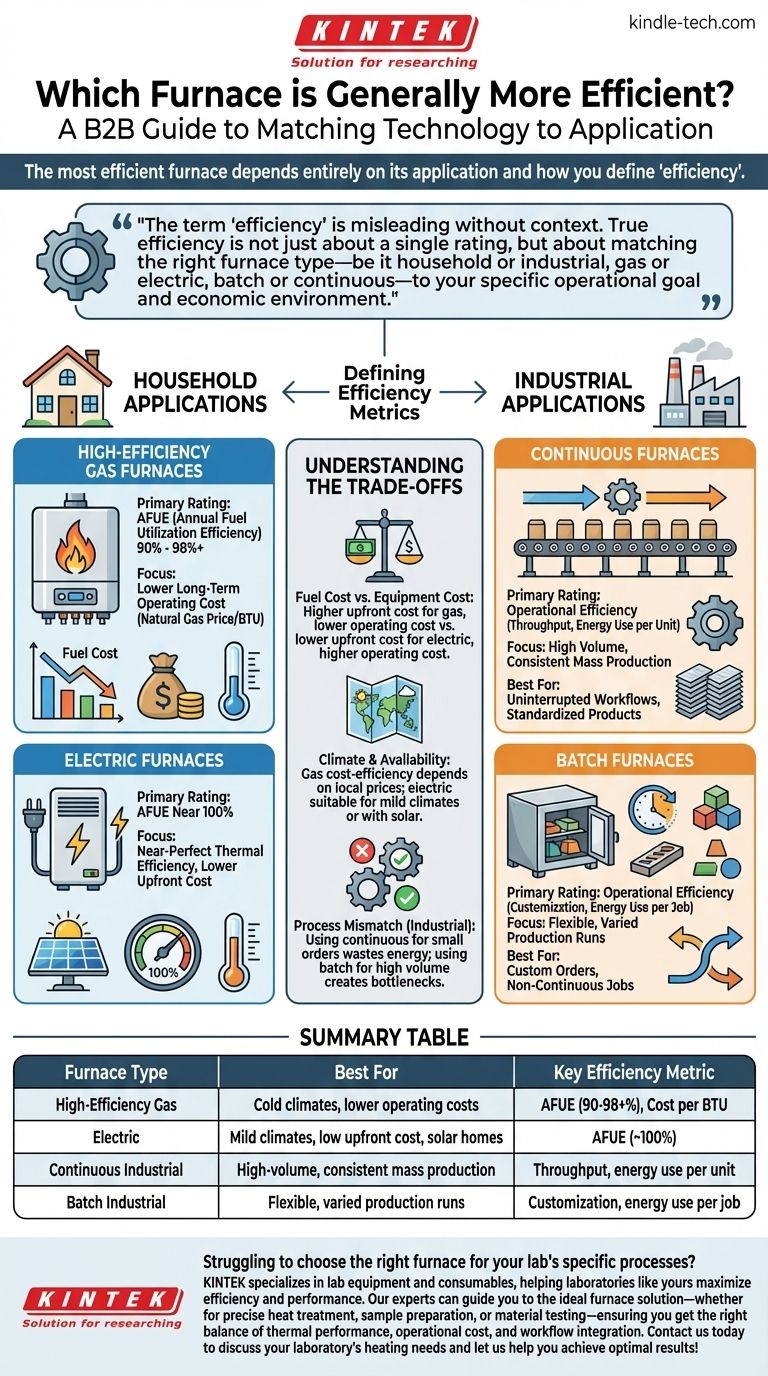
The most efficient furnace depends entirely on its application and how you define "efficiency." For residential heating, a high-efficiency gas furnace is typically more cost-efficient to operate than an electric furnace in most climates. However, in an industrial setting, a continuous furnace is more efficient for mass production, while a batch furnace is more efficient for varied, smaller jobs.
The term "efficiency" is misleading without context. True efficiency is not just about a single rating, but about matching the right furnace type—be it household or industrial, gas or electric, batch or continuous—to your specific operational goal and economic environment.

The Core Problem: Defining "Efficiency"
The first step is to understand that furnace efficiency is measured in several different ways. The "best" choice depends on which metric matters most for your needs.
Thermal Efficiency (AFUE)
For household furnaces, the primary rating is the Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE). This percentage tells you how much of the fuel's energy is converted directly into usable heat for your home.
Electric furnaces are the clear winners in this category, with AFUE ratings of nearly 100%. Virtually all the electricity they consume is converted into heat.
