focus is developing stable biopharmaceuticals like vaccines or antibodies: This technology is essential for converting unstable liquid formulations into a stable powder, simplifying logistics and extending shelf life.
- If your primary focus is transporting sensitive biological samples without refrigeration: Freeze-drying removes the need for a complex cold chain, dramatically reducing the risk of sample degradation during transit.
Freeze-drying is the technology that allows biotechnology to pause time, preserving the delicate integrity of biological materials for future discovery and application.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Benefit in Biotechnology |
|---|---|
| Process | Sublimation removes water without damaging structure |
| Primary Use | Stabilizes vaccines, enzymes, cells, and tissues |
| Key Advantage | Enables room-temperature storage and transport |
| Critical Outcome | Maintains biological activity and reproducibility |
Optimize your biotech preservation with KINTEK's freeze-drying solutions!
Whether you're developing stable vaccines, preserving research samples, or ensuring experimental reproducibility, KINTEK's lab equipment and consumables are designed to meet your specific needs. Our expertise in freeze-drying technology helps you maintain the integrity of sensitive biological materials, simplify logistics, and extend shelf life without compromising quality.
Contact us today to discuss how we can support your biotechnology and pharmaceutical R&D goals with reliable, precision-engineered solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Liquid Nitrogen Cryogenic Grinder Mill Cryomill Airflow Ultrafine Pulverizer
- Touchscreen Automatic Vacuum Heat Press
People Also Ask
- What is the distillate extraction method? Achieve Peak Purity in Cannabis Concentrates
- Where are evaporators used in food industry? Concentrate Products & Reduce Costs
- What types of pharmaceutical products are commonly produced using freeze drying technology? Essential for Vaccines & Biologics
- What can I use instead of rotavap? Find the Perfect Solvent Removal Tool for Your Lab
- What are some common problems to avoid during freeze drying? Prevent Melt-Back and System Overload



















