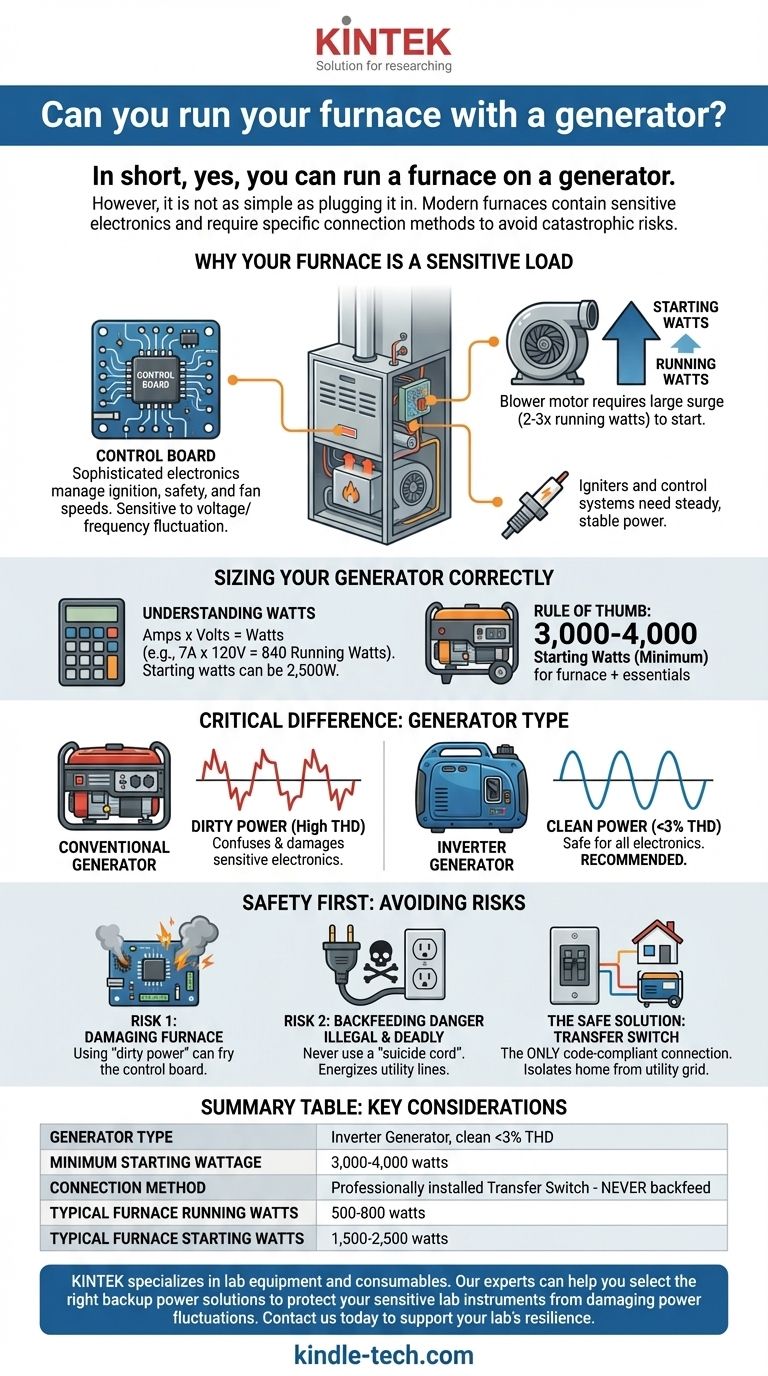
In short, yes, you can run a furnace on a generator. However, it is not as simple as plugging it in. Modern furnaces contain sensitive electronics that can be damaged by the wrong type of generator, and the connection must be made safely to avoid catastrophic risks.
The core issue is not just providing power, but providing the right kind of power. A furnace's sensitive control board requires "clean" electricity, and its motor demands a significant surge of energy to start, which a small or inadequate generator cannot provide safely.

Why Your Furnace is a Sensitive Electrical Load
To understand the requirements, you must first understand that a modern furnace is more like a computer than a simple appliance.
More Than Just a Motor
Today's high-efficiency furnaces are managed by a sophisticated electronic control board. This board handles ignition sequences, safety checks, and fan speeds. It is highly sensitive to fluctuations in electrical voltage and frequency.
The Critical Blower Motor
The largest power consumer in your furnace is the blower motor. This motor requires a large amount of power to start up—known as starting watts or surge watts—which can be two to three times higher than the power it needs to run continuously (running watts).
Igniters and Control Systems
In addition to the motor, the furnace's igniter and control circuits need a steady, stable power source to function correctly. Unstable power can cause ignition failures or lead to lockout modes, leaving you without heat.
