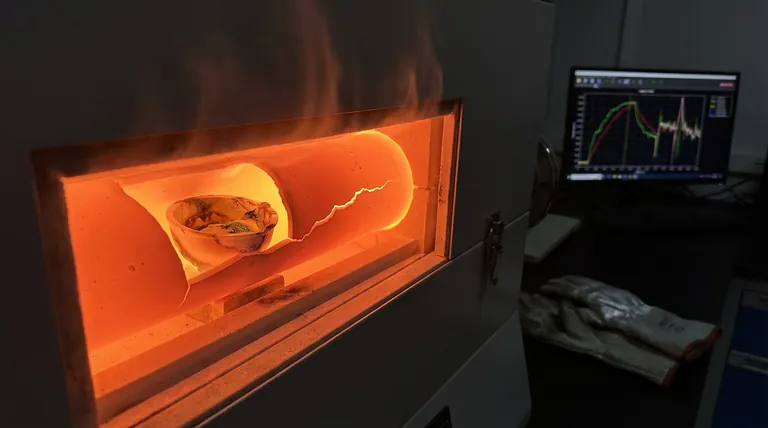
Imagine this: after hours of a meticulously planned high-temperature run, you open the furnace. Instead of a perfect sample, you find a cracked tube, a visibly contaminated product, or worse, results so inconsistent they call the entire experiment into question. It’s a moment of pure frustration that costs time, money, and confidence.
If this scenario feels familiar, you are not alone.
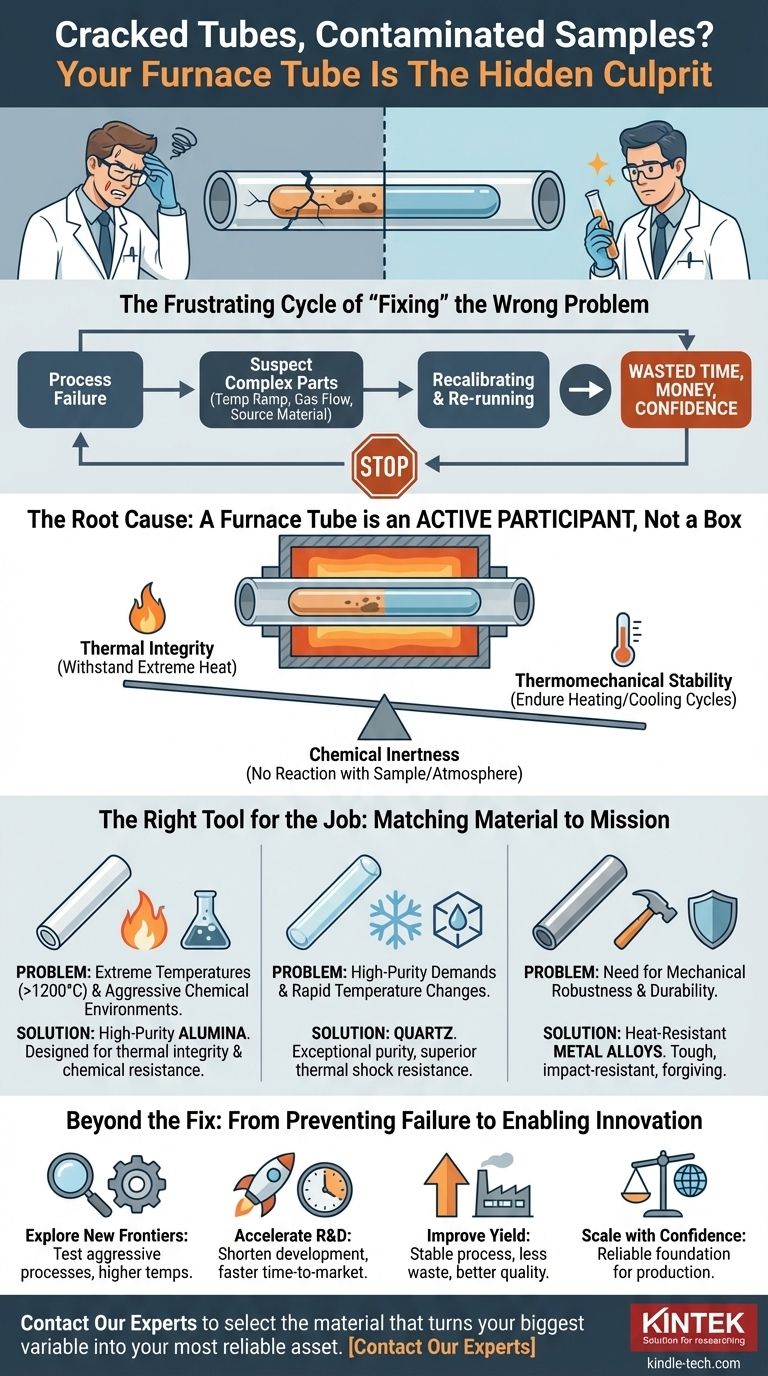
The Frustrating Cycle of "Fixing" the Wrong Problem
When a high-temperature process fails, the troubleshooting checklist is predictable. We immediately suspect the most complex parts of the system:
- "Was the temperature ramp rate too aggressive?"
