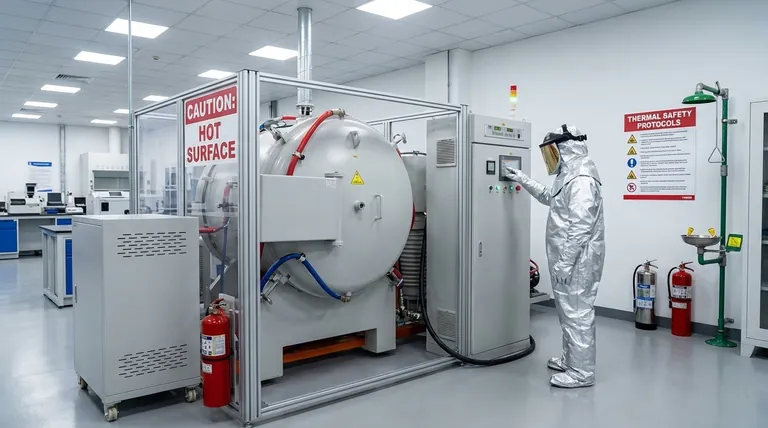
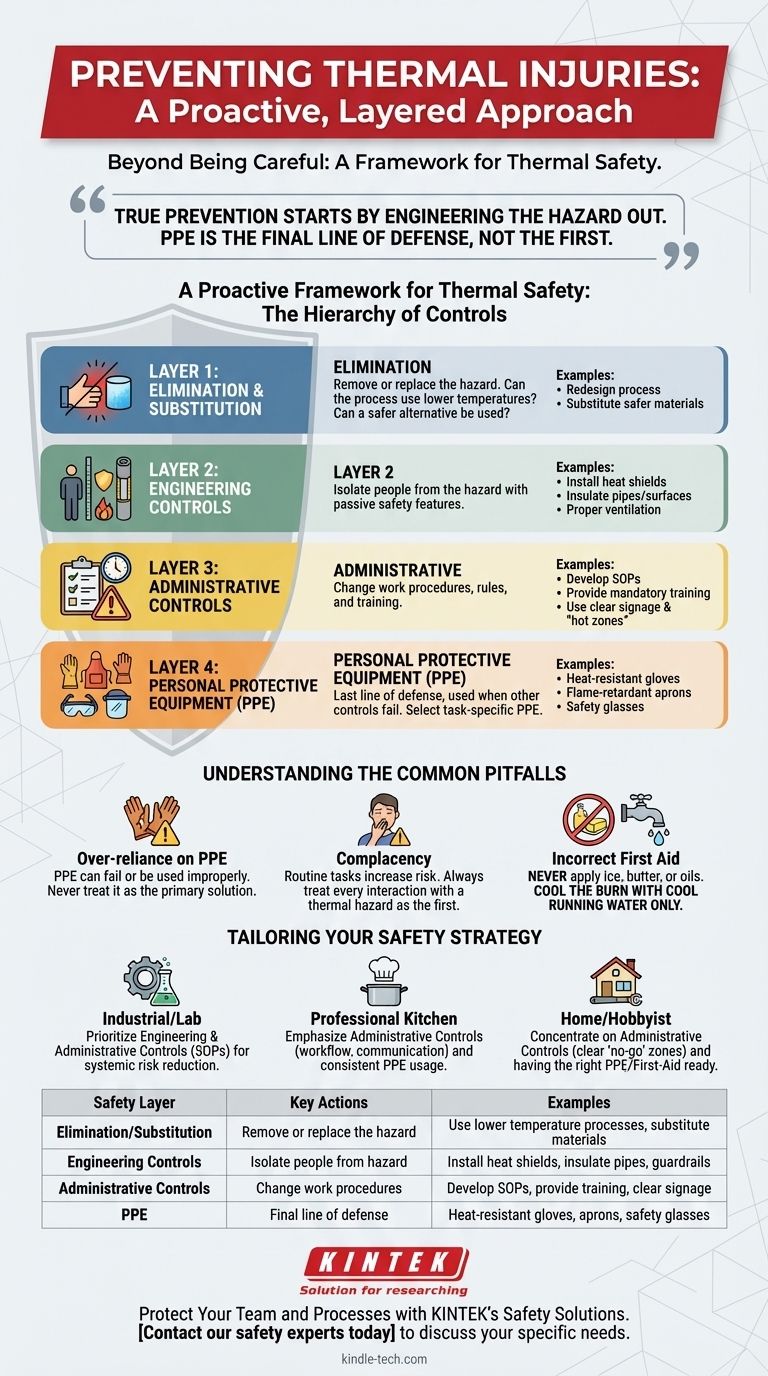
To effectively prevent burns, you must use a layered approach that goes beyond simply being careful. This involves using the correct Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) for the specific hazard, establishing safe work procedures, and ensuring the environment itself is designed to minimize risk. A foundational understanding of these layers is the key to creating a truly safe system.
