Blog

Don't Let Overheating Ruin Your Experiment Use a Chiller for Your Rotavap
2 years agoChillers are essential laboratory equipment used to maintain a constant temperature during experiments. They are especially important when using a rotary evaporator (rotavap) to prevent overheating.
Learn More

The Role of Powder Characteristics in Cold Isostatic Pressing
2 years agoCold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) is a powder compaction technique that involves applying uniform pressure to a powder-filled container from all directions.
Learn More

The Benefits of Using Isostatic Pressing in Manufacturing
2 years agosostatic pressing is a manufacturing process that involves applying uniform pressure to a material to achieve a specific shape or density. The process can be performed at room temperature (cold isostatic pressing or CIP) or at high temperatures (hot isostatic pressing or HIP).
Learn More

Understanding the Technical Aspects of Cold Isostatic Pressing
2 years agoCold isostatic pressing (CIP) is a technique used in the manufacturing industry to achieve high-density materials with uniform properties. It involves applying equal pressure from all directions to a powder compact, resulting in improved compaction compared to traditional cold pressing methods.
Learn More
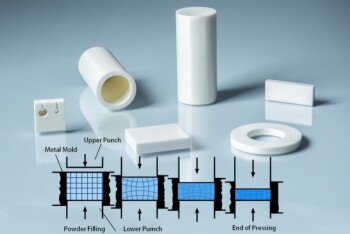
Understanding the Process and Benefits of Zirconia Ceramic Cold Isostatic Pressing
2 years agoCold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) is a fascinating process that offers numerous benefits in the field of ceramic manufacturing. CIP involves the use of a high-pressure pump to generate isotropic uniform pressure on a ceramic material. The resulting uniform pressure distribution leads to enhanced density and high strength of the final product.
Learn More
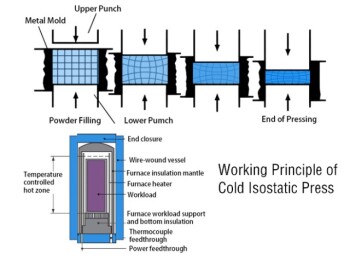
Cold Isostatic Pressing: Techniques and Applications
2 years agoCold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) is a powerful technique used in materials processing to enhance material properties. It involves subjecting a material to uniform pressure from all sides by immersing it in a high-pressure fluid medium and applying hydraulic pressure.
Learn More
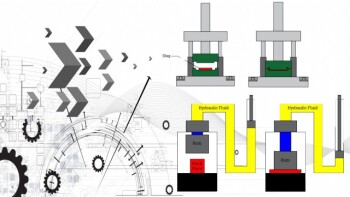
The Science Behind Hydraulic Presses and Their Applications
2 years agoHydraulic presses are machines that use hydraulic pressure to compress, mold, or shape a material. The basic concept of hydraulic presses is Pascal’s principle, which states that a pressure applied to an enclosed fluid is transmitted uniformly in all directions.
Learn More

Cold Isostatic Pressing: An Overview and its Industrial Applications
2 years agoCold isostatic pressing (CIP) is a method of processing materials by using liquid pressure to compact powder. It is similar to metal mold processing and is based on Pascal's law.
Learn More

Discover The Benefits of Using A Rotary Evaporator
2 years agoRotary evaporators are essential laboratory equipment used in the process of separating solvents from samples. These devices work by evaporating the solvent from the sample under a reduced pressure and controlled temperature.
Learn More

Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP): A Proven Process for High-Performance Parts Manufacturing
2 years agoCold isostatic pressing (CIP) is a proven process that stands out when it comes to high-performance part manufacturing. The technology offers a range of advantages, from achieving superior densities in ceramics to compressing materials as diverse as metals and graphite.
Learn More

Comparative Analysis of Hot Pressing and Cold Pressing in Metal Powders Processing
2 years agoHot pressing and cold pressing are two compaction methods in metal powder processing. Hot pressing involves combining discrete powder metallurgy stages into a single chamber where compaction and sintering occur simultaneously, cold pressing applies pressure without the use of heat.
Learn More

An In-depth Analysis of Hot Pressing Technology and Its Applications
2 years agoHot pressing is a high-pressure, low-strain-rate powder metallurgy process used to form powder or powder compact at high temperatures to induce sintering and creep processes. It involves the simultaneous application of heat and pressure to fabricate hard and brittle materials.
Learn More

The Ultimate Guide to Isostatic Pressing
2 years agoIsostatic pressing is a process that involves uniformly applying pressure to a material from all directions. This process is used to produce a range of materials, including ceramics, metals, and polymers.
Learn More

A Comprehensive Guide to Hot Press Machines: Functionality, Application, Features, Principles, Classification, and Technical Requirements
2 years agoThe hot Lab Press is a versatile and efficient tool used in material research, pharmacy, catalytic reactions, ceramics, and electronics. Its compact design allows for mobility in vacuum environments, making it ideal for research labs. Additionally, it can perform hot pressing functions, adding to its versatility in sample preparation.
Learn More