- "Did the gas flow controller malfunction?"
- "Was the source material impure to begin with?"
Engineers and researchers can spend weeks recalibrating controllers, verifying gas purities, and re-running tests, all while treating the furnace tube as a simple, passive container. This cycle of trial-and-error is more than just an academic annoyance. It has direct business consequences: critical projects are delayed, expensive materials and energy are wasted, and the path from R&D to production becomes unreliable. You're stuck treating the symptoms, while the real disease goes undiagnosed.
The Root Cause: A Furnace Tube is an Active Component, Not a Box
Here is the fundamental truth that changes everything: at high temperatures, your furnace tube is not a passive container. It is an active chemical and physical participant in your process.
The common "fixes" fail because they ignore this reality. The problem isn't a faulty setting; it's a fundamental mismatch between the tube's material properties and the demands of the process. Every furnace tube must constantly perform a high-stakes balancing act between three critical factors:
- Thermal Integrity: It must withstand extreme heat without softening, deforming, or melting.
- Chemical Inertness: It must not react with your sample, the process gases, or the atmosphere. At 1400°C, materials that are stable at room temperature can become surprisingly reactive.
- Thermomechanical Stability: It must endure the stress of heating and cooling cycles (thermal shock) without cracking.
Recalibrating your furnace won't stop a metal alloy tube from oxidizing in an air atmosphere. Re-running your experiment won’t prevent an alumina tube from cracking if it’s cooled too quickly. You've been trying to solve a material science problem by adjusting equipment settings.
The Right Tool for the Job: Matching Material to Mission
To permanently solve this issue, you don't need a more complicated furnace; you need a furnace tube material that is explicitly chosen to master the specific challenges of your application. This is where a simple component becomes a precision-engineered tool.
This is not a matter of guesswork. It's an engineering decision based on the underlying principles we've discussed. The solution is to select a material whose properties directly counter the root cause of your failures.
-
Problem: Extreme Temperatures (>1200°C) and Aggressive Chemical Environments.
- Solution: High-purity Alumina tubes are the standard. They are designed for thermal integrity and chemical resistance at temperatures where metals would fail and quartz would soften.
-
Problem: High-Purity Demands and Rapid Temperature Changes.
- Solution: Quartz tubes offer exceptional purity, preventing sample contamination, and boast superior resistance to thermal shock, making them ideal for semiconductor processing and applications requiring fast cycling.
-
Problem: Need for Mechanical Robustness and Durability.
- Solution: Heat-resistant metal alloys are tough. They resist physical impact and are more forgiving than ceramics, making them a reliable choice for applications where mechanical durability is the top priority (within their temperature and atmospheric limits).
At KINTEK, we see the furnace tube not as a simple consumable, but as a critical piece of process equipment. Our role is to help you make this crucial engineering choice correctly the first time, ensuring your setup is built on a foundation of material stability.
Beyond the Fix: From Preventing Failure to Enabling Innovation
Once your furnace tube is no longer the weakest link, the focus shifts from damage control to genuine progress. A reliable thermal process doesn't just mean fewer headaches; it unlocks new potential.
- Explore New Frontiers: You can confidently test more aggressive chemical processes or push your operating temperatures higher, knowing your equipment is stable.
- Accelerate R&D: With repeatable and trustworthy results, you can shorten development cycles and get new materials or products to market faster.
- Improve Yield: In a production environment, process stability translates directly to higher yields, less waste, and better product quality.
- Scale with Confidence: You can move from lab-scale experiments to pilot production knowing that your process is fundamentally sound and repeatable.
Solving the furnace tube problem is the first step toward achieving more ambitious goals. It’s about building a reliable foundation that allows your research and production to thrive. If you're ready to move past the cycle of troubleshooting and start achieving more consistent, predictable results, our team is here to help you analyze your process and select the material that will turn your biggest variable into your most reliable asset. Contact Our Experts to discuss your specific application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- High Temperature Alumina (Al2O3) Furnace Tube for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
Related Articles
- The Silent Partner in Pyrolysis: Engineering the Perfect Thermal Boundary
- Installation of Tube Furnace Fitting Tee
- Your Tube Furnace Is Not the Problem—Your Choice of It Is
- The Anatomy of Control: Why Every Component in a Tube Furnace Matters
- Muffle vs. Tube Furnace: How the Right Choice Prevents Catastrophic Lab Failure




















