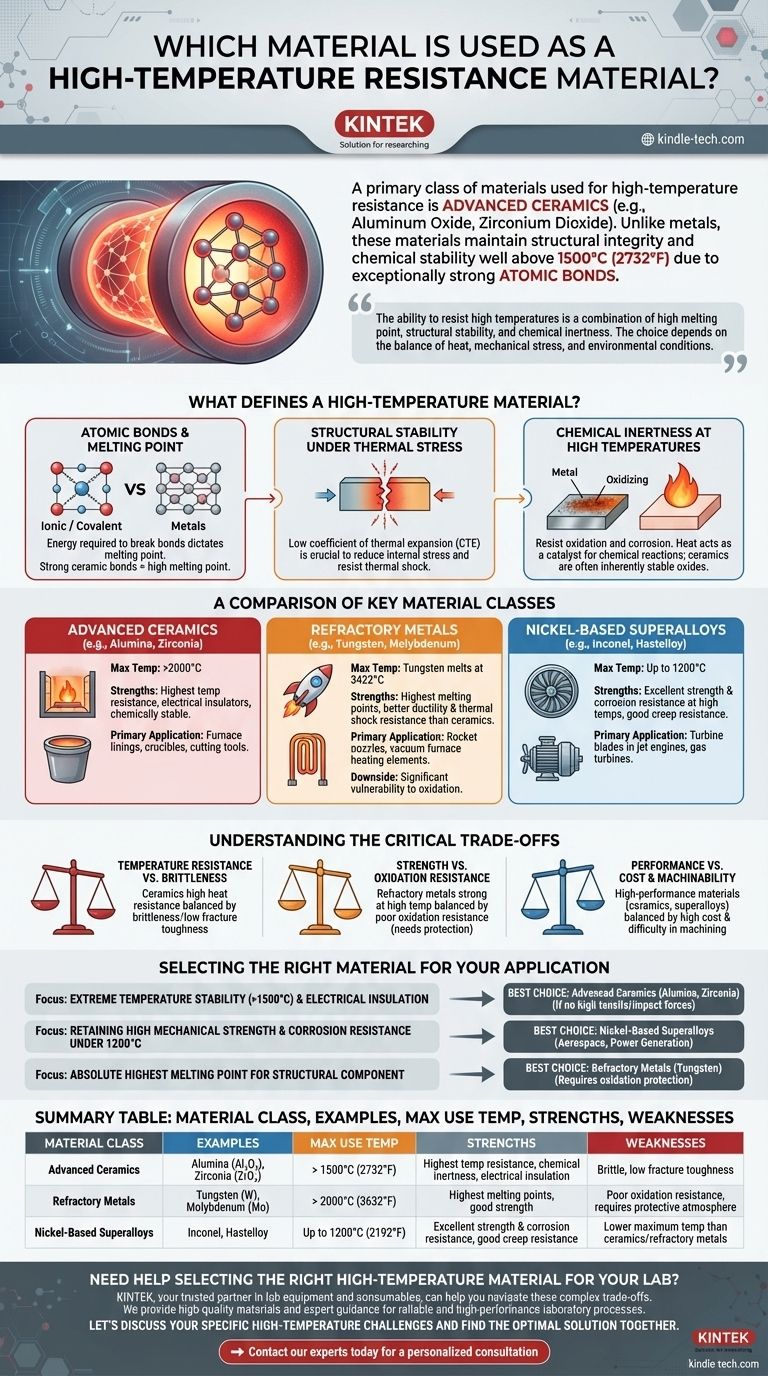
While many materials are considered, a primary class of materials used for high-temperature resistance is advanced ceramics, such as Aluminum Oxide (Alumina) and Zirconium Dioxide (Zirconia). Unlike metals that soften and melt at lower temperatures, these materials maintain their structural integrity and chemical stability well above 1500°C (2732°F) due to their exceptionally strong atomic bonds.
The ability of a material to resist high temperatures is not a single property but a combination of a high melting point, structural stability, and chemical inertness. The choice between ceramics, refractory metals, or superalloys depends entirely on the specific balance of heat, mechanical stress, and environmental conditions of the application.

What Defines a High-Temperature Material?
To select the right material, we must first understand the fundamental principles that govern performance under extreme heat. It is a battle fought at the atomic level.
The Role of Atomic Bonds and Melting Point
The energy required to break the bonds holding atoms together dictates a material's melting point. Materials with very strong ionic or covalent bonds, like those in ceramics, require immense thermal energy to be overcome.
Metals, with weaker metallic bonds, generally have lower melting points. This fundamental difference is why ceramics are often the first choice for applications involving extreme, direct heat.
Structural Stability Under Thermal Stress
High temperature doesn't just threaten to melt a material; it also causes it to expand. A low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) is crucial, as it means the material expands and contracts less with temperature changes, reducing internal stress.
Furthermore, a material must resist thermal shock—the cracking that can occur from rapid temperature changes. Materials with high thermal conductivity and low CTE generally perform better in this regard.
