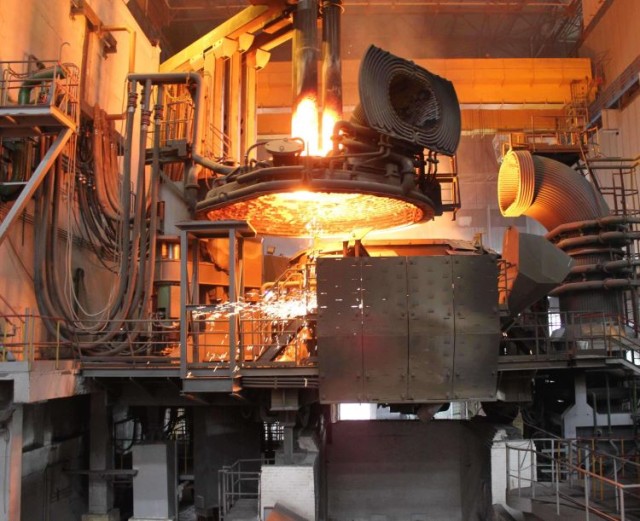
Introduction to Electric Heating Systems
Electric heating systems have revolutionized modern heating technology, offering efficient and versatile solutions for various applications. These systems rely on the principles of resistance heating, utilizing electric furnaces and heating elements to generate warmth. In this article, we delve into the world of electric heating, exploring its benefits, applications, and underlying mechanisms. From understanding the types of heating elements to examining the advantages of electric heating, we uncover the versatility and effectiveness of this technology. Join us on a journey to discover the fundamentals and practicalities of electric heating systems in today's heating landscape.
Types of Electric Heating Elements
Heating element selection is crucial in electric furnaces, impacting heat output, efficiency, and overall performance. Let's delve into the various types of electric heating elements commonly used in these furnaces:
Standard Open Resistance Wire Type
The standard open resistance wire type is a widely used heating element in electric furnaces. It consists of a resistive wire that generates heat when an electric current passes through it. These elements are versatile, cost-effective, and suitable for a range of applications.
-
Application Dependence: The choice of this heating element depends on the furnace application's power requirements and operating conditions. It is ideal for moderate heat output applications.
-
Atmosphere Considerations: Standard open resistance wire elements are exposed to the atmosphere within the furnace. This exposure can impact their longevity and performance, especially in harsh environments or corrosive atmospheres.
Bayonet/Radiant Tube Style
The bayonet/radiant tube style heating element offers distinct advantages in certain furnace setups.
-
Sealed Design: In atmosphere furnaces, these elements can be inserted into sealed tubes, also known as bayonet elements. This design prevents direct contact between the element and the atmosphere or furnace support structure, enhancing durability and performance.
-
Voltage Compatibility: Bayonet elements can operate on different voltages (e.g., 230V or 460V AC), eliminating the need for additional transformers. This simplifies the furnace's electrical setup and maintenance.
-
Optimized Performance: By being shielded within radiant tubes, these elements experience reduced exposure to harsh atmospheres, ensuring better longevity and consistent performance over time.
Factors Influencing Selection
When choosing between these heating element types, several factors come into play:
-
Furnace Application: The specific requirements of the furnace, such as heat output, temperature range, and operational environment, dictate the suitable heating element type.
-
Intended Atmosphere: Consideration of the furnace atmosphere (e.g., air, nitrogen gas) is crucial in determining the most compatible heating element for optimal performance and longevity.
-
Customer Preferences: Some customers may have preferences based on their past experiences or specific needs. Understanding these preferences helps in recommending the most appropriate heating element type.
Conclusion
The selection of electric heating elements for furnaces is a nuanced process, balancing technical specifications, environmental factors, and customer preferences. Whether opting for standard open resistance wire elements or bayonet/radiant tube style elements, the goal is to ensure efficient heat generation, longevity, and minimal maintenance requirements. Each type has its advantages and considerations, making informed selection critical for optimal furnace performance.
