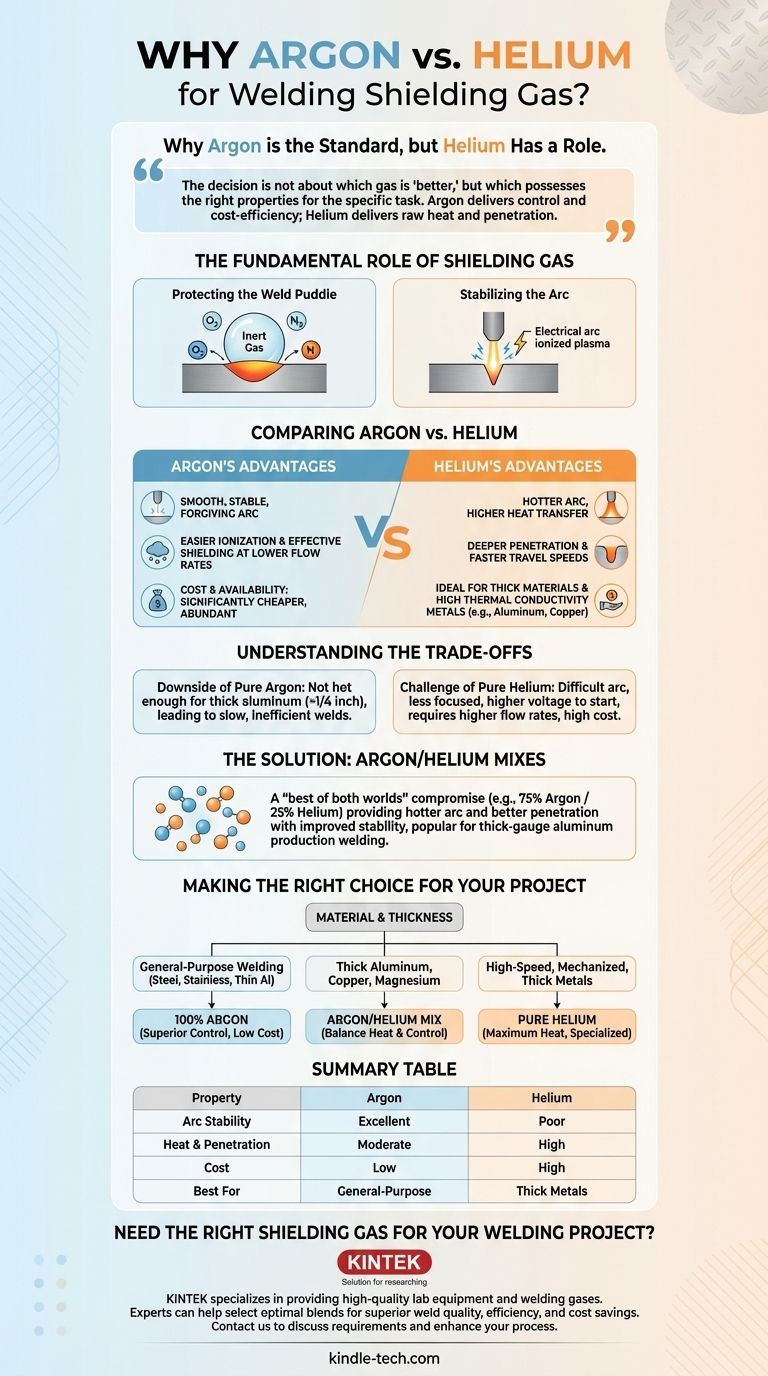
Argon is the standard shielding gas for most welding applications primarily because it is significantly cheaper and creates a more stable, forgiving welding arc. This combination of cost-effectiveness and ease of use makes it the default choice over helium for a vast majority of TIG (GTAW) welding tasks.
The decision between argon and helium is not about which gas is universally "better," but which possesses the right physical properties for the specific task. Argon delivers control and cost-efficiency, while helium delivers raw heat and penetration for more demanding applications.
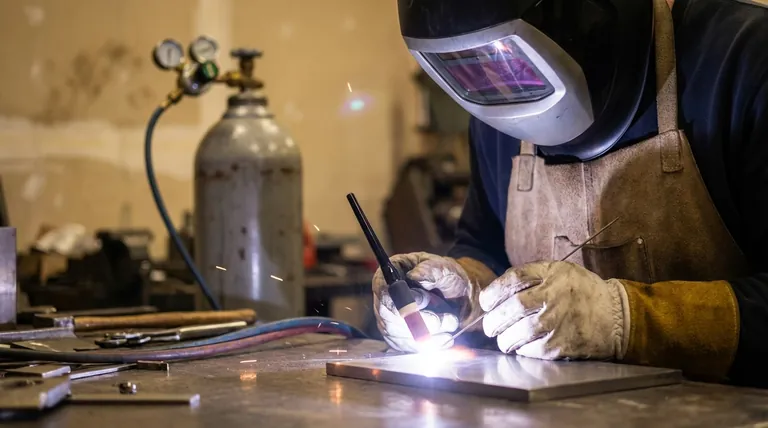

The Fundamental Role of a Shielding Gas
To understand the choice, we must first recognize the two critical functions a shielding gas performs in the TIG welding process.
