The most common chemicals used in heat treatment are liquids like water and oil for rapid cooling, and specific gases within a furnace to intentionally alter the metal's surface chemistry. While the term "chemical" might suggest a complex additive, it often refers to these fundamental agents used for quenching or creating a controlled atmosphere.
The core principle to understand is that chemicals serve two distinct purposes in heat treatment: they either act as a medium for controlling the cooling rate (quenching) or as an active agent to change the surface properties of the material itself.

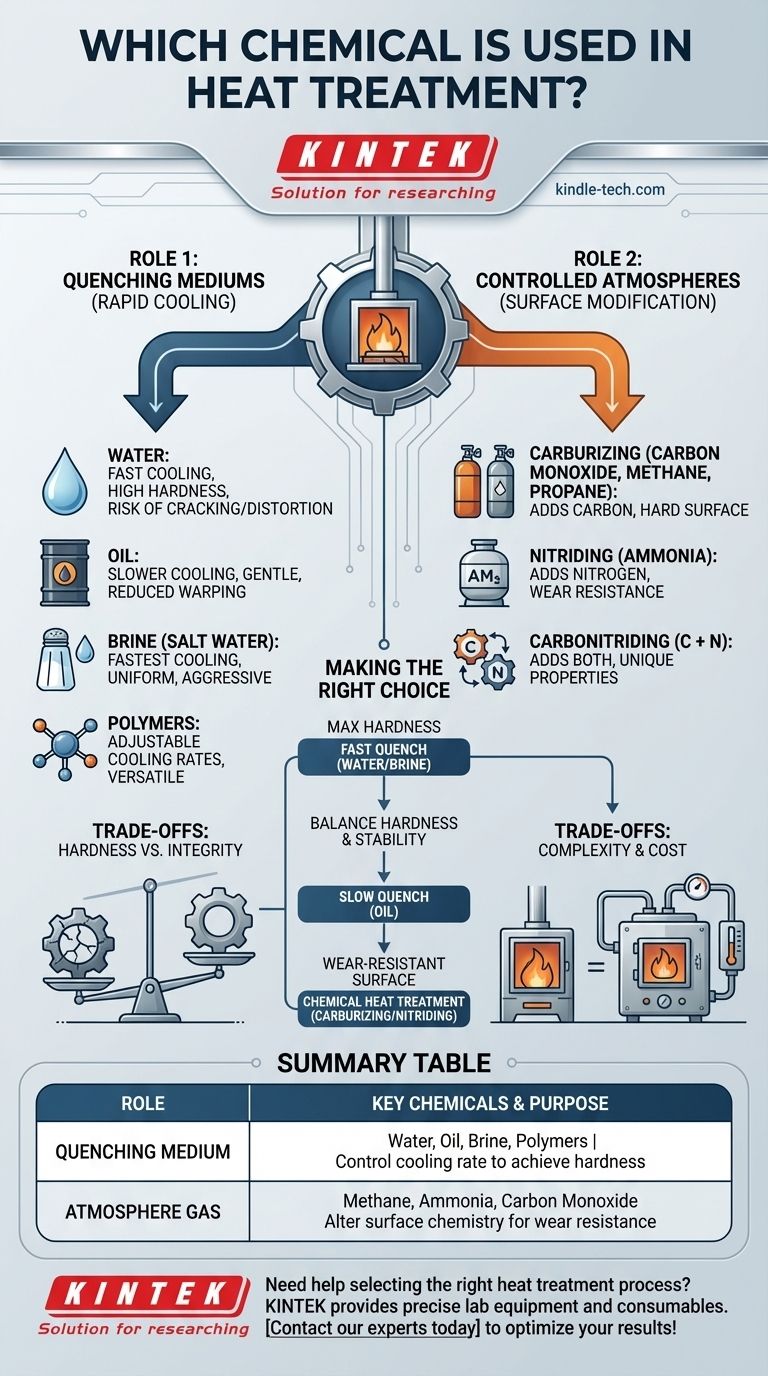
The Two Roles of Chemicals in Heat Treatment
To understand which chemical to use, you must first define your goal. Are you trying to harden the entire part through rapid cooling, or are you trying to create a hard, wear-resistant surface layer?
