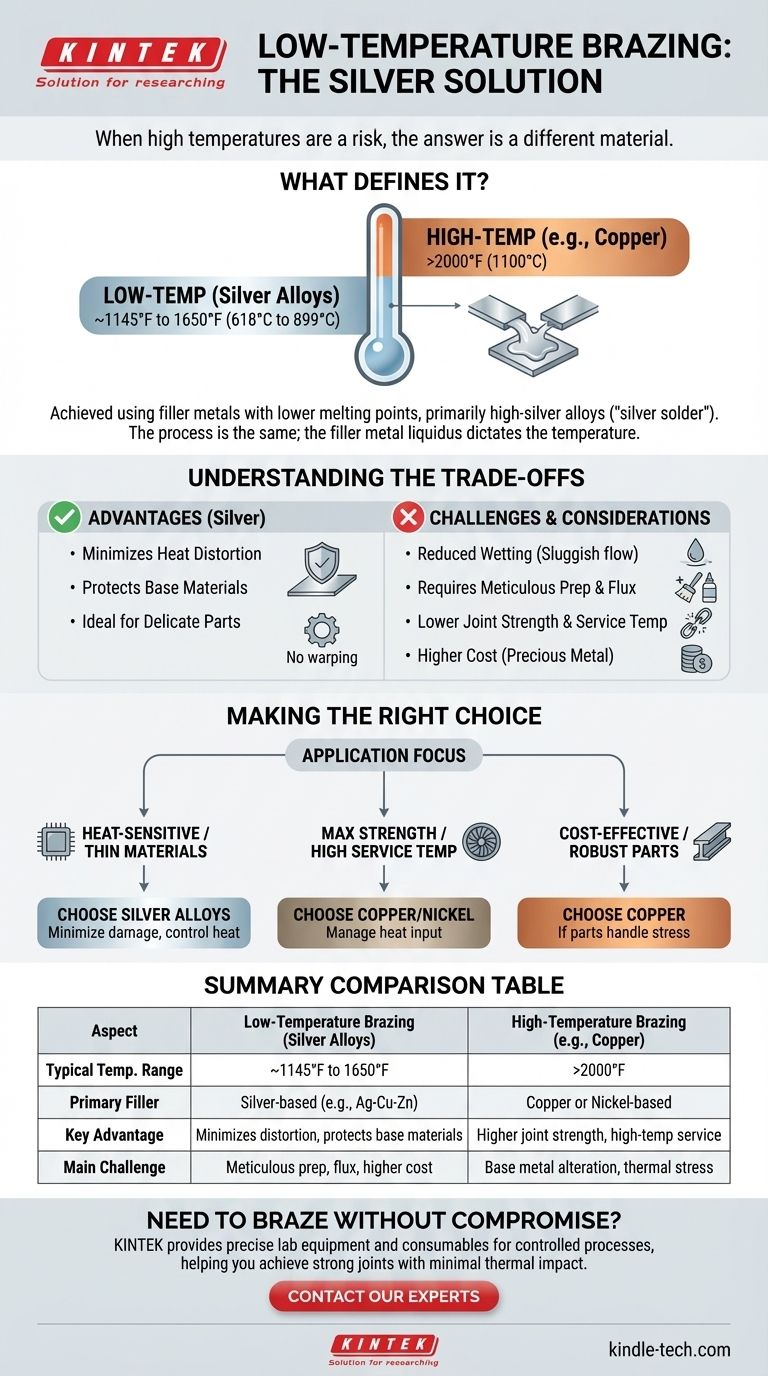
When high temperatures are a risk, the solution is not a different brazing process, but a different brazing material. Low-temperature brazing is achieved by using filler metals with lower melting points, most commonly alloys with a high silver (Ag) content. These alloys, often called "silver solder," allow you to create strong, permanent joints while minimizing heat distortion and damage to the base materials.
The key to low-temperature brazing is selecting a filler metal with a lower melting point, typically a silver-based alloy. This choice directly impacts the joint's properties, cost, and the level of preparation required for a successful bond.

What Defines "Low-Temperature" Brazing?
The distinction between high and low-temperature brazing lies almost entirely in the filler metal alloy being used. The fundamental process of heating two parent metals and drawing a molten filler between them via capillary action remains the same.
