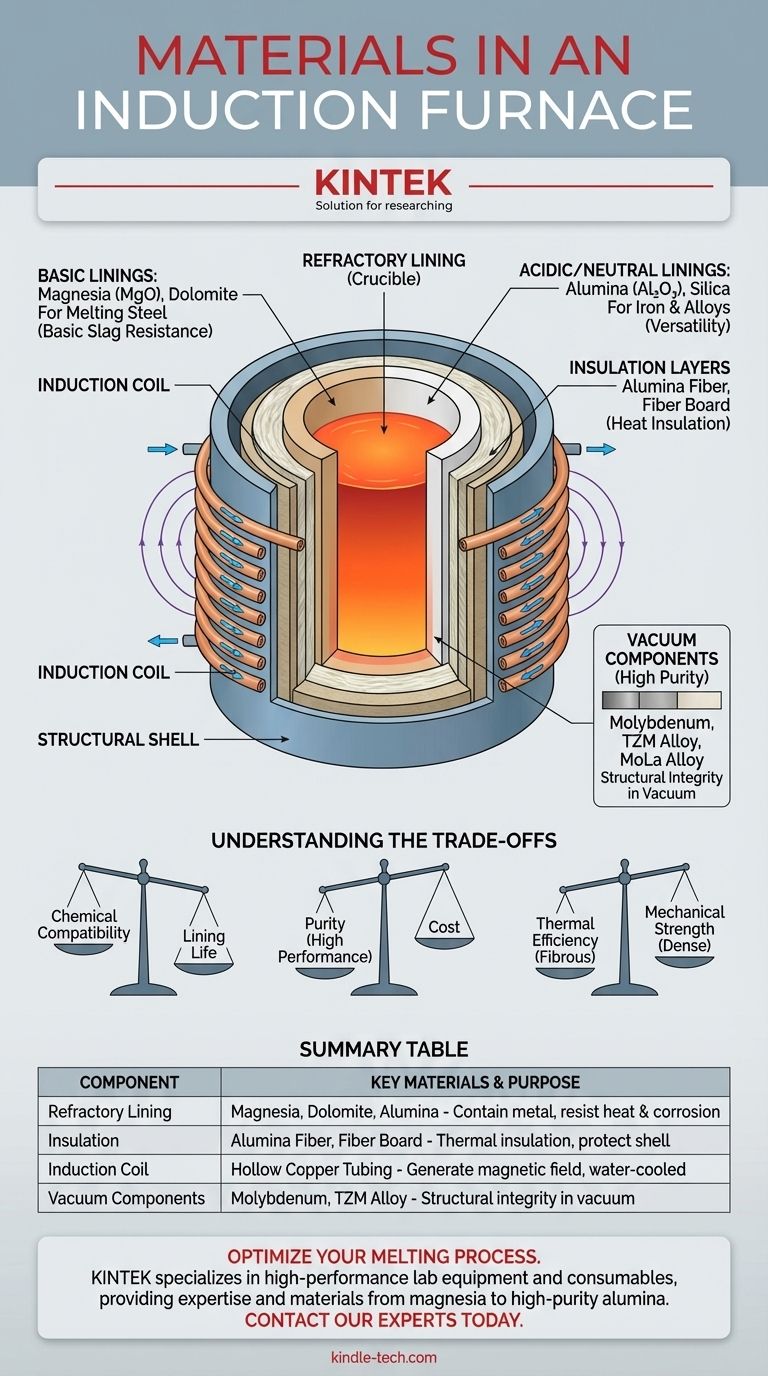
The most critical materials in an induction furnace are the refractories used for the lining, which contain the molten metal. These are primarily high-temperature ceramics like magnesia (MgO), dolomite, and alumina (Al₂O₃). The specific material is chosen based on its ability to withstand extreme heat and resist chemical reactions with the specific metal being melted.
The function of an induction furnace—to melt metal cleanly and efficiently—dictates its material composition. The choice of lining is not arbitrary; it is a precise engineering decision based on thermal resistance, chemical compatibility with the metal charge, and operational cost.

The Anatomy of an Induction Furnace
An induction furnace works by using powerful electromagnetic fields to heat and melt metal. Its construction materials are therefore chosen for two primary functions: containing extreme heat and interacting properly with these powerful fields.
