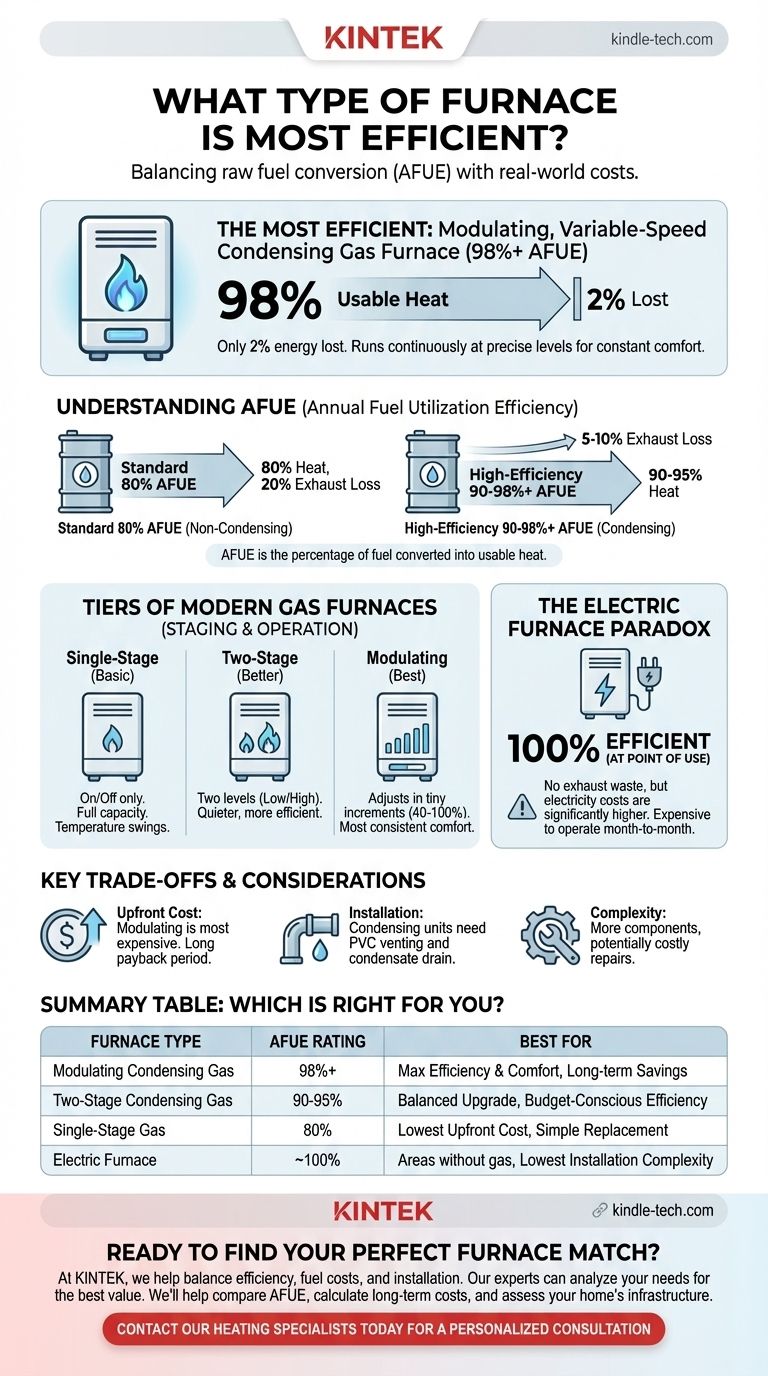
When it comes to raw fuel conversion, the most efficient furnace you can purchase is a modulating, variable-speed condensing gas furnace. These top-tier models can achieve an Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) rating of over 98%, meaning only 2% of the fuel energy is lost during the heating process. However, this number does not tell the whole story.
The highest efficiency rating belongs to condensing gas furnaces, but the truly most efficient choice for your home depends on a crucial balance between the unit's AFUE rating, the local cost of fuel, and the total cost of installation and ownership.

How Furnace Efficiency is Measured (AFUE)
To compare furnaces, you must first understand the industry standard for measuring their performance: the Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) rating.
What AFUE Represents
AFUE is a percentage that tells you how much of the fuel a furnace consumes is converted directly into usable heat for your home over the course of a year.
An 80% AFUE furnace converts 80 cents of every dollar spent on fuel into heat, while the remaining 20 cents are lost through exhaust. A 95% AFUE furnace loses only 5 cents per dollar.
Standard-Efficiency: 80% AFUE
These are often called "non-condensing" furnaces. They are the baseline for modern equipment and typically vent their exhaust gases through a metal flue pipe.
