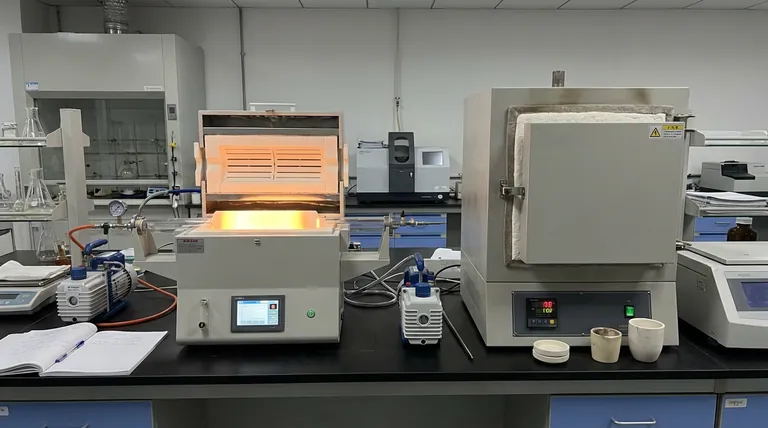
Heat is rarely just heat.
In the laboratory, temperature is merely a baseline. The difference between a successful synthesis and a pile of ruined substrate often lies in the invisible variables surrounding the heat.
Engineers and scientists often fall into the trap of thinking about furnaces as simple commodities—boxes that get hot. But this oversight ignores the fundamental architecture of thermal processing.
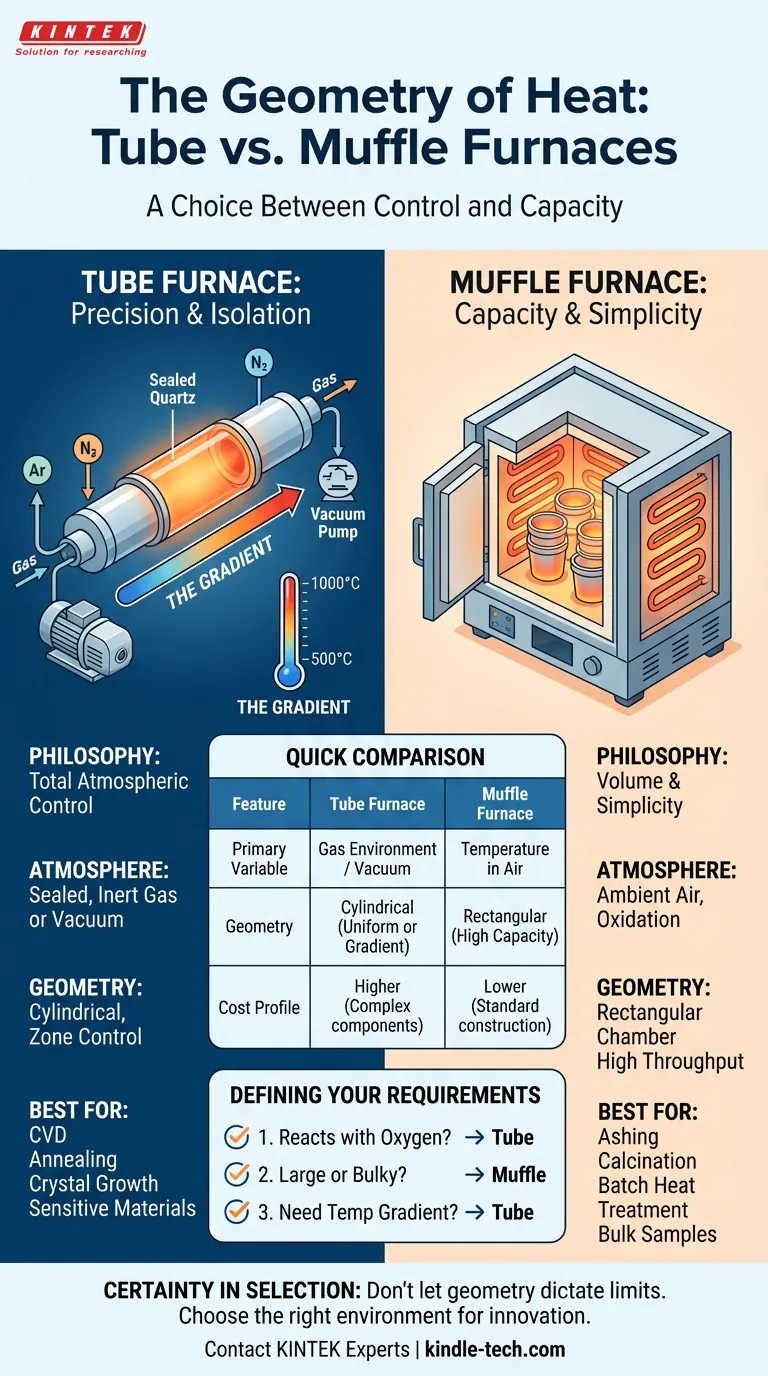
When selecting between a Tube Furnace and a Muffle Furnace, you are not just choosing a piece of equipment. You are choosing a philosophy of control.