The Heart of the Furnace: The Refractory Lining
The lining is the non-metallic ceramic layer that is in direct contact with the molten metal. Its job is to contain the liquid metal at temperatures that can exceed 1600°C (3000°F) and to thermally insulate the rest of the furnace structure.
Basic Linings are used when melting steel. Materials like magnesia and dolomite are chemically "basic" and effectively resist the corrosive effects of the basic slag that forms on top of molten steel.
Acidic and Neutral Linings are used for other metals. High-purity alumina is a common neutral refractory used for a wide variety of ferrous and non-ferrous metals, including aluminum and copper alloys. Silica-based refractories are an "acidic" option often used for melting iron.
The Structural & Functional Components
Beyond the primary lining, other materials are essential for the furnace's operation and integrity.
Insulation Layers are typically found behind the main refractory lining. Materials like high-purity alumina fiber and vacuum-formed fiber board provide excellent thermal insulation. They have low heat storage, meaning the furnace can heat and cool more rapidly, and they protect the structural shell from the intense heat.
The Induction Coil is the component that generates the magnetic field. This is almost universally made from high-conductivity hollow copper tubing. Water is continuously circulated through the tubing to keep the coils from melting, as they are in close proximity to the intense heat of the charge. The refractory lining is what protects these vital coils.
Specialty Components for Vacuum Furnaces are required for high-purity melting applications. In a vacuum environment, certain structural elements might be made from metals with exceptionally high melting points, such as pure molybdenum, TZM (titanium-zirconium-molybdenum alloy), or molybdenum-lanthanum (MoLa) alloy.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting the right materials involves balancing performance, lifespan, and cost. There is no single "best" material, only the most appropriate one for a specific task.
Chemical Compatibility vs. Lining Life
The most critical factor is the chemical interaction between the molten metal and the lining. Using an acidic lining (like silica) to melt a metal that produces a basic slag will result in rapid erosion and premature furnace failure. Matching the lining to the melt chemistry is non-negotiable for ensuring a reasonable campaign life.
Purity vs. Cost
High-purity refractory materials like fused magnesia or alumina offer superior performance and a longer lifespan but come at a significant cost. Lower-cost materials may be suitable for less demanding applications but will likely require more frequent maintenance and relining, leading to more downtime.
Thermal Efficiency vs. Mechanical Strength
Fibrous insulation materials are excellent at preventing heat loss but have no mechanical strength and cannot contain molten metal. Dense, sintered refractories provide the necessary strength and corrosion resistance but are less effective as insulators. A modern furnace uses a combination of both to achieve optimal performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice of material should be driven entirely by the metal you are melting and your operational goals.
- If your primary focus is melting steel: You must use a basic refractory lining, such as one based on magnesia (MgO), to withstand the basic slag.
- If your primary focus is melting cast iron or non-ferrous alloys: An acidic (silica-based) or neutral (alumina-based) refractory will provide the best performance and lifespan.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum purity in a vacuum: You will need a high-quality neutral refractory lining and may require furnace components made from specialized metals like molybdenum or TZM.
Ultimately, the materials used in an induction furnace are a direct reflection of its intended purpose, engineered to control and contain one of the most extreme industrial processes.
Summary Table:
| Component | Key Materials & Their Purpose |
|---|---|
| Refractory Lining | Magnesia (MgO), Dolomite, Alumina (Al₂O₃): Contain molten metal, resist extreme heat & chemical corrosion. |
| Insulation | Alumina Fiber, Fiber Board: Provide thermal insulation, protect the furnace shell. |
| Induction Coil | Hollow Copper Tubing: Generates the magnetic field; water-cooled to prevent melting. |
| Vacuum Components | Molybdenum, TZM Alloy: Used in high-purity applications for structural integrity. |
Optimize your melting process with the right materials. The correct refractory lining is critical for your induction furnace's efficiency, purity, and lifespan. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, providing the expertise and materials—from basic magnesia to high-purity alumina linings—to meet your specific laboratory melting needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss the best furnace lining solution for your application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis



















