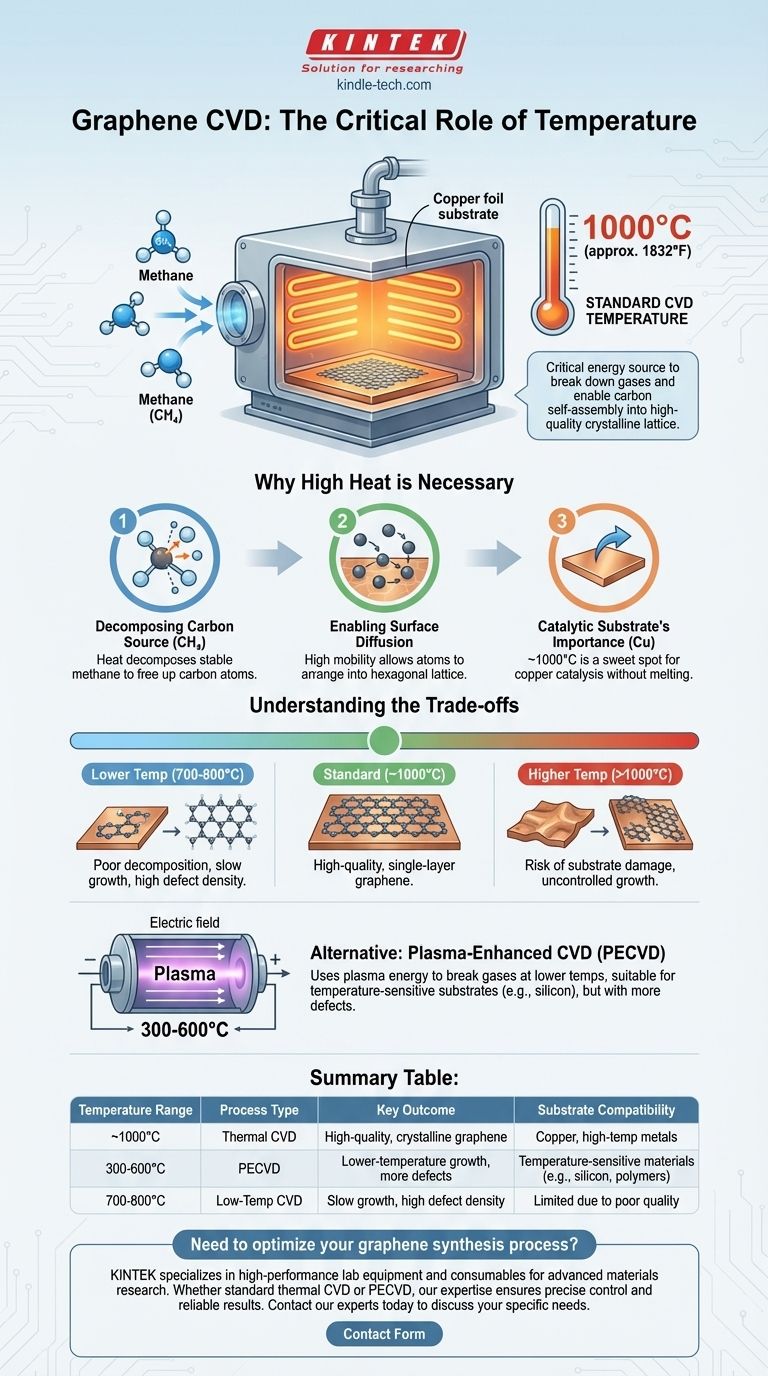
In a standard chemical vapor deposition (CVD) process, graphene is typically grown at extremely high temperatures, most commonly around 1000°C (approximately 1832°F). This process takes place in a vacuum chamber where a carbon-containing gas, such as methane, is introduced over a catalytic metal substrate, most often copper foil.
The high temperature in graphene CVD is not arbitrary; it is the critical energy source required to break down precursor gases and enable carbon atoms to self-assemble into a high-quality, crystalline lattice on the catalyst. This temperature directly controls the trade-off between growth rate, defect density, and the integrity of the substrate itself.