Role 1: Quenching Mediums for Rapid Cooling
Quenching is the process of cooling a hot metal part very quickly to lock in a specific crystalline structure, typically to increase its hardness.
The "chemical" here is the liquid bath, known as the quenchant.
- Water: Provides an extremely fast cooling rate. It is inexpensive and effective but can cause significant internal stress, leading to distortion or even cracking in complex parts.
- Oil: Cools much slower and more gently than water. This reduces the risk of warping and cracking, making it a common choice for many alloy steels.
- Brine (Salt Water): Cools even faster than plain water. The salt helps prevent the formation of insulating vapor bubbles on the metal's surface, ensuring a more uniform and aggressive quench.
- Polymers: Polymer solutions mixed with water can be engineered to provide a wide range of cooling rates, sitting between that of water and oil.
Role 2: Controlled Atmospheres for Surface Modification
This is known as chemical heat treatment or case hardening. Here, the chemical is a gas that changes the chemistry of the metal's surface.
The goal is to create a part with a hard, wear-resistant outer shell (the case) and a softer, tougher inner core.
- Carburizing: This process adds carbon to the surface of low-carbon steel. The part is heated in a sealed atmosphere rich in carbon monoxide (CO) or carbon-rich gases like methane or propane.
- Nitriding: This process adds nitrogen to the surface of the steel. The part is heated in an atmosphere containing a nitrogen-rich gas, most commonly ammonia (NH3), which breaks down on the metal's surface.
- Carbonitriding: As the name implies, this process adds both carbon and nitrogen to the surface, combining aspects of the two processes above for unique surface properties.
These atmospheric treatments prevent undesirable reactions, like the loss of carbon (decarburization) or the formation of scale (oxidation), which can weaken the part.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice of chemical is never without consequences. Each option presents a balance between desired properties and potential risks.
Quenching Risks: Hardness vs. Integrity
A more aggressive quenchant like water or brine will produce higher hardness. However, this rapid temperature change creates immense internal stress.
This stress can cause a part to warp, distort, or even crack, especially if it has sharp corners or varying thicknesses. Choosing a slower quenchant like oil is a deliberate strategy to protect the part's integrity at the cost of some potential hardness.
Atmosphere Control: Complexity and Cost
While chemical heat treatments offer superior surface properties, they require sophisticated equipment.
Sealed furnaces, precise temperature regulation, and careful management of gas flow are essential. This adds complexity and cost compared to a simple heat-and-quench operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your final decision must be guided by the intended application of the component.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness on a simple shape: A fast quench in water or brine is often the most direct method.
- If your primary focus is balancing hardness with dimensional stability: A slower, less severe quench in oil is the standard for most alloy steel parts.
- If your primary focus is creating a highly wear-resistant surface: A chemical heat treatment process like carburizing or nitriding is necessary to fundamentally alter the surface chemistry.
Ultimately, selecting the right chemical is about defining whether you need to manage thermal energy through cooling or modify the material's surface composition.
Summary Table:
| Role | Key Chemicals | Primary Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Quenching Medium | Water, Oil, Brine, Polymers | Control cooling rate to achieve hardness |
| Atmosphere Gas | Methane, Ammonia, Carbon Monoxide | Alter surface chemistry for wear resistance |
Need help selecting the right heat treatment process for your materials? KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for effective quenching and controlled atmosphere treatments. Our expertise ensures you achieve the perfect balance of hardness, durability, and dimensional stability for your laboratory's metal components. Contact our experts today to optimize your heat treatment results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What binder is used in sintering? Key Types for Complex Part Manufacturing
- What are the different types of physical vapour deposition processes? A Guide to Evaporation, Sputtering & More
- What are the main components of an industrial furnace? Explore Essential Elements for Precision Heating
- What is the internal storage volume range of Ultra Freezers? From 200L to 800L+ to Match Your Lab's Needs
- Why is flux important when brazing? It Removes the Invisible Barrier for a Perfect Bond
- What happens during sintering of ceramics? A Guide to Transforming Powder into Dense, Strong Parts
- How does a centrifuge work and for what purpose? Unlock the Power of Rapid Sample Separation
- How thick is carbon coating for SEM? Optimize Sample Conductivity & Analysis Accuracy



