The Invisible Variable: Atmosphere
The most defining characteristic of a thermal process is not how hot it gets, but what the air is doing while it heats.
The Tube Furnace is designed for the isolationist.
It features a sealed cylindrical tube—usually ceramic or quartz—passing through heating elements. This isn't just a design choice; it is an engineering necessity for exclusion. The tube allows you to evacuate the air (creating a vacuum) or flood the chamber with specific gases like argon or nitrogen.
If your work involves Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) or annealing sensitive materials, oxygen is your enemy. The tube furnace is the only vessel that effectively locks the enemy out.
The Muffle Furnace, by contrast, embraces the ambient environment.
It is a highly insulated box designed to heat samples in air. It creates a "muffle"—a barrier between the heating elements and the sample—but it does not seal the sample off from the atmosphere of the lab itself.
It is designed for oxidation. It is designed for simplicity.
The Architecture of Space
The physical shape of the furnace dictates the workflow of the laboratory.
There is a psychological trade-off here between precision and throughput.
The Constraint of the Cylinder
The tube furnace offers a specific kind of romance to the engineer: The Gradient.
Because the tube is long and narrow, advanced models can control different zones along the length of the tube. You can heat one end to 1000°C and keep the other at 500°C. This allows for transport reactions and purification processes that a box furnace simply cannot simulate.
However, the cylinder is unforgiving regarding volume. You are limited by the diameter of the tube. It is a tool for the specific, not the massive.
The Generosity of the Box
The muffle furnace prioritizes volume.
The rectangular chamber is designed for the "heavy lifting" of the lab:
- Ashing organic materials.
- Calcination of powders.
- Batch heat treatment.
If you have ten crucibles that need to reach 1100°C and the atmosphere is irrelevant, the muffle furnace is the rational choice. It is the workhorse where the tube furnace is the scalpel.
The Psychology of the Trade-off
Why do labs choose the wrong one?
Usually, it comes down to a misunderstanding of cost versus value.
A tube furnace is generally more expensive. It requires gas flow controllers, vacuum flanges, and sealed systems. It is complex because it has to be.
A muffle furnace is simpler and often cheaper. But buying a muffle furnace for a process that requires an inert atmosphere is not a cost-saving measure; it is a guarantee of failure. Conversely, using a precision tube furnace for bulk ashing is a waste of a high-precision asset.
Quick Comparison
| Feature | Tube Furnace | Muffle Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Philosophy | Total Atmospheric Control | Volume & Simplicity |
| Primary Variable | Gas Environment / Vacuum | Temperature in Air |
| Geometry | Cylindrical (Uniform or Gradient) | Rectangular (High Capacity) |
| Best For | CVD, Annealing, Crystal Growth | Ashing, Calcination, Pre-heating |
| Cost Profile | Higher (Complex components) | Lower (Standard construction) |
Defining Your Requirements
The choice is not about which furnace is "better." It is about understanding the vulnerability of your material.
Ask yourself three questions:
- Does my sample react with oxygen? If yes, you need the sealed environment of a tube furnace.
- Is my sample large or bulky? If yes, the geometry of the muffle furnace is required.
- Do I need a temperature gradient? If yes, only the tube furnace can provide this thermal landscape.
Certainty in Selection
At KINTEK, we see laboratory equipment as a system, not just a catalog of specs.
We understand that a furnace is the environment where your innovation survives or fails. Whether you need the surgical precision of a controlled atmosphere or the robust capacity of a high-temperature chamber, the goal is repeatability.
Don't let the geometry of your equipment dictate the limits of your research.
Contact Our Experts to discuss your specific thermal requirements, and let us help you engineer the perfect environment for your work.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
Related Articles
- The Anatomy of Control: Why Every Component in a Tube Furnace Matters
- Why Your Ceramic Furnace Tubes Keep Cracking—And How to Choose the Right One
- Cracked Tubes, Contaminated Samples? Your Furnace Tube Is The Hidden Culprit
- Beyond the Spec Sheet: The Hidden Physics of a Tube Furnace's True Limit
- Muffle vs. Tube Furnace: How the Right Choice Prevents Catastrophic Lab Failure




