Protecting the Weld Puddle
The primary job of the shielding gas is to displace the surrounding atmosphere. It creates an inert bubble around the molten weld puddle, protecting it from oxygen, nitrogen, and water vapor, which would otherwise cause severe defects like porosity and brittleness.
Stabilizing the Arc
The gas also serves as the medium for the electrical arc. The high voltage from the welder ionizes the gas, turning it into a plasma that conducts current between the tungsten electrode and the workpiece. The properties of this plasma directly influence the arc's stability, heat, and overall character.
Comparing Argon vs. Helium
The distinct physical properties of argon and helium are what define their performance as shielding gases.
Arc Stability and Control (Argon's Advantage)
Argon is easier to ionize than helium. This lower ionization potential means it takes less voltage to start and maintain the welding arc.
The result is a remarkably smooth, stable, and focused arc that is less sensitive to variations in the distance between the electrode and the workpiece (arc length). This forgiveness is invaluable for manual welding, where maintaining a perfectly steady hand is difficult.
Furthermore, argon is about ten times heavier than helium. This density allows it to provide effective shielding coverage at lower flow rates, further reducing operational costs.
Heat and Penetration (Helium's Advantage)
Helium has a much higher thermal conductivity than argon. When ionized into a plasma, it transfers heat far more efficiently.
This creates a significantly hotter arc, which is a major advantage when welding thick materials or metals that rapidly pull heat away from the weld, such as aluminum and copper. A hotter arc allows for deeper weld penetration and faster travel speeds.
Cost and Availability (Argon's Decisive Win)
Argon is the third most abundant gas in Earth's atmosphere, making it relatively simple and inexpensive to produce through air separation.
Helium, in contrast, is a finite resource extracted from natural gas deposits. It is far rarer and, consequently, dramatically more expensive. This cost difference is often the single most important factor in gas selection for production environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither gas is perfect for every situation. Choosing the right one involves balancing their strengths and weaknesses.
The Downside of Pure Argon
While stable and controllable, an argon arc may not be hot enough for welding very thick sections of aluminum (>1/4 inch). This can lead to slow, inefficient work or welds that lack the necessary fusion and penetration.
The Challenge of Pure Helium
The primary drawback of helium is its difficult arc characteristics. The arc is less focused and highly sensitive to changes in length, making it challenging to control manually. It also requires a higher voltage to start, which can be an issue for some power sources. Its low density means you need higher gas flow rates for adequate shielding, compounding its already high cost.
The Solution: Argon/Helium Mixes
For many demanding applications, the best solution is a blend. Adding helium to argon (e.g., a 75% Argon / 25% Helium mix) provides a "best of both worlds" compromise.
You gain a hotter arc and better penetration than pure argon, while retaining much of the arc stability and control that pure helium lacks. This makes blended gas a popular choice for production welding on thick-gauge aluminum.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Your material, thickness, and welding goals should dictate your shielding gas selection.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose welding on steel, stainless steel, or thin aluminum: 100% argon is your best choice for its superior control, arc stability, and low cost.
- If your primary focus is welding thick aluminum, copper, or magnesium: An argon/helium mix (typically 25-75% helium) is ideal for achieving the necessary heat input while maintaining good arc control.
- If your primary focus is high-speed, mechanized welding on thick, thermally conductive metals: Pure helium may be justified for its maximum heat and travel speed, but this is a specialized application where process control is paramount.
By understanding these properties, you can move from simply following a chart to strategically selecting the correct shielding gas for a high-quality weld.
Summary Table:
| Property | Argon | Helium |
|---|---|---|
| Arc Stability | Excellent (easy to ionize) | Poor (sensitive to arc length) |
| Heat & Penetration | Moderate | High (ideal for thick metals) |
| Cost | Low (abundant) | High (finite resource) |
| Best For | General-purpose welding (steel, thin aluminum) | Thick aluminum, copper, high-speed welding |
Need the Right Shielding Gas for Your Welding Project?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including welding gases and supplies tailored to your specific needs. Whether you're working with steel, aluminum, or other metals, our experts can help you select the optimal gas blend for superior weld quality, efficiency, and cost savings.
Contact us today to discuss your requirements and let KINTEK enhance your welding process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Thermally Evaporated Tungsten Wire for High Temperature Applications
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Tungsten Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
- 50L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between metallic and non-metallic coating? A Guide to Sacrificial vs. Barrier Protection
- How does hardness change with temperature? Understand the Inverse Relationship to Prevent Failure
- Why is platinum unreactive? The Atomic Secrets Behind Its Remarkable Stability
- What are the disadvantages of using metal? Understanding Corrosion, Weight, and Cost Challenges
- What are the advantages disadvantages and uses of sheet metal? The Ultimate Guide to Material Selection










