The most dangerous thing in a laboratory is not a chemical reaction. It is assumption.
We assume that because a material is capable of withstanding 1700°C, it is invincible. We assume that a furnace tube that looks clean is actually clean.
But ceramics like alumina are paradoxical. They are incredibly robust against heat, yet fragile against time and haste.
The difference between a failed experiment and a breakthrough often lies in the invisible history of the vessel you use. Residue from a previous run isn't just dirt; it is a contaminant that alters the physics of your next sample.
Here is how to fight entropy in high-temperature environments.
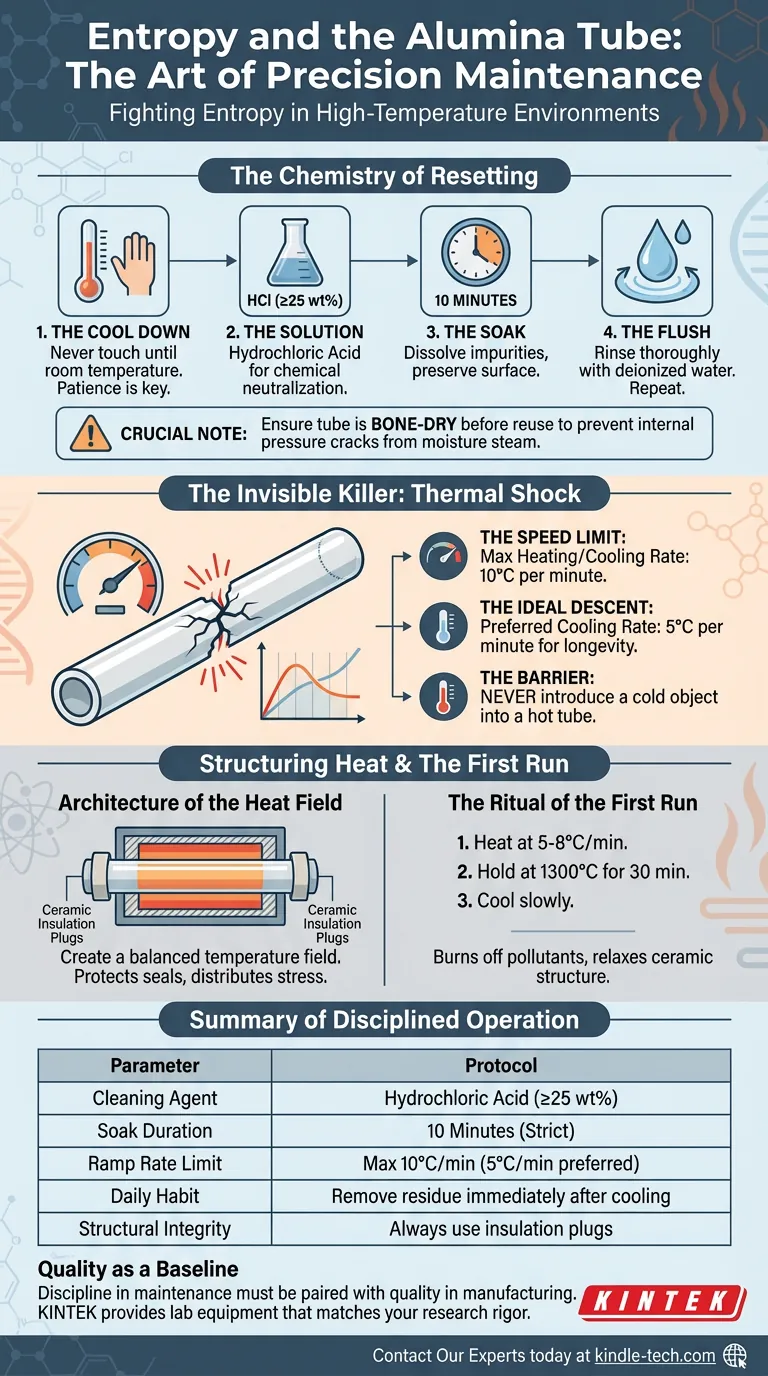
The Chemistry of Resetting
Cleaning an alumina tube is not about scrubbing. It is about chemical neutralization.
