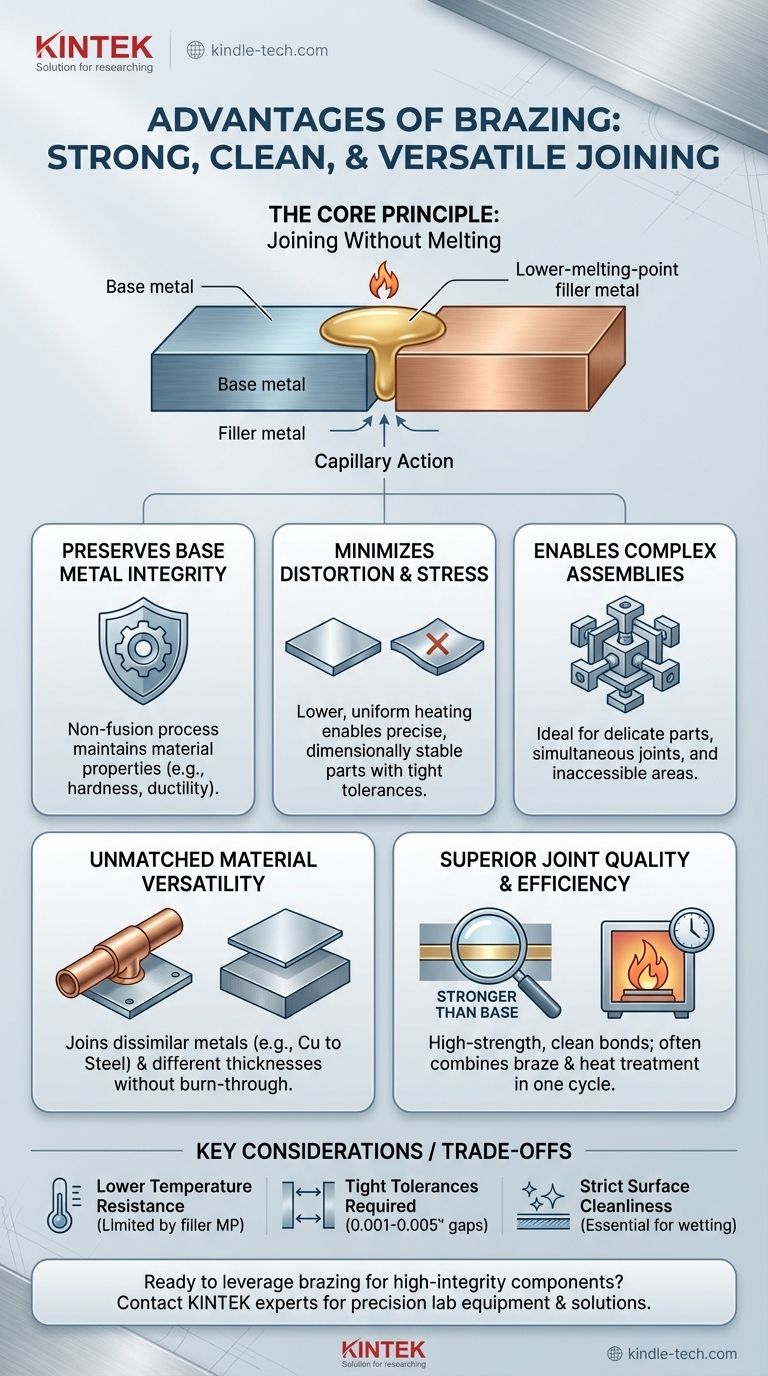
A primary advantage of brazing is its ability to join dissimilar metals with a bond that can be stronger than the base materials themselves. Because the process heats and joins components without melting them, it preserves their original properties, minimizes distortion, and allows for the creation of incredibly complex and delicate assemblies that would be impossible with other methods.
The core benefit of brazing stems from a single principle: it uses a filler metal with a lower melting point than the base materials. This fundamental distinction allows for strong, clean joints without the high heat, distortion, and material limitations associated with fusion welding.

The Core Principle: Joining Without Melting
Brazing operates in a "sweet spot" of temperature—hot enough to melt a filler metal but well below the melting point of the components being joined. This is the source of its most significant advantages.
Preserving Base Metal Integrity
Unlike welding, which fuses parts together by melting them, brazing leaves the base metals intact.
This non-fusion process ensures that the carefully engineered metallurgical properties of the parent materials, such as hardness or ductility, are not compromised by the joining process.
