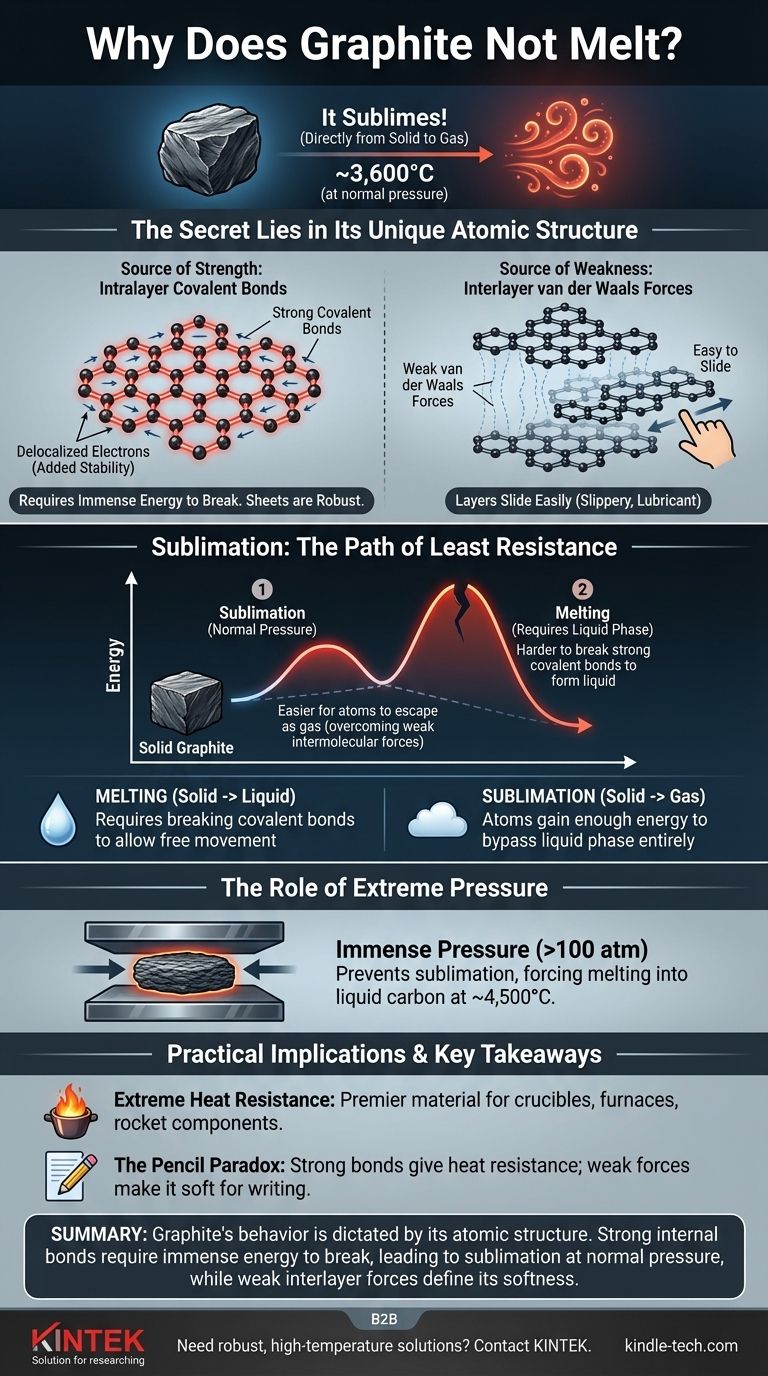
It's a common misconception that graphite doesn't melt. Under normal atmospheric pressure, graphite does something different: it sublimes, turning directly from a solid into a gas at an incredibly high temperature of around 3,600°C (6,500°F). This behavior is a direct result of the immense strength of the chemical bonds holding its carbon atoms together.
The core reason for graphite's extreme heat resistance is its unique atomic structure. It consists of layers of carbon atoms joined by exceptionally strong covalent bonds, which require a tremendous amount of energy to break and allow the substance to change state.
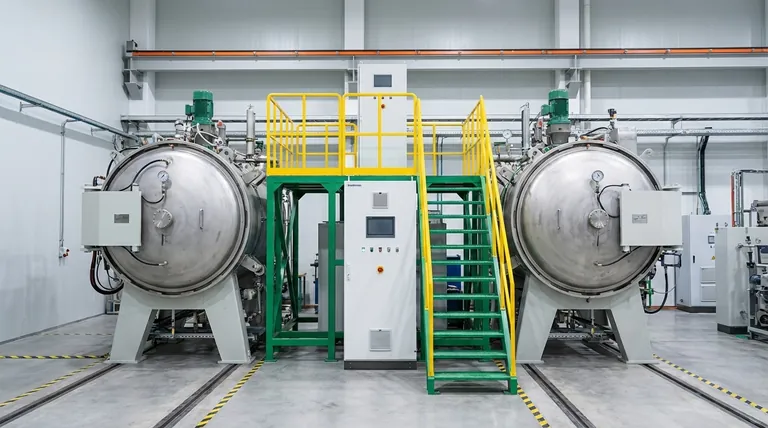

Deconstructing Graphite's Atomic Structure
To understand why graphite behaves this way, we must look at how its carbon atoms are arranged. Its structure is defined by two very different types of chemical bonds working at the same time.