High-Efficiency: 90% - 98%+ AFUE
Known as "condensing" furnaces, these units have a second heat exchanger that captures additional heat from the exhaust gases. This process cools the exhaust enough for water vapor to condense, releasing latent heat that would otherwise be wasted.
The Tiers of Modern Gas Furnaces
Beyond the AFUE rating, the way a furnace operates—its "staging"—has a major impact on both efficiency and home comfort.
Single-Stage Furnaces
This is the most basic design. The furnace has only one setting: 100% "on" or "off." It runs at full capacity until the thermostat's set temperature is reached, then shuts down completely. This can create noticeable temperature swings.
Two-Stage Furnaces
These furnaces have two levels of operation: a "low" setting (around 60-70% of full capacity) and the full "high" setting. They will run on the lower, quieter, and more efficient setting most of the time, only kicking into high gear on the coldest days.
Modulating Furnaces
This is the most advanced and efficient type. A modulating furnace can adjust its heat output in tiny increments, often between 40% and 100% capacity. It runs almost continuously at the precise level needed to maintain a constant temperature, maximizing efficiency and providing the most consistent comfort.
What About Electric Furnaces?
While gas furnaces dominate discussions of efficiency ratings, electric furnaces present a different kind of efficiency.
The Efficiency Paradox
An electric furnace is technically almost 100% efficient at the point of use. Every kilowatt of electricity it draws is converted directly into heat, with no waste exhaust. From a pure conversion standpoint, they are unbeatable.
The Cost Reality
The paradox is that while the furnace itself is efficient, the cost of electricity in most regions is significantly higher than the cost of natural gas. This makes an electric furnace far more expensive to operate month-to-month, even though it wastes no energy on-site.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The furnace with the highest AFUE rating is not automatically the best choice. Objective analysis requires weighing the benefits against the costs and practical limitations.
Upfront Cost vs. Long-Term Savings
High-efficiency modulating furnaces are the most expensive units to purchase. While they save you money on monthly fuel bills, it can take several years for those savings to offset the higher initial investment.
Installation and Infrastructure
Condensing (90%+) furnaces produce acidic water condensate that must be drained away. They also require PVC piping for their cool exhaust, not traditional metal flues. If your home isn't set up for this, installation costs can increase significantly. An 80% furnace can often use existing metal venting, simplifying replacement.
Complexity and Maintenance
A modulating furnace contains more sophisticated electronics and components than a simple single-stage unit. While generally reliable, potential repairs down the line can be more complex and costly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your furnace based on a clear-eyed assessment of your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum efficiency and comfort: Choose a modulating, variable-speed condensing gas furnace with a 95%+ AFUE rating, provided the installation is feasible.
- If your primary focus is a balanced upgrade on a budget: A two-stage, high-efficiency (90-95% AFUE) furnace offers significant savings and comfort improvements over older models without the premium cost of a modulating unit.
- If your primary focus is the lowest upfront cost or gas is unavailable: A standard 80% AFUE gas furnace or an electric furnace is the most economical choice for initial purchase and installation.
Ultimately, the most efficient furnace is the one that best aligns your performance goals with your home's unique constraints and your long-term budget.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | AFUE Rating | Key Features | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Modulating Condensing Gas | 98%+ | Precise heat output, variable-speed, maximum comfort | Maximum efficiency & comfort, long-term savings |
| Two-Stage Condensing Gas | 90-95% | Two capacity levels, quieter operation | Balanced upgrade, budget-conscious efficiency |
| Single-Stage Gas | 80% | Basic on/off operation, simple design | Lowest upfront cost, simple replacement |
| Electric Furnace | ~100% | No exhaust loss, simple installation | Areas without gas, lowest installation complexity |
Ready to find your perfect furnace match?
At KINTEK, we understand that choosing the right heating system involves balancing efficiency ratings, fuel costs, and installation requirements. Our experts can help you analyze your specific needs to determine whether a high-efficiency condensing gas furnace, electric model, or modulating system will deliver the best value for your home.
We'll help you:
- Compare AFUE ratings against your local fuel costs
- Calculate long-term operating expenses vs. upfront investment
- Assess your home's existing infrastructure for optimal installation
Contact our heating specialists today for a personalized consultation and discover how the right furnace can maximize your comfort while minimizing energy costs.
Get Your Custom Furnace Recommendation Now
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature of a quartz tube furnace? Master the Limits for Safe, High-Temp Operation
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- How do you clean a tubular furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What is the difference between upflow and horizontal furnace? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Home's Layout
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control



