Benefits of Electric Heating Systems
Electric heating systems offer several advantages that make them a popular choice for various applications. Here are some key benefits to consider:
Customizable Heating Solutions
One of the significant advantages of electric heating systems is their capability to offer customizable heating solutions. When designed by an engineer, these systems can be tailored to meet specific requirements, allowing for precise temperature control and distribution. This flexibility enables users to place temperature zones wherever they are ideal for the appliance, optimizing performance and efficiency.
Simplified Design and Easy Maintenance
Electric heating systems feature a simplified design compared to traditional heating elements. They have fewer components, which translates to less frequent damage or maintenance requirements. Repairing or replacing elements is relatively straightforward, contributing to the longevity of the product and reducing downtime.
Energy Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness
Electric furnaces are known for their energy efficiency and cost-effectiveness. They can convert electrical energy into heat with high efficiency, minimizing energy wastage. Compared to other heating systems, electric furnaces offer improved energy utilization, which can lead to lower operational costs over time.
Compact and Lightweight
Another advantage of electric heating systems is their compact size and lightweight nature. They occupy less space and are easier to install in various settings, making them suitable for both residential and commercial applications. Their smaller footprint also contributes to easier integration into existing infrastructure.

Other Considerations
In addition to the above benefits, electric heating systems offer specific advantages over alternative heating methods:
-
Cracked Oil Gas: While cracked oil gas is a high-calorific-value fuel, it is often limited to small-scale plants due to the higher cost of oil compared to coal. Electric heating provides a more versatile and cost-effective solution for larger-scale applications.
-
Electricity: Electric furnaces are increasingly replacing gas-fired furnaces due to their simplicity in design, uniformity of temperature control, and precise automation. They offer reduced heating time, high efficiency (often exceeding 90%), and improved control over heating processes. Induction heating, in particular, reduces wasted heat and enhances power density, further optimizing energy utilization.
-
Versatility: Electric heating encompasses various systems such as space heaters, central heating, and portable heating options. This versatility allows users to choose the most suitable electric heating solution based on their specific needs and preferences.
In summary, electric heating systems offer a range of benefits, including customizable solutions, simplified design, energy efficiency, compactness, and versatility. These advantages make them a preferred choice for heating applications across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors.
Applications of Electric Heating Systems
Electric heating systems offer customizable solutions designed by engineers, enabling the placement of temperature zones according to the appliance's requirements. This simplified design, with fewer components compared to traditional heating elements, reduces the frequency of damage or maintenance, enhancing product longevity.
Benefits of Electric Heating:
- Energy Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness: Electric heating systems are known for their energy efficiency, resulting in lower operating costs over time.
- Compact and Lightweight Design: Electric heating elements are smaller, more compact, and lighter than other heating alternatives, making them suitable for various applications.
Electric heating encompasses various systems, including space heaters, central heating, and portable heating. Each system offers unique advantages tailored to specific environments and industries.
High-Temperature Furnaces (HTFs):
High-temperature furnaces utilize electric heating systems, advanced insulation materials, and innovative designs to achieve temperatures as high as 3000 °C. These furnaces play a crucial role in scientific and industrial applications, particularly in clean technology, where they contribute to clean energy production at multiple stages.
Induction Heating (IH):
Induction heating technology, powered by solid-state generators utilizing new power semiconductor technologies, has expanded beyond industrial environments since the late 1980s. Domestic applications have emerged, with a recent focus on induction heating for medical treatments due to its precise and targeted local heating capabilities.