Cooking with a Rotary Evaporator A New Way to Enhance Your Dishes
2 years agoA rotary evaporator, also known as a rotovap, is a laboratory equipment used for distillation.
Learn More

10 Essential Safety Steps for Pressure Reactor Use in Laboratories
2 years agoSafety is paramount when conducting chemical reactions under pressurized conditions. It is important to carefully prepare pressure reactors and laboratory safety equipment to prevent potential hazards that, if not controlled, can have catastrophic consequences. In order to ensure the safety of using a pressure reactor, it is important to understand the specifications of the reactor. Become familiar with the chemistry of the reactor material and make sure it is chemically resistant enough to withstand the substances used in the reaction.
Learn More
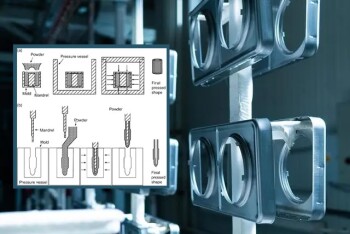
Understanding the Basics of Isostatic Pressing
2 years agoIsostatic pressing is a manufacturing process used to shape and consolidate materials by applying equal pressure from all directions. The technique involves placing a material in a pressure vessel and applying hydrostatic pressure to the material.
Learn More

Concentrate Your Samples with a Rotary Evaporator
2 years agoRotary evaporators are laboratory equipment used for the separation of solvents from samples. They are commonly used in chemistry, research, and pharmaceutical industries for the concentration of solutions and extraction of active compounds.
Learn More

Warm Isostatic Pressing An Overview of the Process and Equipment
2 years agoWarm Isostatic Pressing (WIP) is a process used to improve the quality of materials by applying high pressure and temperature. WIP is used to improve the density, mechanical properties, and microstructure of materials.
Learn More

Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using a Rotary Vacuum Evaporator
2 years agoA rotary vacuum evaporator, also known as a rotovap, is a laboratory equipment used for distillation purposes. It is a highly efficient system used for the removal of solvents from samples under low pressure and low temperature.
Learn More

Warm Isostatic Pressing for High-Density and Low-Defect Materials
2 years agoWarm Isostatic Pressing (WIP) is a high-pressure technique used to enhance the density and reduce the defects of materials. It involves subjecting a material to high pressure and high temperature while simultaneously applying an inert gas, which uniformly compresses the material.
Learn More

Choosing the Right Rotary Vacuum Evaporator for Your Lab
2 years agoRotary vacuum evaporators are essential tools for any laboratory that needs to concentrate or isolate solutions. These devices work by heating a sample under vacuum to increase its surface area and effectively remove solvent.
Learn More
What Makes Hot Isostatic Pressing So Effective
2 years agoHot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) is a manufacturing process that uses high temperature and pressure to improve the mechanical properties of materials. The process involves placing a part in a sealed chamber and subjecting it to high temperatures and pressures.
Learn More

Boost Your Efficiency Why A Rotary Evaporator Is Better
2 years agoRotary evaporation is a technique used to remove solvents from samples, typically with the use of a vacuum. This method is widely used in laboratories due to its efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness.
Learn More
XRF Pelletising for Solid Samples Tips and Tricks
2 years agoX-ray fluorescence (XRF) analysis is a non-destructive analytical technique used to determine the elemental composition of solid, liquid, and powdered samples.
Learn More

Affordable Rotavapor How to Save on Your Purchase
2 years agoRotavapor is a laboratory equipment that is used for distillation, purification, and concentration of liquid samples. It is a vital tool for chemists, biologists, and other researchers who work with various types of solvents and chemicals.
Learn More

Cold Isostatic Pressing vs. Hot Isostatic Pressing Which is Better
2 years agoIsostatic pressing is a process used in the production of high-performance materials and components. It involves applying uniform pressure on all sides of a material or part, resulting in a more uniform density and improved mechanical properties.
Learn More

Advantages of Using a Rotary Evaporator for Solvent Removal
2 years agoRotary evaporators are laboratory instruments used for solvent removal. They work by rotating a flask containing a liquid sample, which creates a thin film on the surface of the flask.
Learn More

Cold Isostatic Pressing for Medical Applications Challenges and Solutions
2 years agoCold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) is a process used to compact and densify powders, ceramics, and metals. This process uses high-pressure fluids, usually water or oil, to apply uniform pressure to the material from all directions.
Learn More

A Step-by-Step Guide to Using a Rotary Vacuum Evaporator for Solvent Removal
2 years agoA rotary vacuum evaporator is a laboratory instrument used for solvent removal, concentration, and purification. It is composed of a vacuum pump, a heating bath, a rotating flask, and a condenser.
Learn More