Chemical Inertness at High Temperatures
Heat acts as a catalyst for chemical reactions. A superior high-temperature material must resist oxidation and corrosion when exposed to air or other reactive chemicals at elevated temperatures.
This is a common failure point for many metals, which can rapidly degrade, whereas many ceramics are oxides already and are therefore inherently stable.
A Comparison of Key Material Classes
No single material is perfect for every high-temperature scenario. The three primary categories each offer a unique profile of strengths and weaknesses.
Advanced Ceramics (e.g., Alumina, Zirconia)
These materials possess the highest temperature resistance, often exceeding 2000°C. They are excellent electrical insulators and are chemically very stable.
Their primary application is in environments where extreme heat and compressive strength are needed, such as furnace linings, crucibles, and cutting tools.
Refractory Metals (e.g., Tungsten, Molybdenum)
This group has the highest melting points of all metals. Tungsten, for example, melts at 3422°C (6192°F), making it suitable for applications like rocket nozzles and heating elements in vacuum furnaces.
They offer better ductility and thermal shock resistance than most ceramics but come with a significant downside.
Nickel-Based Superalloys (e.g., Inconel, Hastelloy)
Superalloys are engineered to retain exceptional mechanical strength at high temperatures, close to their melting points. They offer an excellent balance of strength, creep resistance, and corrosion resistance.
This makes them the definitive choice for dynamic, high-stress components like turbine blades in jet engines and gas turbines.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
The selection of a high-temperature material is always a game of compromises. Understanding these trade-offs is essential for successful engineering design.
Temperature Resistance vs. Brittleness
This is the classic dilemma of ceramics. While they offer unparalleled heat resistance, they are notoriously brittle. They have very low tolerance for tensile stress and can fracture suddenly without warning, a property known as low fracture toughness.
Strength vs. Oxidation Resistance
Refractory metals are strong at high temperatures but have a critical vulnerability: they oxidize very easily in the presence of air. This requires them to be used in a vacuum or with protective coatings, which adds complexity and cost.
Performance vs. Cost and Machinability
The highest-performing materials are also the most challenging to work with. Ceramics, refractory metals, and superalloys are all significantly more expensive and difficult to machine than common steels or aluminum alloys. This impacts both initial production costs and the feasibility of creating complex shapes.
Selecting the Right Material for Your Application
Your final choice must be guided by the most critical demand of your specific project.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature stability (>1500°C) and electrical insulation: Advanced ceramics like Alumina or Zirconia are your best choice, provided the part is not subject to high tensile or impact forces.
- If your primary focus is retaining high mechanical strength and corrosion resistance under 1200°C: Nickel-based superalloys are the industry standard for demanding applications like aerospace and power generation.
- If your primary focus is the absolute highest melting point for a structural component: Refractory metals like Tungsten are required, but you must design a strategy to protect them from oxidation.
Ultimately, choosing the right material requires a clear understanding that you are balancing a set of competing properties, not just maximizing one.
Summary Table:
| Material Class | Key Examples | Max Use Temperature (Approx.) | Primary Strengths | Key Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced Ceramics | Alumina (Al₂O₃), Zirconia (ZrO₂) | > 1500°C (2732°F) | Highest temperature resistance, chemical inertness, electrical insulation | Brittle, low fracture toughness |
| Refractory Metals | Tungsten (W), Molybdenum (Mo) | > 2000°C (3632°F) | Highest melting points, good strength | Poor oxidation resistance, requires protective atmosphere |
| Nickel-Based Superalloys | Inconel, Hastelloy | Up to 1200°C (2192°F) | Excellent strength & corrosion resistance at high temps, good creep resistance | Lower maximum temperature than ceramics/refractory metals |
Need Help Selecting the Right High-Temperature Material for Your Lab?
Choosing between advanced ceramics, refractory metals, and superalloys is critical for your application's success. KINTEK, your trusted partner in lab equipment and consumables, can help you navigate these complex trade-offs.
We provide high-quality materials and expert guidance to ensure your laboratory processes—from heat treatment to chemical synthesis—are built on a foundation of reliability and performance.
Let's discuss your specific high-temperature challenges and find the optimal solution together.
➡️ Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Tube
- Advanced Engineering Fine Ceramics Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Parts
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Purity Zinc Foil for Battery Lab Applications
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a vacuum drying oven in the preparation of PEO/LSTZ composite polymer electrolyte membranes?
- What is the role of a vacuum heating chamber? Protect Material Integrity During 12%Cr Steel Heat Treatment
- What is a calciner in chemistry? A Guide to High-Temperature Material Transformation
- What are the different types of annealing? A Guide to Softening and Strengthening Metals
- What is classification of heating furnace? A Guide to Selecting the Right Industrial Furnace
- What metals Cannot be brazed? Understanding the Challenges of Low Melting Points and Reactive Oxides
- Why is a vacuum oven necessary for drying conductive polymer powders like PEDOT and PANI? Preserve Your Material Purity
- What are the hazards of quenching? Avoid Material Failure and Personnel Injury



