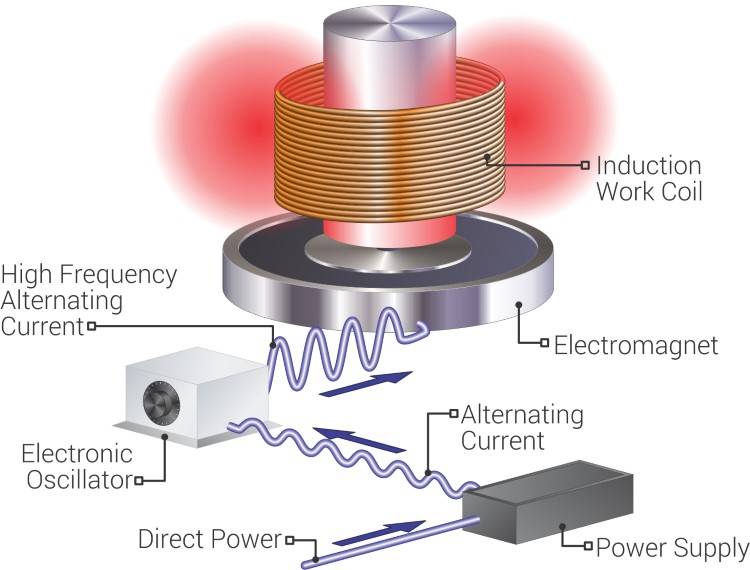
Today, induction heating technology offers highly efficient and reliable systems for a wide range of applications, including medical treatments and industrial processes.
Overall, electric heating systems provide versatile solutions with benefits such as energy efficiency, compact design, and precise heating capabilities, making them ideal for various environments and industries.
Understanding Electric Furnaces
Electric furnaces play a critical role in industrial processes, providing controlled heating environments for various applications. In this section, we delve into the intricacies of electric furnaces, including their components and operational principles, with a focus on furnace controllers and their integration within the system.
Furnace Controllers
Furnace controllers serve as the nerve center of electric furnaces, regulating temperature, heat delivery, and other crucial variables essential for optimal furnace performance. These controllers are designed to meticulously control the burner flame, air mixture, and trim, ensuring precise temperature management and energy efficiency.
Components and Functionality
-
Temperature Measurement and Control: Furnace controllers receive inputs from thermocouples and sensors to accurately gauge the temperature within the furnace. They utilize sophisticated algorithms to adjust heat delivery and maintain the desired temperature setpoints.
-
Power Supply and Controls: The power supply for electric furnaces typically comprises a three-phase to DC, SCR-controlled transformer package capable of ramping the furnace up to extreme temperatures, reaching up to 3000°C. This power supply system is housed within a dedicated cabinet, integrating various components such as circuit breakers, contactors, auxiliary transformers, and instruments for efficient operation.
-
Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) Integration: Many modern electric furnaces feature PLC integration, enabling seamless communication between the furnace controller and other industrial control systems. PLC systems enhance automation and provide advanced functionalities such as data logging, alarms, and remote monitoring.
-
Human-Machine Interface (HMI): Some furnace controllers offer optional HMI control packages, facilitating user interaction and providing intuitive interfaces for system monitoring and adjustment.
Integration with Electric Heating Systems
Electric furnaces employ various styles of resistance-type electric heaters to generate heat and maintain the desired thermal environment. These heaters can be configured as standard open resistance wire types or bayonet/radiant tube styles, depending on the specific furnace application and thermal requirements.
SCR Power Controllers
SCR (Silicon Controlled Rectifier) power controllers play a pivotal role in regulating the power delivered to electric heaters, ensuring precise control over heating elements' output. Equipped with control panel door-mounted diagnostics displays, SCR power controllers provide real-time monitoring and diagnostic capabilities, allowing operators to identify and address potential issues promptly.
PLC and PC Systems Integration
For enhanced automation and control, electric furnaces often feature integration with PLC and PC systems. PLCs serve as versatile controllers, executing logic-based operations and coordinating various furnace functions. PC integration enables comprehensive supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA), empowering operators with insights into furnace performance and facilitating remote management capabilities.
Conclusion
Electric furnaces, equipped with advanced furnace controllers and integrated control systems, represent a cornerstone of modern industrial heating processes. By leveraging cutting-edge technology and precise control mechanisms, these furnaces ensure optimal performance, efficiency, and reliability across diverse applications.