Minimizing Distortion and Stress
The lower temperatures and uniform heating associated with brazing, particularly furnace brazing, drastically reduce thermal distortion.
This allows for the assembly of high-precision components with very tight tolerances, as the parts remain dimensionally stable. The slow, controlled cooling cycles also minimize residual stress, improving the final part's mechanical performance.
Enabling Complex Assemblies
The gentle nature of the process makes it ideal for manufacturing intricate or delicate parts. It allows for multiple joints to be made simultaneously and can fill long, inaccessible joints through capillary action, which would be unachievable with other methods.
Unmatched Material Versatility
Because brazing does not require the base metals to be chemically compatible for fusion, it offers unparalleled flexibility in material selection.
Joining Dissimilar Metals
This is one of brazing's most celebrated advantages. It is an effective and reliable method for creating strong bonds between completely different types of metals, such as joining copper to steel or aluminum to stainless steel.
Accommodating Different Thicknesses
Brazing excels at joining thin components to thick ones. A common problem in welding is burning through the thinner material, but brazing's lower, uniform heat application eliminates this risk entirely.
Superior Joint Quality and Process Efficiency
Modern brazing techniques, especially vacuum and controlled atmosphere furnace brazing, deliver highly repeatable and clean results suitable for high-volume production.
High-Strength, Clean Joints
When properly designed, a brazed joint relies on capillary action to draw the molten filler metal into the tight gap between components.
This creates a complete, void-free bond that is often stronger than the parent metals. Furthermore, processes like vacuum brazing create an extremely clean environment, producing bright, shiny joints that require no post-process cleaning or flux removal.
Combining Processes in a Single Cycle
Brazing can often be integrated with other heat-treatment processes. A single furnace cycle can be used to braze an assembly and simultaneously harden or anneal it, saving significant time, handling, and cost.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No process is perfect. To use brazing effectively, you must understand its limitations.
Lower Temperature Resistance
The service temperature of a brazed component is fundamentally limited by the melting point of the filler alloy used. The joint will fail if exposed to temperatures that approach the filler's melting point, making it unsuitable for some very high-temperature applications where a welded joint would excel.
Requirement for Tight Tolerances
The capillary action that creates a strong joint only works if the gap between the parts is very small and precisely controlled (typically 0.001 to 0.005 inches). This means parts intended for brazing often require more precise machining than parts intended for welding.
Surface Cleanliness is Non-Negotiable
Brazing is highly sensitive to surface contamination. The base metals must be thoroughly cleaned of all oils, oxides, and debris before the process. Any contaminants will prevent the filler metal from wetting and flowing properly, resulting in a failed joint.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Choosing a joining method depends entirely on the specific requirements of your design and application.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar materials or metals of different thicknesses: Brazing is often the only viable and most effective method.
- If your primary focus is maintaining the precise dimensions of a complex assembly: The low heat input and minimal distortion of brazing make it superior to high-heat fusion processes.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of clean, repeatable joints: The batch processing and integrated heat-treating capabilities of furnace brazing offer significant efficiency and quality control.
By understanding these principles, you can leverage brazing not just as a joining technique, but as a strategic manufacturing process for high-integrity components.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Joins Dissimilar Metals | Creates strong bonds between different metals like copper and steel. |
| Minimizes Distortion | Low heat input preserves part dimensions and integrity. |
| Enables Complex Assemblies | Ideal for intricate or delicate parts with multiple joints. |
| Superior Joint Strength | Capillary action creates void-free bonds stronger than base materials. |
| Process Efficiency | Can be combined with heat treatment in a single furnace cycle. |
Ready to leverage brazing for your high-integrity components?
At KINTEK, we specialize in precision lab equipment and consumables for advanced manufacturing processes. Our expertise can help you implement brazing solutions that deliver strong, clean joints for complex assemblies, ensuring minimal distortion and superior performance.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our brazing solutions can enhance your production efficiency and product quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- Can dissimilar metals be brazed or braze welded? A Guide to Strong, Reliable Joints
- What are vacuum furnaces used for? Unlock Ultimate Material Purity and Performance
- What is the cost of a vacuum brazing furnace? A guide to key factors and investment strategy
- Where are vacuum furnaces used? Essential for High-Purity Heat Treatment in Critical Industries
- What is vacuum brazing? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity, Flux-Free Metal Joining



















