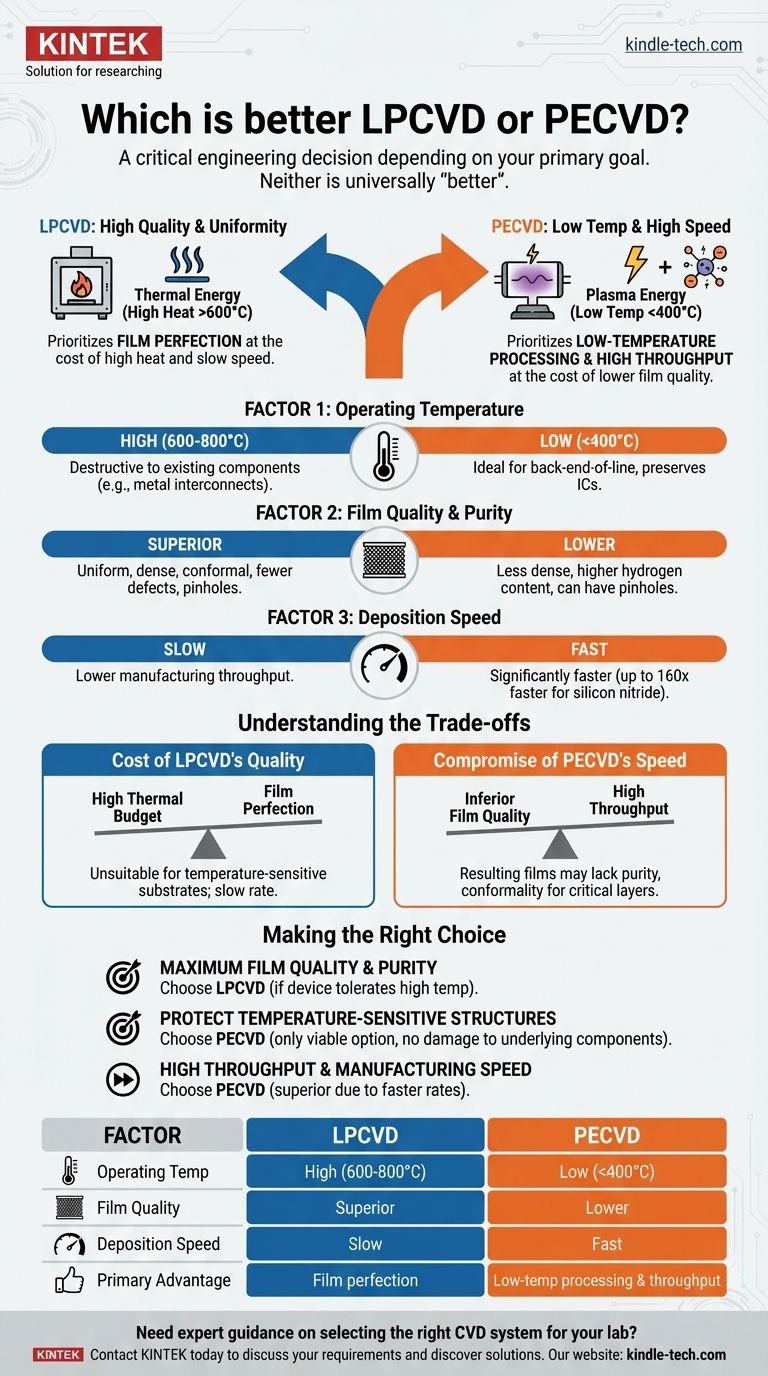
The short answer is neither is universally "better." The choice between Low-Pressure Chemical Vapor Deposition (LPCVD) and Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) is a critical engineering decision that depends entirely on your primary goal. LPCVD is chosen for its superior film quality and uniformity, while PECVD is selected for its low processing temperature and high deposition speed.
The core decision hinges on a fundamental trade-off: LPCVD prioritizes film perfection at the cost of high heat and slow speed, whereas PECVD prioritizes low-temperature processing and high throughput at the cost of lower film quality.

The Fundamental Difference: Thermal vs. Plasma Energy
To understand the trade-offs, you must first understand how each process supplies the energy needed for the chemical reaction that creates the film.
