At its core, sintering is a critical manufacturing process used to fuse powdered materials into a solid, functional object using heat below the material's melting point. This technique is essential across a vast range of industries, from the foundational production of steel in blast furnaces to the creation of high-tech medical implants, advanced ceramics, and custom 3D-printed metal parts.
Sintering is not a niche technique; it is a foundational platform for manufacturing. Its value comes from its unique ability to efficiently process materials with high melting points, precisely control the final density of an object, and create complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible with traditional melting and casting methods.

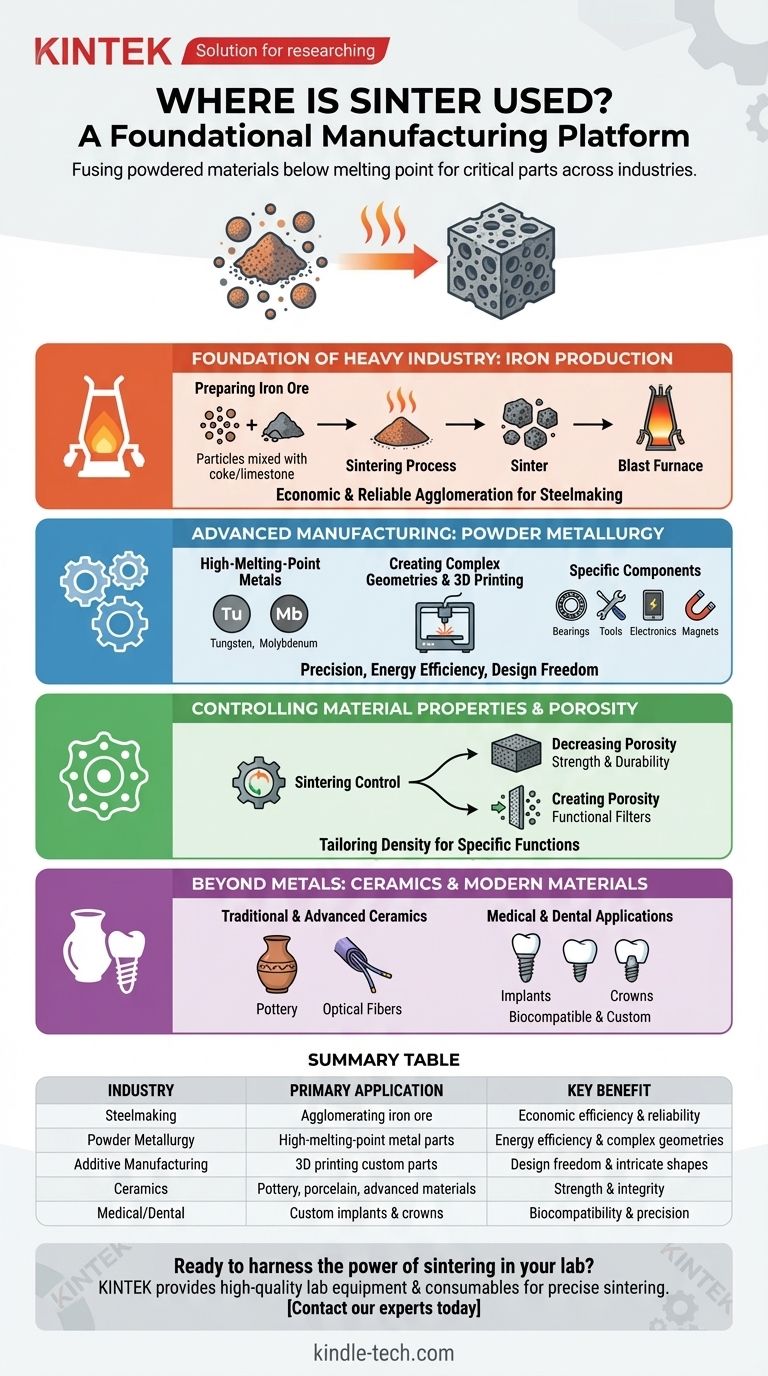
The Foundation of Heavy Industry: Iron Production
Sintering's most significant application by volume is in the preparation of raw materials for steelmaking. It is the dominant method for agglomerating fine iron ore particles into a solid, porous mass suitable for a blast furnace.
Preparing Iron Ore for the Blast Furnace
Iron ore fines, which are too small to be used directly, are mixed with other materials like coke and limestone and heated. The sintering process fuses these fines into larger, more uniform chunks called sinter.
This product is then charged into the blast furnace. Its consistency and porosity are critical for allowing hot gases to flow efficiently, enabling the chemical reactions that produce molten iron.
The Economic Advantage
For preparing iron ore, sintering is the most economic and widely used agglomeration process globally. Its efficiency and reliability make it an indispensable first step in the primary production of steel.