The most common mistake in thermal safety is treating Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) as the primary solution. True prevention starts by engineering the hazard out of the process entirely. PPE should always be considered the final line of defense, not the first.

A Proactive Framework for Thermal Safety
The most effective safety programs do not rely on human behavior alone. They are built on a formal hierarchy of controls that prioritizes systematic changes over individual actions. Think of this as building layers of protection, starting with the most effective.
H3: Layer 1: Elimination and Substitution
This is the highest and most effective level of control. Before dealing with a hot object, ask if it's truly necessary.
Can the process be redesigned to use a lower temperature? Can a hazardous hot substance be substituted with a safer, cooler alternative? Removing the hazard entirely is the only way to guarantee a burn cannot occur.
H3: Layer 2: Engineering Controls
If the hazard cannot be eliminated, the next step is to physically isolate people from it. These are passive safety features that do not require active user engagement.
Examples include installing heat shields on equipment, insulating pipes and hot surfaces, or using guardrails to prevent accidental contact. Proper ventilation systems to remove hot steam or vapor also fall into this category.
H3: Layer 3: Administrative Controls
This layer involves changing the way people work around the hazard. These are the rules, procedures, and training that govern behavior.
This includes developing Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs), providing mandatory safety training, and using clear warning signs and labels. Designating "hot zones" and ensuring clear communication protocols (e.g., calling out "hot pan coming through") are critical administrative controls.
H3: Layer 4: Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
PPE is the last line of defense and is used when the previous controls cannot eliminate all risk. It is a critical layer, but it is also the most prone to failure.
This includes items like heat-resistant gloves, flame-retardant aprons, safety glasses, and face shields. The key is selecting PPE specifically rated for the type and temperature of the hazard you are facing. A glove rated for a hot oven offers no protection from a splash of 400°F oil.
Understanding the Common Pitfalls
Recognizing common failure points is just as important as knowing the proper procedures. Complacency and misinformation create significant, often unseen, risks.
H3: The Fallacy of Over-reliance on PPE
Many injuries occur not because PPE was absent, but because it was the wrong type, worn improperly, or seen as an excuse for reckless behavior.
PPE can fail. A glove can have a small tear, or a hot liquid can run down the outside of the glove and become trapped against the skin. Always handle hot objects with the same respect, whether you are wearing PPE or not.
H3: Complacency in Familiar Environments
The risk of injury is often highest in tasks that are performed routinely. Familiarity can lead to a gradual erosion of safety protocols and a lack of situational awareness.
Always treat every interaction with a thermal hazard as if it were the first. Consciously run through a mental safety checklist before handling hot materials, even for tasks you have done a thousand times.
H3: Incorrect First Aid Response
Panic and myths often lead to actions that can make a burn injury worse.
Never apply ice, butter, creams, or oils to a fresh burn. Ice can cause further tissue damage, and greasy substances trap heat and increase the risk of infection. The only correct immediate action is to cool the burn with cool (not cold) running water.
Making the Right Choice for Your Environment
Your safety strategy must be tailored to your specific context. A universal approach is rarely the most effective.
- If your primary focus is an industrial or laboratory setting: Prioritize engineering controls and formal administrative procedures (SOPs), as these are the most reliable methods for systemic risk reduction.
- If your primary focus is a professional kitchen: Emphasize administrative controls like workflow design, clear communication ("hot behind!"), and consistent use of appropriate, task-specific PPE.
- If your primary focus is home or hobbyist safety: Concentrate on administrative controls like creating clear "no-go" zones for children and pets, and ensure you have the right PPE and first-aid knowledge ready before you begin.
A principled approach to safety transforms it from a checklist of rules into an instinctive culture of prevention.
Summary Table:
| Safety Layer | Key Actions | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Elimination/Substitution | Remove or replace the hazard | Use lower temperature processes, substitute safer materials |
| Engineering Controls | Isolate people from the hazard | Install heat shields, insulate pipes, use guardrails |
| Administrative Controls | Change work procedures | Develop SOPs, provide training, use clear signage |
| Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) | Final line of defense | Heat-resistant gloves, flame-retardant aprons, safety glasses |
Protect Your Team and Processes with KINTEK's Safety Solutions
Creating a truly safe environment requires more than just individual caution—it demands the right equipment and a systematic approach. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the reliable lab equipment and consumables that form the foundation of your thermal safety strategy. From heat-resistant tools to engineered safety systems, our products help you implement effective controls at every layer.
Let us help you build a culture of prevention. Contact our safety experts today to discuss your specific needs and discover how KINTEK can support your commitment to safety in the laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the most commonly used metals in a vacuum furnace's hot zone? Discover the Key to High-Purity Processing
- What is a vacuum furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Contamination-Free Thermal Processing
- What are the safety precautions in a heat treatment process? A Guide to Engineering, Administrative, and PPE Controls
- Is heat Cannot travel in a vacuum True or false? Discover How Heat Crosses the Void of Space
- What are the different types of brazing methods? Find the Right Heating Technique for Your Project














