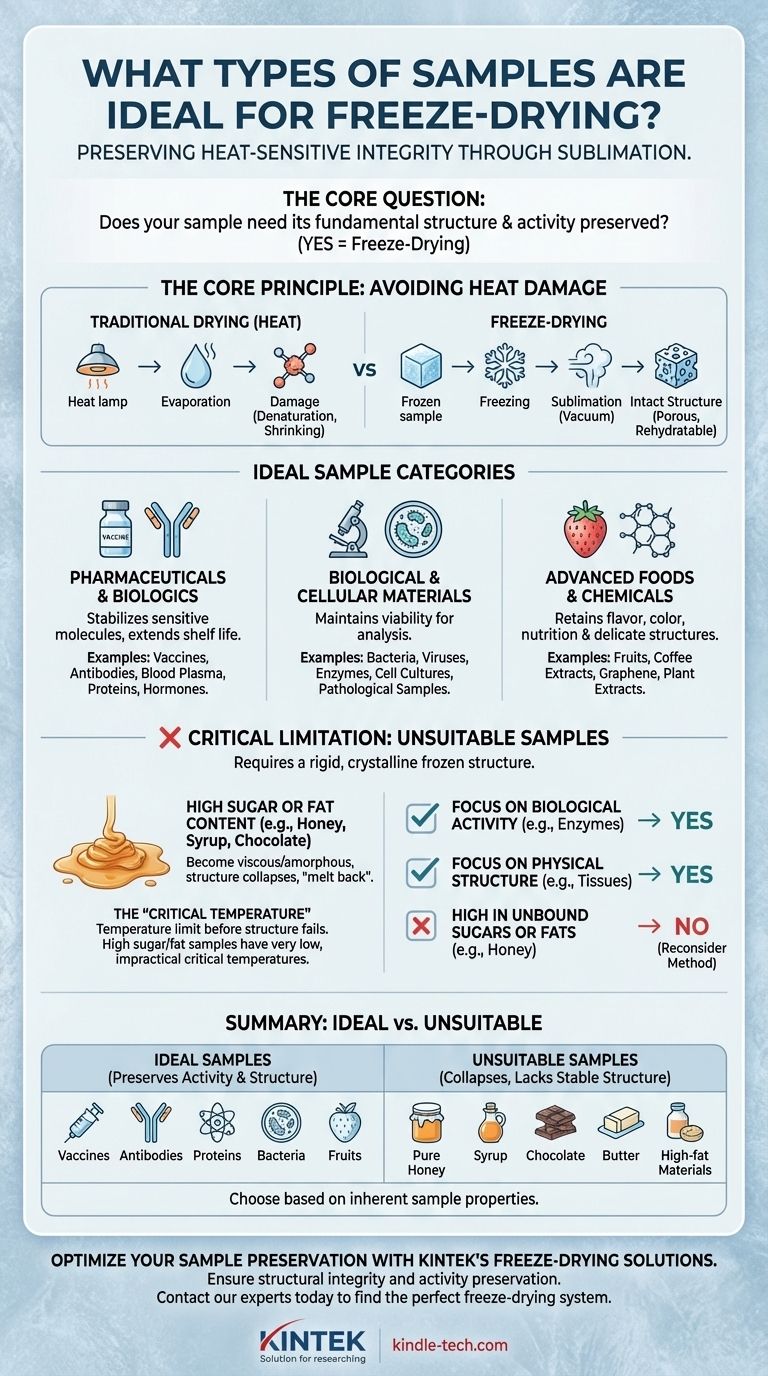
Ultimately, the ideal samples for freeze-drying are those whose structural or biological integrity would be compromised by heat. This technique, also known as lyophilization, is the gold standard for preserving delicate, heat-sensitive materials like vaccines, proteins, enzymes, and other biologically active substances by removing water at low temperatures.
The core decision to use freeze-drying hinges on one question: Does your sample need its fundamental structure and activity preserved? If the answer is yes, especially for biological or pharmaceutical materials, freeze-drying is the superior method. However, it is not a universal solution and fails on samples that cannot form a stable frozen structure, such as those high in fats or sugars.

The Core Principle: Why Freeze-Drying Works
Freeze-drying is fundamentally a process of dehydration under cold, vacuum conditions. Its unique advantage lies in preserving the sample's original structure, which is critical for many applications.