The Central Role of the Filler Metal
Brazing, by definition, occurs above 840°F (450°C). "Low-temperature" is a relative term within this context, referring to processes at the lower end of this spectrum. The process temperature is dictated by the liquidus (fully molten) temperature of the chosen filler alloy.
Silver Alloys: The Industry Standard
Filler metals containing silver are the primary choice for lowering brazing temperatures. These alloys, often combined with copper, zinc, and sometimes cadmium or tin, can have liquidus temperatures ranging from around 1145°F (618°C) to 1650°F (899°C).
Contrasting with High-Temperature Brazing
This stands in sharp contrast to high-temperature brazing, which often uses copper or nickel-based alloys. For example, brazing steel with a pure copper filler requires temperatures exceeding 2000°F (1100°C), which can significantly alter the properties of the base metal.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
Choosing a low-temperature approach is a strategic decision that comes with a distinct set of advantages and disadvantages. It is not a universally superior method.
Reduced Reactivity and Wetting
At lower temperatures, the molten braze alloy is naturally more sluggish and less chemically reactive with the base metal. This reduced "wetting" action means that surface cleanliness and the use of an appropriate flux are absolutely critical for the filler to flow properly and form a strong bond.
Joint Strength and Service Temperature
Lower melting point fillers generally create joints with lower ultimate strength than their high-temperature counterparts. Furthermore, the maximum temperature the finished joint can withstand in service will be correspondingly lower.
The Cost Factor of Silver
Silver is a precious metal, making these filler alloys significantly more expensive than common copper or bronze fillers. For large-scale production, this cost difference can be a major factor in the decision-making process.
Risk of Damaging Sensitive Materials
While the goal is to protect the base metals, improper technique can still cause damage. It is crucial to use a controlled heat source and heat the joint evenly to avoid overheating and warping thin sections or undoing a prior heat treatment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct brazing temperature is a calculated balance between protecting your materials and achieving the required joint performance.
- If your primary focus is joining heat-sensitive or thin materials: A silver-based brazing alloy is your best option to minimize the heat-affected zone and prevent damage.
- If your primary focus is maximum joint strength at high service temperatures: You will need to use higher-temperature copper or nickel-based filler metals and develop a process to manage the heat input.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness on robust parts (like thick steel): High-temperature copper brazing is often the more economical and stronger choice, provided the components can handle the thermal stress.
Ultimately, understanding your material's limits and your joint's performance requirements will guide you to the correct brazing temperature.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Low-Temperature Brazing (Silver Alloys) | High-Temperature Brazing (e.g., Copper) |
|---|---|---|
| Typical Temp. Range | ~1145°F to 1650°F (618°C to 899°C) | >2000°F (1100°C) |
| Primary Filler Metal | Silver-based alloys (e.g., Ag-Cu-Zn) | Copper or Nickel-based alloys |
| Key Advantage | Minimizes heat distortion, protects base materials | Higher joint strength, suitable for high-temp service |
| Main Challenge | Requires meticulous surface prep and flux; higher material cost | Risk of base metal property alteration; higher thermal stress |
Need to Braze Heat-Sensitive Components Without Compromise?
KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for controlled brazing processes. Whether you're working with delicate instruments, thin-walled assemblies, or materials prone to heat distortion, our solutions help you achieve strong, reliable joints with minimal thermal impact.
Let us help you select the right materials and equipment for your low-temperature brazing application.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and ensure optimal results for your laboratory or production environment.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electrode Polishing Material for Electrochemical Experiments
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Conductive Boron Nitride BN Ceramics Composite for Advanced Applications
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
People Also Ask
- How does sample size affect analysis? Maximize the Reliability of Your Research
- What is the purpose of using electrolytic polishing on copper foils? Optimize Your CVD Graphene & hBN Growth Surface
- What is the step-by-step process for polishing, testing, and cleaning an electrode? A Pro Guide for Precision Results
- Why are an electrolytic polishing system and specific electrolytes necessary for Inconel 625? Expert Analysis
- What is the purpose of alumina polishing powder in GCE pretreatment? Master Surface Prep for Electrochemistry












