Yes, ceramics are exceptional electrical insulators. It is one of their most defining engineering properties, rooted in their fundamental atomic structure. While materials like polymers also insulate, ceramics are often specified for applications where high voltage, high temperatures, and structural rigidity are required.
The value of ceramics as electrical insulators stems directly from their atomic structure, which immobilizes electrons and prevents the flow of current. However, this electrical strength is balanced by their inherent mechanical brittleness, which is the critical trade-off in any design consideration.
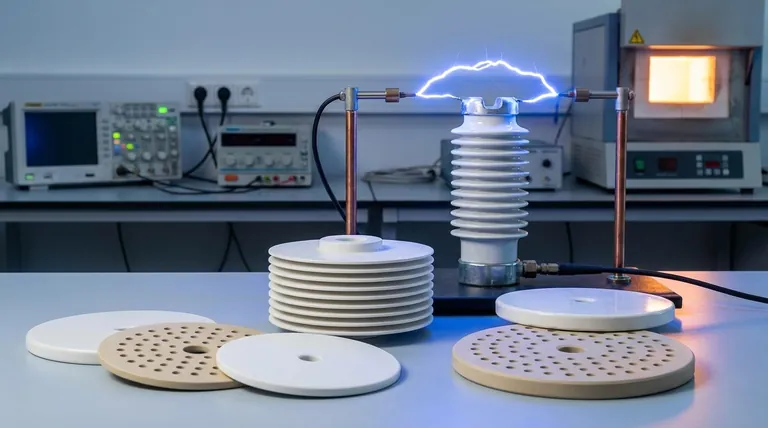

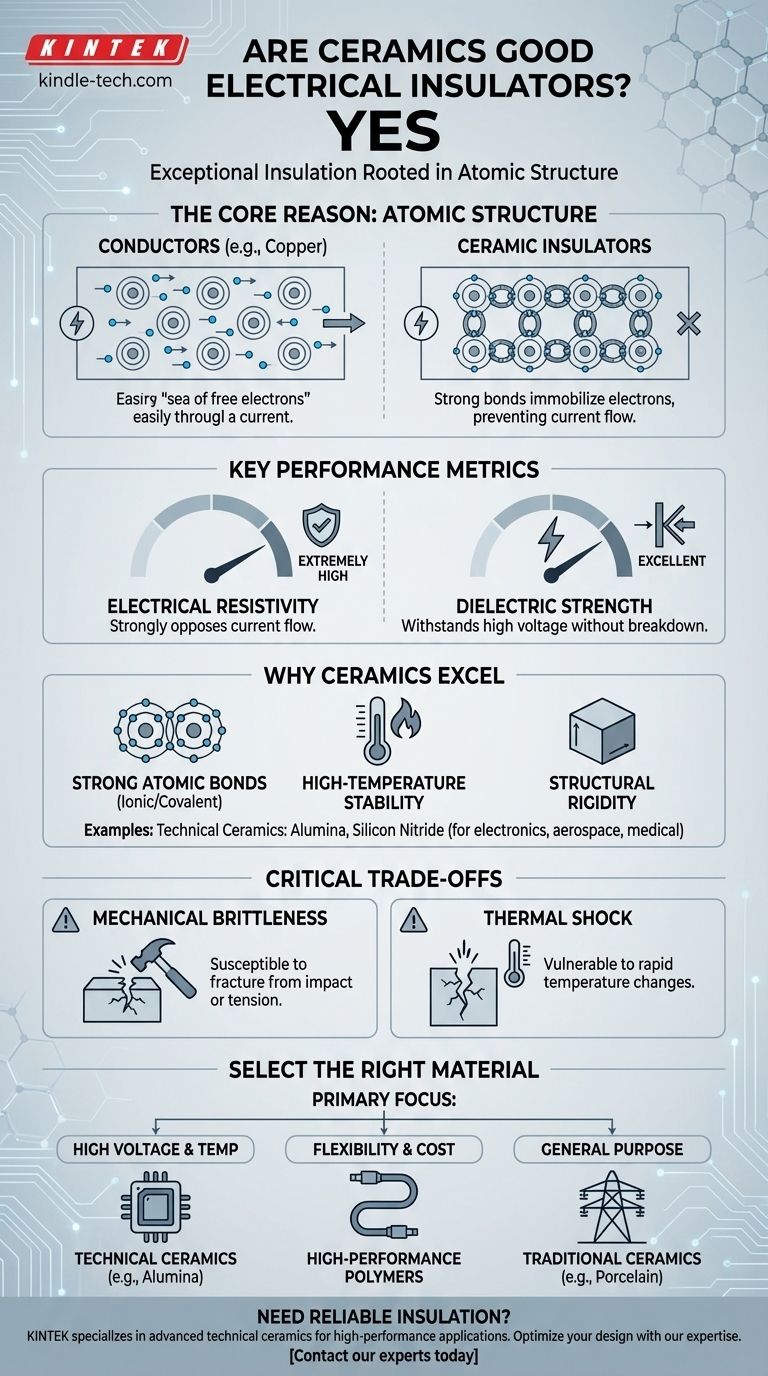
The Defining Characteristic of an Electrical Insulator
To understand why ceramics are effective, we must first define what makes any material an insulator. The primary factor is the availability of charge carriers—typically electrons—that are free to move through the material.