The Source of Strength: Covalent Bonds Within Layers
Graphite is composed of flat, two-dimensional sheets of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal, honeycomb-like lattice.
Within each sheet, every carbon atom is linked to three others by strong covalent bonds. These are among the most powerful chemical bonds in nature.
Furthermore, one electron from each carbon atom becomes delocalized, meaning it's free to move across the entire sheet. This sharing of electrons among all atoms in the layer adds significant stability and further strengthens the bonds, making the sheets incredibly robust and difficult to break apart.
The Source of Weakness: Forces Between Layers
While the atoms within a layer are bonded powerfully, the layers themselves are held together by much weaker forces known as van der Waals forces.
These forces are weak enough that the layers can easily slide past one another. This is why graphite feels slippery and is used as a lubricant and in pencils—writing leaves behind layers of graphite on the paper.
Sublimation: The Path of Least Resistance
The extreme difference between the strong bonds within the layers and the weak forces between them dictates how graphite responds to heat.
Melting vs. Subliming
Melting is the process of a solid turning into a liquid. For this to happen, the atoms must gain enough energy to break free from their fixed positions but still remain attracted to each other.
Sublimation is the direct transition from a solid to a gas. In this case, atoms gain so much energy they bypass the liquid phase entirely and escape into the air.
Why Sublimation Wins at Normal Pressure
At standard atmospheric pressure, the energy required to break the powerful covalent bonds within graphite's layers is immense.
Before the structure can absorb enough energy to melt into a liquid, the atoms at the surface gain enough energy to overcome the weak intermolecular forces and simply fly off as a gas. It is energetically easier for the atoms to escape directly into a gaseous state than it is to break the covalent bonds required to form a liquid.
The Role of Extreme Pressure
Graphite can be forced to melt, but only under extraordinary conditions.
By applying immense pressure (over 100 times normal atmospheric pressure), you can prevent the carbon atoms from escaping as a gas. Under these conditions, graphite will melt into liquid carbon at a temperature of approximately 4,500°C (8,132°F).
The Practical Implications of This Structure
This unique dual-bonding structure gives graphite a set of properties that seem contradictory but are essential for its industrial applications.
Extreme Heat Resistance
The high sublimation point makes graphite a premier material for high-temperature environments. It is used to make crucibles for melting metals, linings for furnaces, and components in rocket engines that must withstand enormous heat.
The Pencil Paradox
Graphite's structure explains how it can be both incredibly heat-resistant and surprisingly soft. The strength comes from the covalent bonds within the layers, while the softness and lubricating properties come from the ease with which these layers slide over each other.
Key Takeaways for Understanding Graphite
- If your primary focus is its behavior under heat: Remember that at normal pressure, graphite sublimes directly to a gas because the energy needed to do so is less than the energy required to break the covalent bonds and form a liquid.
- If your primary focus is its physical properties: The key is its layered structure. Strong bonds within layers provide heat resistance, while weak forces between layers make it soft and an effective lubricant.
- If your primary focus is the technical definition of melting: Graphite absolutely can melt, but only under extremely high pressure that prevents the atoms from sublimating first.
Ultimately, graphite's behavior is a perfect illustration of how a material's atomic structure dictates its real-world properties.
Summary Table:
| Property | Description | Key Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Sublimation Point | ~3,600°C (at normal pressure) | Weak van der Waals forces between layers allow atoms to escape as gas before melting. |
| Melting Point | ~4,500°C (under extreme pressure >100 atm) | High pressure prevents sublimation, forcing covalent bonds to break for melting. |
| Heat Resistance | Excellent for high-temperature applications | Extremely strong covalent bonds within carbon layers require immense energy to break. |
Need robust, high-temperature solutions for your lab?
Graphite's unique properties make it an essential material for demanding applications. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including graphite crucibles and furnace components, designed to withstand extreme conditions.
Let our experts help you select the right materials to enhance your laboratory's efficiency and safety. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific high-temperature needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the hazards of KBr? Avoid Procedural Errors That Ruin Your Lab Results
- What is the RF sputtering technique? A Guide to Depositing Insulating Thin Films
- What are the technical requirements for vacuum chambers in desalination? Boost Efficiency with Graphene Technology
- What are the components of a pyrolysis reactor? A Guide to Core Parts & Designs
- What materials are used in welding brazing? A Guide to Filler Metals, Fluxes, and Shielding Gases
- What type of plastic is usually used with compression molding and transfer molding? Master Thermosets for Superior Performance
- What are the techniques of sintering? Choose the Right Method for Your Material
- What materials can be applied using sputtering and what forms can the coatings take? Versatile Coating Solutions



