High-efficiency gas furnaces have AFUE ratings that typically range from 90% to over 98%. The remaining energy is lost as exhaust.
Overall Cost Efficiency
While an electric furnace is more thermally efficient, it is not always the most cost-efficient to run. This metric considers the price of the energy source (natural gas vs. electricity).
In most regions, natural gas is significantly cheaper per unit of energy (BTU) than electricity. This means that a 95% efficient gas furnace can often heat a home for a lower monthly cost than a 100% efficient electric furnace.
Operational Efficiency
In an industrial context, efficiency is often measured by throughput, consistency, and energy use relative to production goals. The goal is to minimize energy waste during production cycles.
This type of efficiency depends less on the fuel source and more on matching the furnace's operating style (e.g., continuous vs. batch) to the manufacturing process.
Efficiency in Household Furnaces: Gas vs. Electric
For most homeowners, the decision comes down to a choice between natural gas and electricity, which involves a direct trade-off between thermal performance and operating cost.
The Case for Gas Furnaces
The primary advantage of a natural gas furnace is lower long-term operating cost. If you live in an area with cold winters and access to a natural gas line, a high-AFUE gas model is almost always the more economical choice.
The Case for Electric Furnaces
Electric furnaces offer near-perfect thermal efficiency and typically have a lower upfront installation cost. They are an excellent choice for homes in milder climates where heating is not needed as often, or for homes equipped with solar panels that can offset the high cost of electricity.
Efficiency in Industrial Furnaces: Continuous vs. Batch
For industrial applications, efficiency is about aligning the equipment with the production workflow.
Continuous Furnaces for High Volume
A continuous furnace operates at a constant temperature, moving products through it on a conveyor. This design is extremely efficient for mass-producing a high volume of similar products.
Its efficiency comes from eliminating the need for repeated heat-up and cool-down cycles, which waste significant energy and time.
Batch Furnaces for Flexibility
A batch furnace is designed to heat a single load of products at a time. The temperature and duration can be adjusted for each specific job.
This makes batch furnaces more efficient for processes that require varied temperatures or for businesses that produce a wide range of different products in smaller quantities. Running a large continuous furnace for a small, custom job would be highly inefficient.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace based on a single metric can lead to poor outcomes. You must consider the complete picture.
Fuel Cost vs. Equipment Cost
A top-of-the-line, 98% AFUE gas furnace has a high upfront cost but will save money on utility bills over its lifespan. An electric furnace is cheaper to install but will likely result in higher monthly bills in a cold climate.
Climate and Availability
The cost-efficiency of a gas furnace is entirely dependent on the local price of natural gas. In areas where gas is unavailable or unusually expensive, an electric model or a heat pump may be a more logical choice.
Process Mismatch in Industry
The single biggest source of inefficiency in an industrial setting is a process mismatch. Using a massive continuous furnace for small, custom orders wastes enormous energy, just as using a small batch furnace for a high-volume process creates a production bottleneck.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the most efficient furnace, start by defining your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is minimizing monthly utility bills in a cold climate: A high-efficiency natural gas furnace (95%+ AFUE) is typically the most cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is the lowest installation cost or you live in a mild climate: An electric furnace is often the simpler and more thermally efficient option.
- If your primary focus is industrial mass production of a consistent product: A continuous furnace designed for a constant temperature will provide the best operational efficiency.
- If your primary focus is flexible, varied production runs in a factory: A batch furnace offers the efficiency of tailoring energy use to specific, non-continuous jobs.
Ultimately, true efficiency comes from precisely matching the furnace technology to its specific task and economic environment.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Best For | Key Efficiency Metric |
|---|---|---|
| High-Efficiency Gas | Cold climates, lower operating costs | AFUE (90-98+%), Cost per BTU |
| Electric | Mild climates, low upfront cost, solar homes | AFUE (~100%) |
| Continuous Industrial | High-volume, consistent mass production | Throughput, energy use per unit |
| Batch Industrial | Flexible, varied production runs | Customization, energy use per job |
Struggling to choose the right furnace for your lab's specific processes? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, helping laboratories like yours maximize efficiency and performance. Our experts can guide you to the ideal furnace solution—whether for precise heat treatment, sample preparation, or material testing—ensuring you get the right balance of thermal performance, operational cost, and workflow integration. Contact us today to discuss your laboratory's heating needs and let us help you achieve optimal results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance



