Avoiding Heat-Induced Damage
Traditional drying methods use heat to evaporate water. This process can be destructive, causing proteins to denature, bacteria to die, and the physical structure of a sample to shrink or collapse.
Freeze-drying completely avoids this by first freezing the sample. The frozen water is then removed through sublimation—turning ice directly into vapor under a vacuum—bypassing the destructive liquid phase entirely.
Preserving Molecular and Physical Structure
Because the water is removed from a solid, frozen state, the sample's underlying scaffold remains intact. This results in a porous, lightweight final product that can be easily and quickly rehydrated, often returning to its original state with its biological activity fully preserved.
A Breakdown of Ideal Sample Categories
The principle of structural preservation makes freeze-drying essential across several key fields, from pharmaceuticals to advanced material science.
Pharmaceuticals and Biologics
This is the most common application. Freeze-drying stabilizes sensitive molecules for storage and transport, dramatically extending shelf life without refrigeration.
Ideal samples include vaccines, antibodies, antibiotics, blood plasma, proteins, and hormones. For these products, maintaining biological activity is non-negotiable.
Biological and Cellular Materials
Researchers rely on freeze-drying to preserve samples for analysis or future use. The process can maintain the viability of certain microorganisms or perfectly preserve tissues for microscopy.
This category includes bacteria, viruses, enzymes, cell cultures, and pathological samples where structural integrity is paramount for accurate study.
Advanced Foods and Chemicals
In food science, freeze-drying creates high-quality products that retain nearly all of their original flavor, color, and nutritional value. The process is also used for delicate, porous materials.
Examples range from fruits, vegetables, and coffee for consumer goods to complex materials like graphene and plant extracts in laboratory settings.
The Critical Limitation: Unsuitable Samples
Freeze-drying is not a universal solution. Its effectiveness depends entirely on the sample's ability to form a rigid, crystalline frozen structure.
The Problem with High Sugar and Fat Content
Samples with high concentrations of unbound sugars or fats are poor candidates. Materials like pure honey, syrup, chocolate, and butter do not truly freeze into a solid ice matrix.
Instead, they become highly viscous, amorphous (glassy) solids. When a vacuum is applied, this structure can collapse or "melt back," resulting in a sticky, improperly dried product.
Understanding the 'Critical Temperature'
Every product has a critical temperature, which is the maximum temperature it can withstand during drying before its structure collapses.
For ideal samples like a protein solution, this temperature is relatively high and manageable. For high-sugar or high-fat samples, the critical temperature is often so low that the freeze-drying process becomes impractical or impossible to perform effectively.
Making the Right Choice for Your Sample
To determine if freeze-drying is appropriate, evaluate the fundamental nature and goal of your preservation needs.
- If your primary focus is preserving biological activity: Freeze-drying is the gold standard for vaccines, enzymes, antibodies, and other active pharmaceutical ingredients.
- If your primary focus is maintaining physical structure: The process is ideal for preserving the delicate architecture of foods, tissues for analysis, and porous materials.
- If your sample is high in unbound sugars or fats: You must reconsider your approach, as these materials lack the stable frozen structure required for successful freeze-drying and will likely collapse.
Choosing the correct preservation method begins with understanding the inherent properties of your sample.
Summary Table:
| Ideal Samples | Unsuitable Samples | Key Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Vaccines, Antibodies | Pure Honey, Syrup | Preserves biological activity |
| Proteins, Enzymes | Chocolate, Butter | Maintains structural integrity |
| Bacteria, Cell Cultures | High-fat materials | Avoids heat-induced damage |
| Fruits, Coffee Extracts | High-sugar solutions | Requires stable frozen structure |
Optimize your sample preservation with KINTEK's freeze-drying solutions. Whether you're working with sensitive pharmaceuticals, biological materials, or advanced food and chemical samples, our lab equipment ensures structural integrity and activity preservation. Don't let improper drying compromise your results—contact our experts today to find the perfect freeze-drying system for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory freeze dryer play in the synthesis of graphene-based electrocatalysts? Preserve 3D Structures
- What is the purpose of an evaporator? The Key Component That Creates Cooling
- Why is a laboratory freeze-drying system essential for fermentation biomass? Preserve Sample Integrity for Analysis
- What is the function of a freeze dryer in the ice-templating process? Preserving Aligned Pore Scaffolds for LAGP
- What are the advantages of using freeze drying for phase change materials with biopolymer shells? Optimize Stability



