The Role of Temperature in Graphene Growth
To understand why such high heat is necessary, we must look at the key steps of the CVD process that are directly governed by thermal energy.
Decomposing the Carbon Source
The process begins with a carbon-containing gas, typically methane (CH₄). At room temperature, methane is very stable.
The intense heat inside the CVD chamber provides the energy needed to catalytically decompose these gas molecules on the surface of the metal foil, breaking them down and freeing up carbon atoms for growth.
Enabling Surface Diffusion
Once carbon atoms are available, they must arrange themselves into the specific hexagonal lattice structure of graphene.
High temperature gives these atoms high surface mobility, allowing them to move freely across the catalyst surface until they find a low-energy position within the growing crystal lattice. Without this mobility, the carbon would deposit randomly, forming a defective or amorphous film rather than high-quality graphene.
The Catalytic Substrate's Importance
The choice of metal substrate is crucial and is directly linked to the temperature. Copper (Cu) is the most common catalyst for producing high-quality, single-layer graphene.
The growth process occurs just below copper's melting point (~1085°C), which is why the ~1000°C range is a thermodynamic sweet spot for effective catalysis without damaging the substrate.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The 1000°C figure is an industry standard for a reason, but deviating from it has significant consequences. Understanding these trade-offs is key to controlling the final material's properties.
The Problem with Lower Temperatures
Attempting the process at significantly lower temperatures (e.g., 700-800°C) results in poor outcomes. The methane precursor does not decompose efficiently, leading to extremely slow or non-existent growth.
Any film that does form will likely have a high density of defects because the carbon atoms lack the energy to arrange themselves correctly, resulting in poor electronic and mechanical properties.
The Risks of Higher Temperatures
Pushing the temperature much higher than 1000°C brings you dangerously close to the melting point of the copper substrate.
This can cause the foil to deform, sublimate, or restructure its grain boundaries, which negatively impacts the uniformity of the graphene growth. While it might increase the growth rate, it can also lead to less controlled, lower-quality films.
Alternative: Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD)
To overcome the high-temperature limitation, especially for applications on substrates that cannot withstand such heat, Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) is used.
PECVD uses an electric field to create a plasma, which bombards the gas molecules with enough energy to break them apart at much lower temperatures (e.g., 300-600°C). However, this more energetic process can often create more defects than traditional high-temperature CVD.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal temperature and method are dictated entirely by the requirements of your final application.
- If your primary focus is maximum crystalline quality and electronic performance: Stick with the industry-standard thermal CVD process at ~1000°C on a copper catalyst.
- If your primary focus is integration with temperature-sensitive substrates (like silicon or polymers): Explore lower-temperature PECVD methods, but be prepared to accept a potential compromise in graphene's structural perfection.
Ultimately, controlling the temperature is the primary lever for tuning the fundamental properties of the final graphene film.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Process Type | Key Outcome | Substrate Compatibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| ~1000°C | Thermal CVD | High-quality, crystalline graphene | Copper, other high-temp metals |
| 300-600°C | PECVD | Lower-temperature growth, more defects | Temperature-sensitive materials (e.g., silicon, polymers) |
| 700-800°C | Low-Temp CVD | Slow growth, high defect density | Limited due to poor quality |
Need to optimize your graphene synthesis process? KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables tailored for advanced materials research. Whether you're working with standard thermal CVD or exploring PECVD for temperature-sensitive applications, our expertise ensures you achieve precise temperature control and reliable results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs in graphene and other 2D material growth.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using an alumina liner in a tube furnace for biomass combustion corrosion simulations?
- What are the advantages of a tube furnace? Achieve Superior Temperature Uniformity and Control
- What is the pressure on a tube furnace? Essential Safety Limits for Your Lab
- Why is an Alumina Ceramic Tube Support Necessary for 1100°C Experiments? Ensure Data Accuracy and Chemical Inertness
- What is the ceramic tube high temperature? From 1100°C to 1800°C, Choose the Right Material



