Sizing Your Generator Correctly
Choosing a generator that is too small is a primary cause of failure.
Understanding Starting vs. Running Watts
Your generator must have a "Starting Wattage" rating high enough to handle the initial surge from the furnace's blower motor. If the generator can't meet this peak demand, it will either stall or trip its own breaker, and the furnace will not start.
How to Find Your Furnace's Wattage
Look for a data plate on the furnace itself. It will list the power requirements in Amps (A). To find the running watts, use the formula: Amps x Volts = Watts. In the US, household voltage is 120V.
For example, a furnace drawing 7 amps requires 840 running watts (7A x 120V). Its starting watts could be as high as 2,500W. A safe estimate for a typical residential furnace is 500-800 running watts and 1,500-2,500 starting watts.
A Rule of Thumb for Sizing
To safely power a furnace and have capacity for a few other small essentials like lights or a refrigerator, a generator with at least 3,000 to 4,000 starting watts is a realistic minimum.
The Critical Difference: Inverter vs. Conventional Generators
The type of generator you use is even more important than its size. This comes down to the quality of the electricity it produces.
"Dirty Power" from Conventional Generators
Standard, non-inverter generators often produce electricity with high Total Harmonic Distortion (THD). You can think of this as "dirty" or "jagged" power. This type of power can confuse and permanently damage the sensitive electronic control board in a modern furnace.
"Clean Power" from Inverter Generators
Inverter generators produce a pure sine wave, which is "clean" power identical to what you get from the utility grid (typically <3% THD). This stable output is safe for all electronics, including your furnace's control board. For any furnace made in the last 20 years, an inverter generator is the recommended choice.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Safety Risks
Connecting a generator improperly is dangerous and can cause more problems than the power outage itself.
Risk 1: Damaging Your Furnace
Using a conventional generator with high THD is a gamble. You might get away with it, but you risk frying the furnace's control board, which can lead to a repair bill of several hundred dollars or more.
Risk 2: The Danger of Backfeeding
Never use a "suicide cord"—a cord with two male ends—to plug your generator directly into a wall outlet. This illegal practice, known as backfeeding, energizes the utility lines outside your home and can electrocute and kill line workers trying to restore power.
The Safe Solution: A Transfer Switch
The only code-compliant and safe way to connect a generator to your furnace is with a transfer switch. This device is installed by an electrician and completely isolates your home's circuits from the utility grid before drawing power from the generator, making it impossible to backfeed the grid.
Extension Cords Are Not an Option
Since furnaces are hardwired directly into your home's electrical system, you cannot simply run an extension cord to them. The connection must be made at the circuit panel via a transfer switch.
Making the Right Choice for Your Situation
Your approach should be determined by your equipment and commitment to safety.
- If your primary focus is safely powering a modern furnace: Invest in an inverter generator with at least 4,000 starting watts and have a licensed electrician install a manual transfer switch for the furnace circuit.
- If you have a very old furnace (pre-1990s) with no electronic board: A conventional generator might work without causing damage, but an inverter is always the safer investment for overall flexibility.
- If your absolute priority is safety and code compliance: A transfer switch is the only acceptable connection method; never attempt to use an extension cord or backfeed your electrical panel.
Properly matching your generator and connection method to your furnace's needs transforms a potential crisis into a manageable inconvenience.
Summary Table:
| Key Consideration | Requirement / Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Generator Type | Inverter Generator (produces clean, <3% THD power) |
| Minimum Starting Wattage | 3,000 - 4,000 watts (to handle motor surge) |
| Connection Method | Professionally installed Transfer Switch (NEVER backfeed) |
| Typical Furnace Running Watts | 500 - 800 watts |
| Typical Furnace Starting Watts | 1,500 - 2,500 watts |
Ensure your laboratory's critical equipment, like furnaces and ovens, never loses power. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving the precise needs of laboratories. Our experts can help you select the right backup power solutions to protect your sensitive instruments from damaging power fluctuations. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your lab's resilience and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum furnace play in treating the C/SiC pre-coating? Optimize Your Cf/SiC Composites
- Why is a high vacuum annealing furnace required for irradiated material samples? Ensure Pure Defect Analysis
- Which furnace is used for annealing? Find the Right Equipment for Your Material's Needs
- What is the main advantage of a vacuum oven? Gentle Drying for Heat-Sensitive Materials
- Why is it necessary for a high-temperature furnace to maintain a constant 750°C for Sc1/3Zr2(PO4)3 DC electrolysis?
- Should I use flux when brazing aluminum? The Critical Role of Flux in Achieving a Strong Bond
- What are the two purposes of case hardening? Achieve Superior Wear and Impact Resistance
- What role does a high-performance vacuum furnace play in the reduction of Magnéli phase titanium oxide?



