When metallic or oxide residues fuse to the tube wall, mechanical force will only damage the ceramic matrix. You need a solvent that targets the contaminant without dissolving the vessel.
The standard protocol is precise:
- The Cool Down: Never touch a tube until it has returned to room temperature. Patience is the first safety layer.
- The Solution: Use a hydrochloric acid (HCl) solution diluted to at least 25 wt%.
- The Soak: Fill the tube and let it sit for 10 minutes. This is the "Goldilocks" window—long enough to dissolve impurities, short enough to preserve the alumina surface.
- The Flush: Rinse thoroughly with deionized water. Then rinse again. Any acid left behind becomes a contaminant itself when heated.
Crucial Note: Ensure the tube is bone-dry before reusing it. Moisture trapped in the pores of the ceramic will turn to steam at high temperatures, creating internal pressure that cracks the tube from the inside out.
The Invisible Killer: Thermal Shock
Most alumina tubes do not die from old age. They are murdered by speed.
Alumina is a ceramic. It has high thermal mass but low elasticity. When you heat it, it expands. When you cool it, it contracts.
If one part of the tube expands faster than another—or if the whole tube changes temperature too quickly—stress fractures develop. This is thermal shock.
It is the engineer’s version of whiplash.
To prevent this, you must adopt a philosophy of slow control:
- The Speed Limit: Never exceed a heating or cooling rate of 10°C per minute.
- The Ideal Descent: Cooling is often where impatience takes over. A rate of 5°C per minute is the gold standard for longevity.
- The Barrier: Never introduce a cold object into a hot tube. The temperature differential causes immediate localized cracking.
The Architecture of the Heat Field
Maintenance is not just about cleaning; it is about how you structure the heat.
A furnace tube is an open system. Without proper insulation, heat escapes rapidly from the ends, creating a chaotic temperature gradient.
Insulation plugs are not optional accessories. They are structural necessities. By placing ceramic plugs at both ends, you create a balanced temperature field. This protects the O-ring seals from overheating and ensures that the physical stress is distributed evenly across the tube’s length.
The Ritual of the First Run
A new alumina tube carries the invisible stress of its manufacturing process. It requires a "break-in" period.
Before running an actual experiment, perform a conditioning cycle:
- Heat at 5-8°C per minute.
- Hold at 1300°C for 30 minutes.
- Cool slowly.
This burns off manufacturing pollutants and relaxes the ceramic structure, preparing it for service.
Summary of Disciplined Operation
Success in high-temperature materials processing is a checklist, not a talent.
| Parameter | The Protocol |
|---|---|
| Cleaning Agent | Hydrochloric Acid (≥25 wt%) |
| Soak Duration | 10 Minutes (Strict) |
| Ramp Rate Limit | Max 10°C/min (5°C/min preferred for cooling) |
| Daily Habit | Remove all sample residue immediately after cooling |
| Structural Integrity | Always use insulation plugs to balance heat |
Quality as a Baseline
You can follow every protocol perfectly, but if the underlying material is flawed, the result will be failure.
Discipline in maintenance must be paired with quality in manufacturing.
At KINTEK, we understand that a furnace tube is not just a consumable; it is the foundation of your data. We specialize in providing lab equipment that matches the rigor of your research, from high-purity alumina tubes to the consumables that keep them running.
Don't let equipment failure be the variable you didn't account for.
Contact Our Experts today to discuss your high-temperature applications and find the right solutions for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3) Protective Tube for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- High Temperature Alumina (Al2O3) Furnace Tube for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
Related Articles
- Installation of Tube Furnace Fitting Tee
- Your Tube Furnace Is Not the Problem—Your Choice of It Is
- Why Your Ceramic Furnace Tubes Keep Cracking—And How to Choose the Right One
- Cracked Tubes, Contaminated Samples? Your Furnace Tube Is The Hidden Culprit
- Why Your Furnace Components Keep Failing—And the Material Science Fix




















