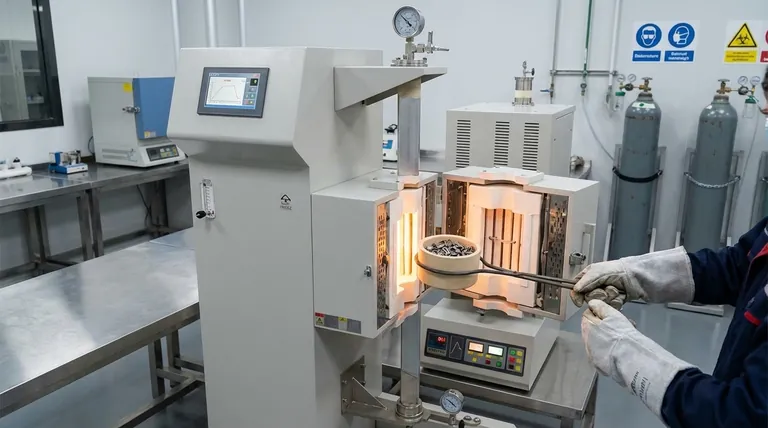
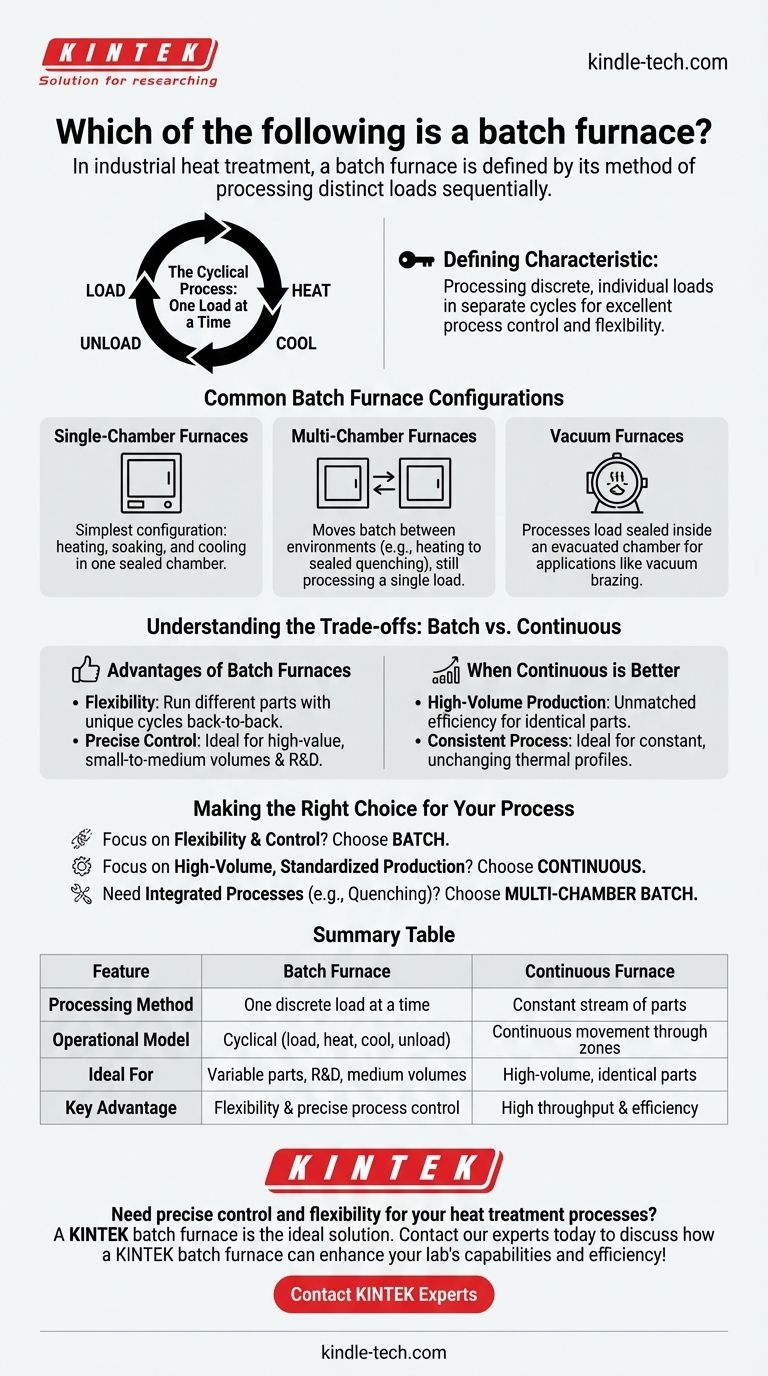
In industrial heat treatment, a batch furnace is defined by its method of processing. It is a furnace specifically designed to heat treat one distinct load, or "batch," of material at a time. Once a full thermal cycle is complete on that load, the treated parts are removed, and a new, untreated batch is loaded to begin the process again.