Advanced Manufacturing with Powder Metallurgy
Powder metallurgy is a broad field where sintering is the central process. It involves compacting metal powders into a desired shape and then heating them to bond the particles together.
Working with High-Melting-Point Metals
Sintering is the ideal method for fabricating parts from materials with extremely high melting points, such as tungsten and molybdenum.
Because the process operates below the melting temperature, it consumes significantly less energy and allows for greater control over the final product's microstructure compared to melting and casting.
Creating Complex Geometries and 3D Printing
Modern manufacturing, especially additive manufacturing (3D printing), relies heavily on sintering to create custom metal forms.
Processes like selective laser sintering (SLS) use a laser to fuse powdered material layer by layer, building intricate parts that would be impossible to machine or cast.
Specific Industrial Components
Sintering is the method of choice for producing a wide array of specialized parts, including:
- Self-lubricating bearings: Made by creating a porous metal structure that can be impregnated with oil.
- Cutting tools and structural parts: Combining different metal powders to create materials with superior hardness and wear resistance.
- Electrical contacts and components: Manufacturing precise parts for semiconductors and other electronics.
- Magnetic materials: Creating magnets with specific properties for various applications.
Controlling Material Properties and Porosity
One of the most powerful features of sintering is the ability to control the final density and porosity of an object. This allows engineers to design materials for specific functions.
Decreasing Porosity for Strength
For many applications, the goal of sintering is to reduce or eliminate the empty space (porosity) between the initial powder particles. This densification process significantly improves the material's strength, durability, and other mechanical properties.
Creating Porosity for Function
Conversely, sintering can be controlled to create objects with a specific, interconnected network of pores. This is essential for manufacturing porous metal or plastic filters, which are used in countless industrial and consumer applications.
Beyond Metals: Ceramics and Modern Materials
While heavily used in metallurgy, sintering has its roots in ceramics and is now applied to a diverse range of materials.
Traditional and Advanced Ceramics
Sintering is the traditional method for firing clay to create pottery, porcelain, and industrial ceramics. The process bonds the ceramic particles, giving the final object its strength and integrity. It is also used to produce advanced materials like optical fibers.
Medical and Dental Applications
The ability to create complex, biocompatible parts makes sintering invaluable in the medical field. It is used to produce custom dental crowns and medical implants that are both strong and tailored to the individual patient.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, sintering is not without its technical considerations. Understanding these limitations is key to its successful application.
Dimensional Control and Shrinkage
As the particles fuse and the pores close, the part will shrink. This change in dimension is predictable but must be carefully accounted for in the initial design to achieve tight tolerances.
Achieving Full Density
Eliminating all porosity to achieve 100% density can be difficult and may require advanced techniques like hot isostatic pressing. For highly demanding structural applications, any residual porosity can be a point of failure.
Initial Powder Quality is Critical
The final properties of a sintered part are directly dependent on the quality, size, and shape of the starting powder. Contamination or inconsistency in the raw material can compromise the integrity of the finished product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use sintering depends entirely on the material, the complexity of the part, and the desired final properties.
- If your primary focus is mass production for heavy industry: Sintering is the undisputed standard for preparing iron ore for steelmaking.
- If your primary focus is creating complex parts from high-performance metals: Powder metallurgy and 3D printing via sintering offer unmatched design freedom, especially for high-melting-point materials.
- If your primary focus is engineering specific material properties: Sintering provides unique control over a material's density, allowing you to create either ultra-strong components or functional porous structures like filters and bearings.
Ultimately, sintering is the definitive process when you need to transform a powder into a precise, solid part without fully melting it.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Primary Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Steelmaking | Agglomerating iron ore for blast furnaces | Economic efficiency & reliability |
| Powder Metallurgy | Fabricating parts from high-melting-point metals | Energy efficiency & complex geometries |
| Additive Manufacturing | 3D printing of custom metal parts | Design freedom & intricate shapes |
| Ceramics | Producing pottery, porcelain, and advanced materials | Strength and integrity |
| Medical/Dental | Creating custom implants and crowns | Biocompatibility and precision |
Ready to harness the power of sintering in your lab?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables needed for precise sintering processes. Whether you're developing new materials in powder metallurgy, advancing 3D printing applications, or creating specialized ceramics, our solutions help you achieve superior results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory needs and drive your innovations forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
People Also Ask
- What is the core function of a high-temperature atmosphere sintering furnace in the fabrication of Ni-Al2O3-TiO2 composites?
- Why is a high-precision atmosphere furnace essential for high-nickel cathode sintering? Unlock Battery Performance
- What is the role of an atmosphere-controlled tube furnace in Cu-Mo sintering? Achieve High-Purity Densification
- What is the function of a tube atmosphere furnace in Li2MnSiO4 synthesis? Achieve High-Purity Battery Materials
- Why is precise temperature control in a sintering furnace critical for NASICON electrolytes? Ensure Material Purity



