Cost Considerations and Efficiency
Electric heating systems encompass various technologies such as space heaters, central heating, and portable heating. When evaluating the benefits of electric heating, it's important to consider several factors:

Benefits of Electric Heating
-
Efficiency: Electric furnaces offer high efficiency, with properly designed and insulated models reaching utilization rates of 96 to 98%.
-
Ease of Control: Electric heating systems can be easily controlled with automatic temperature controllers and timers, providing convenience and energy savings.
-
No Emissions: Unlike gas or coal furnaces, electric heating produces no emissions, making it environmentally friendly.
-
Quiet Operation: Electric heating systems operate quietly, minimizing noise pollution in residential and commercial spaces.
-
Safety: Electric furnaces pose fewer safety risks than combustion-based heating systems, as there is no risk of carbon monoxide leaks or gas explosions.
-
Installation Flexibility: Electric heating systems are often easier and less expensive to install compared to systems that require ductwork or gas lines.
-
Zoning Capabilities: Electric heating allows for zoning, enabling users to heat specific areas of a building as needed, leading to energy savings.
Analyzing Furnace Technologies
To select the most suitable furnace technology or supplier, it's crucial to evaluate various criteria and compare them against an "Ideal Furnace Rating." These criteria may include:
- Efficiency: Measure of how effectively the furnace converts energy into heat.
- Cost: Initial purchase cost as well as long-term operational expenses.
- Reliability: Dependability and longevity of the furnace.
- Performance: Ability to consistently maintain desired temperatures.
- Energy Source Compatibility: Compatibility with available energy sources, such as electricity or natural gas.
- Environmental Impact: Assessment of the furnace's carbon footprint and emissions.
- Technology Integration: Compatibility with smart home systems and advanced controls.
- Maintenance Requirements: Frequency and complexity of maintenance tasks.
- Warranty Coverage: Length and comprehensiveness of warranty protection.
- Customer Reviews: Feedback from previous users regarding performance and satisfaction.
By comparing potential technologies or suppliers against these criteria, one can identify the furnace that best meets their specific requirements.
Consideration of Energy Source Costs
When evaluating the cost of different energy sources, it's essential to consider both the direct cost of fuel and the efficiency of utilization. While natural gas may have a lower initial cost compared to electricity, electric furnaces can achieve significantly higher utilization efficiencies, ranging from 96 to 98%. Additionally, in regions where electricity prices are competitive or paired with heat pumps, electric heating can offer cost savings compared to gas furnaces alone.
While solid fuels like coal were historically used for heating, they are now rarely utilized due to environmental and efficiency concerns.
In summary, when choosing between electric and gas heating systems, factors such as cost, efficiency, environmental impact, and ease of control must be carefully weighed to determine the most suitable option for individual needs and circumstances.
Conclusion
In summary, electric furnaces consist of several key components, each playing a crucial role in the heating process. From the heating elements that generate heat to the contactors, sequencers, and transformers that regulate electrical flow and control system operations, every component contributes to the overall efficiency and functionality of the furnace. Understanding these components and their functions is essential for maximizing the performance and longevity of electric furnaces across various industrial applications.
If you are interested in our products, please visit our company website, where innovation has always been a priority. Our R&D team consists of experienced engineers and scientists who closely follow industry trends and are constantly pushing the boundaries of what is possible. Our laboratory equipment incorporates the latest technology to ensure that you can obtain accurate and repeatable results during your experiments. From high-precision instruments to intelligent control systems, our products will provide you with unlimited possibilities for your experimental work.
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- High Temperature Constant Temperature Heating Circulator Water Bath Chiller Circulator for Reaction Bath
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- 5L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
Related Articles
- Exploring the Benefits and Applications of Rotary Furnaces: A Comprehensive Guide
- A Comprehensive Guide to Rotary Kilns: Applications, Types, and Working Principles
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace: Design, Operation, and Applications
- Rotary Furnaces: A Comprehensive Guide to Advanced Materials Processing
- Rotary Furnaces: Advanced Materials Processing and Applications