Preventing the Flow of Current
In conductive materials like copper, the outer electrons of each atom are not tightly bound and form a "sea" of free electrons. When a voltage is applied, these electrons move easily, creating an electrical current.
Insulators, by contrast, have very few or no free electrons. Their atomic structure holds electrons in tight, stable bonds, preventing them from moving and carrying a current.
Key Metrics for Insulators
Two primary properties quantify an insulator's effectiveness:
- Electrical Resistivity: This measures how strongly a material opposes the flow of electric current. Insulators have extremely high resistivity.
- Dielectric Strength: This measures the maximum electric field a material can withstand without "breaking down" and conducting electricity. High dielectric strength is crucial for high-voltage applications.
Why Ceramics Excel as Insulators
Ceramics possess a unique combination of atomic bonding and structural stability that makes them premier insulating materials, especially in demanding environments.
The Role of Strong Atomic Bonds
Most ceramics are defined by strong ionic or covalent bonds. In these bond types, electrons are either transferred or shared in a highly stable configuration that locks them in place.
This chemical stability is the root cause of their insulating properties. There are simply no loose electrons available to form an electrical current.
From Traditional to Technical Ceramics
While traditional ceramics like porcelain have been used as insulators for over a century in applications like power line standoffs, modern engineering demands more.
Technical ceramics, such as alumina (aluminum oxide) and silicon nitride, are engineered with extreme purity and controlled microstructures. This process maximizes their dielectric strength and thermal stability far beyond traditional materials, making them essential in electronics, aerospace, and medical devices.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect. The same properties that make ceramics excellent insulators also introduce significant design challenges that must be managed.
Mechanical Brittleness
The primary drawback of most ceramic materials is their brittleness. Unlike metals, which bend or deform under stress, ceramics tend to fracture without warning.
This means they are highly susceptible to failure from sharp impacts or high tensile loads. Designs must carefully manage mechanical stress to avoid catastrophic failure.
Susceptibility to Thermal Shock
The rigidity and low thermal conductivity of some ceramics can make them vulnerable to thermal shock. A rapid change in temperature can create internal stresses that cause the material to crack.
This is a critical consideration for applications involving rapid heating and cooling cycles.
Performance at Extreme Temperatures
While ceramics are known for their high-temperature stability, their electrical resistivity is not infinite. As temperature increases to extreme levels, atomic vibrations can eventually allow some electron movement, slightly decreasing their insulating effectiveness.
How to Select the Right Insulating Material
Choosing an insulator depends entirely on the demands of the application. The decision is a balance between electrical requirements, mechanical stress, and operating temperature.
- If your primary focus is high-voltage and high-temperature performance: Technical ceramics like alumina or silicon nitride are the definitive choice for their superior dielectric strength and stability.
- If your primary focus is mechanical flexibility and low cost: High-performance polymers may be a more suitable alternative, provided the temperature and voltage are within their operational limits.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose, cost-effective insulation: Traditional ceramics like porcelain offer a reliable and time-tested solution for standard electrical applications.
Understanding these core principles allows you to select a material not just because it works, but because it is the optimal choice for your specific design constraints.
Summary Table:
| Property | Why It Matters for Ceramic Insulators |
|---|---|
| Electrical Resistivity | Extremely high, preventing current flow by locking electrons in place. |
| Dielectric Strength | Excellent, allowing them to withstand high voltages without breaking down. |
| High-Temperature Stability | Maintains insulating properties in demanding thermal environments. |
| Mechanical Brittleness | Key trade-off: offers rigidity but requires careful design to manage stress. |
Need a reliable insulating solution for your lab equipment?
Ceramics are the material of choice for high-performance insulation, but selecting the right type is critical. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including components made from advanced technical ceramics like alumina and silicon nitride. Our expertise ensures you get materials with the perfect balance of dielectric strength, thermal stability, and durability for your specific application—from electronics to aerospace.
Let us help you optimize your design and enhance performance. Contact our experts today to discuss your requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Aluminum Oxide Al2O3 Heat Sink for Insulation
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Non-Standard Insulator Customization
- Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Tube
- Advanced Engineering Fine Ceramics Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Parts
- Precision Machined Zirconia Ceramic Ball for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- Why is silicon carbide so important? Unlock Superior Performance in Extreme Conditions
- Where are ceramics used in the body? Key Applications in Orthopedics, Dentistry & Bone Repair
- What is sintered ceramic? A Durable, Non-Porous Material for Modern Surfaces
- What are the advantages of ceramic sintering? Achieve Dense, High-Performance Ceramic Parts
- How long does ceramic insulation last? Unlock 20+ Years of Performance
- Does ceramic break with heat? The Real Culprit is Thermal Shock
- How much temperature can porcelain withstand? Unlock Its True Heat Resistance & Avoid Thermal Shock
- Why is silicon carbide more efficient? Unlock Higher Power Density with SiC's Superior Material Properties



