How LPCVD Works: High Heat for High Quality
LPCVD relies exclusively on thermal energy to drive the deposition reaction. Gaseous precursors are introduced into a high-temperature furnace (often above 600°C), where the heat causes them to react and deposit a solid film onto the substrate.
This high-temperature, low-pressure environment results in films that are highly uniform, dense, and conformal, with very few defects.
How PECVD Works: Plasma as the Catalyst
PECVD uses an electric field to generate a plasma, which is an energized gas. This plasma provides most of the energy needed to break down the precursor gases and drive the reaction.
Because the plasma supplies the energy, the substrate itself can be kept at a much lower temperature (typically below 400°C). This is the single most important advantage of the PECVD process.
Comparing Key Process Outcomes
The difference in energy sources leads to starkly different results in temperature, quality, and speed.
Factor 1: Operating Temperature
LPCVD operates at high temperatures, often in the 600-800°C range. This high thermal budget can be destructive to components already fabricated on a wafer, such as metal interconnects or specific doping profiles.
PECVD operates at low temperatures, often below 400°C. This makes it ideal for later stages of manufacturing (back-end-of-line processes) where preserving the existing integrated circuit is paramount.
Factor 2: Film Quality and Purity
LPCVD is the clear winner for film quality. The films are more uniform, have fewer defects and pinholes, and offer superior step coverage over complex device topographies.
PECVD films are generally of lower quality. They tend to be less dense, have higher residual hydrogen content from the precursor gases, and can suffer from pinholes. This can impact their electrical properties and long-term stability.
Factor 3: Deposition Speed
PECVD is significantly faster than LPCVD. The plasma-enhanced reaction is far more efficient at converting gas to solid film.
For example, when depositing silicon nitride, a PECVD process can be over 160 times faster than a comparable LPCVD process. This has massive implications for manufacturing throughput.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these methods requires acknowledging their inherent compromises.
The Cost of LPCVD's Quality
The primary drawback of LPCVD is its high thermal budget. It cannot be used on substrates or devices that cannot withstand high temperatures. Its slow deposition rate also makes it less suitable for applications requiring very thick films or high throughput.
The Compromise of PECVD's Speed
The main drawback of PECVD is its inferior film quality. The resulting films may not be suitable for applications that demand high purity, low stress, excellent insulation, or perfect conformity, such as gate dielectrics or critical passivation layers.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your deposition method based on what you are trying to achieve.
- If your primary focus is maximum film quality, purity, and conformality: LPCVD is the correct choice, provided your device can tolerate the high processing temperature.
- If your primary focus is protecting temperature-sensitive structures: PECVD is the only viable option, as its low thermal budget will not damage underlying components.
- If your primary focus is high throughput and manufacturing speed: PECVD is the superior choice due to its dramatically faster deposition rates.
By understanding this core trade-off between quality and temperature, you can select the deposition method that aligns perfectly with your specific engineering requirements.
Summary Table:
| Factor | LPCVD | PECVD |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Temperature | High (600-800°C) | Low (<400°C) |
| Film Quality | Superior (uniform, dense, conformal) | Lower (less dense, higher hydrogen content) |
| Deposition Speed | Slow | Fast (up to 160x faster) |
| Primary Advantage | Film perfection | Low-temperature processing & throughput |
Need expert guidance on selecting the right CVD system for your lab?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for all your deposition needs. Whether you require the superior film quality of LPCVD or the low-temperature capabilities of PECVD, our team can help you choose the perfect solution for your specific application and budget.
Contact our experts today to discuss your requirements and discover how KINTEK can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- What role does in-situ Argon (Ar) plasma pretreatment play in PECVD? Achieve Superior Adhesion for Aluminum Alloys
- What is the difference between thermal CVD and PECVD? Choose the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What is the process of PACVD coating? A Guide to Low-Temperature, High-Performance Thin Films
- What materials are deposited in PECVD? Discover the Versatile Thin-Film Materials for Your Application
- What are the differences between direct and remote plasma-enhanced CVD? Choosing the Right PECVD Method for Your Materials
- What are the properties of silicon dioxide film deposited by PECVD at low temperature pressure? Achieve Superior Insulation on Sensitive Substrates
- How plasma is generated in PECVD? A Step-by-Step Breakdown of the Process



