The defining characteristic of a batch furnace is not its size or temperature but its operational model: processing discrete, individual loads in separate cycles. This approach provides excellent process control and flexibility for varying part types and treatment requirements.

The Core Principle: One Load at a Time
A batch furnace operates on a cyclical basis, which is fundamentally different from a continuous furnace that processes a constant stream of material.
Defining the "Batch"
A "batch" or "load" is simply a collection of parts or a single large component that is treated as one cohesive unit. This entire unit is loaded into the furnace, subjected to a specific thermal profile, and then unloaded together.
The Cyclical Process
The operation is sequential. A typical cycle involves loading the material, running the prescribed heating and soaking program, executing a cooling or quenching step, and finally unloading the finished batch.
The Key Distinction
This method contrasts directly with continuous furnaces, where parts move steadily through different temperature zones on a conveyor belt or walking beam. In a continuous system, the process is constant, not cyclical.
Common Batch Furnace Configurations
While the "one load at a time" principle is universal, batch furnaces come in various designs to accommodate different processes.
Single-Chamber Furnaces
This is the simplest configuration, often a box-style furnace. The entire process—heating, soaking, and often slow cooling—occurs within a single, sealed chamber before the door is opened for unloading.
Multi-Chamber Furnaces
More complex processes require moving the batch between environments. A sealed quench furnace, for example, has a heating chamber and an integrated cooling or quenching chamber.
The batch is heated in the first chamber and then mechanically transferred to the second for rapid cooling, all without exposure to the outside atmosphere. Even though it has multiple stages, it is still a batch furnace because it processes a single, discrete load through this sequence. These are sometimes called semi-continuous furnaces.
Vacuum Furnaces
Many vacuum furnaces are also batch systems. A load is sealed inside a chamber, the air is evacuated, and the thermal cycle is run. These can also be single- or dual-chamber designs for processes like vacuum brazing or hardening.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Batch vs. Continuous
Choosing between a batch and continuous furnace depends entirely on the production goals and the nature of the parts being treated.
Advantages of Batch Furnaces
The primary advantage is flexibility. You can run completely different parts with unique thermal cycles back-to-back. This provides precise process control over each load, making it ideal for high-value components, small-to-medium production volumes, or R&D applications.
Limitations of Batch Furnaces
Batch processing generally has a lower overall throughput than a continuous system. It also requires more labor or automation for the loading and unloading steps between each cycle.
When Continuous is Better
Continuous furnaces are built for high-volume production of identical or very similar parts. They offer unmatched efficiency and consistency when the thermal process does not change.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct furnace type is critical for both metallurgical quality and operational efficiency.
- If your primary focus is flexibility and precise control: A batch furnace is the superior choice, as it allows you to tailor the entire thermal cycle for each specific load of varied parts.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, standardized production: A continuous furnace is more efficient, offering higher throughput by processing a constant stream of identical parts with a single, unchanging thermal profile.
- If you need integrated processes like controlled quenching: A multi-chamber batch furnace provides the process control of a batch system while seamlessly integrating multiple thermal steps.
Ultimately, understanding the distinction between batch and continuous processing is the first step in selecting the most effective and efficient thermal solution for your manufacturing goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Batch Furnace | Continuous Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Processing Method | One discrete load at a time | Constant stream of parts |
| Operational Model | Cyclical (load, heat, cool, unload) | Continuous movement through zones |
| Ideal For | Variable parts, R&D, medium volumes | High-volume, identical parts |
| Key Advantage | Flexibility and precise process control | High throughput and efficiency |
Need precise control and flexibility for your heat treatment processes? A KINTEK batch furnace is the ideal solution for processing high-value components, R&D projects, or medium-volume production runs with varying requirements. Our expertise in lab equipment ensures you get a system tailored to your specific thermal cycle needs. Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK batch furnace can enhance your lab's capabilities and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control
- What is quartz tube heating? Achieve Instant, Targeted Heat with Infrared Radiation
- What temperature is tube annealing? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges for Optimal Results
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan
- What is the difference between upflow and horizontal furnace? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Home's Layout



















