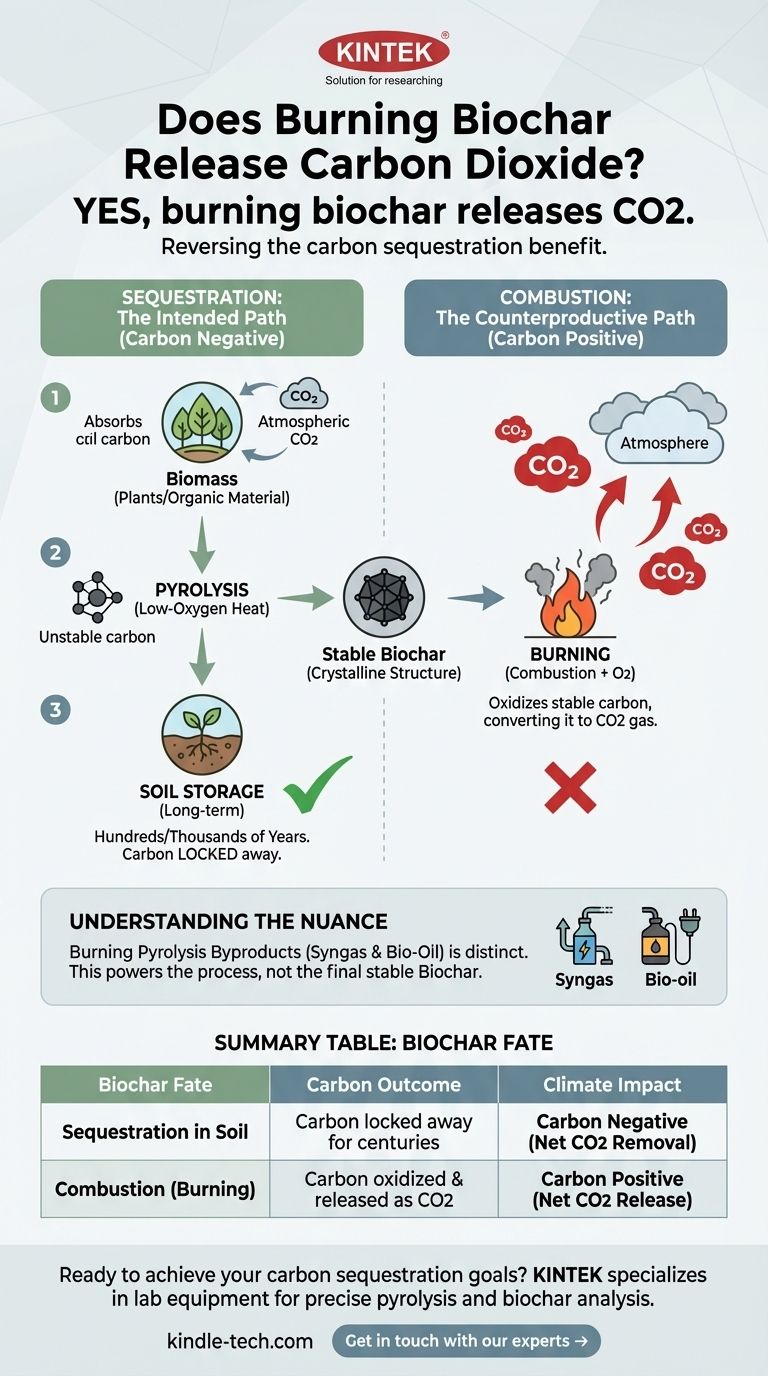
Yes, burning biochar releases carbon dioxide. The process of combustion oxidizes the stable carbon that makes up biochar, converting it back into CO2 gas and releasing it into the atmosphere. This action directly reverses the carbon sequestration benefit that biochar is created to provide.
The fundamental purpose of creating biochar for climate mitigation is to lock carbon into a stable, solid form for long-term storage in soil. Burning this biochar as a fuel source negates this entire purpose by releasing that stored carbon back into the atmosphere.

The Journey of Carbon: From Atmosphere to Biochar
To understand why burning biochar is counterproductive, we must first trace the path of the carbon itself. It's a journey from a temporary state in the air to a long-term state in the ground.
The Source: Carbon in Biomass
Plants and other organic materials (biomass) absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through photosynthesis. This carbon is a core component of their structure.
When this biomass dies and decomposes, microbes break it down, releasing the carbon back into the atmosphere, primarily as CO2 and methane. This is part of the fast carbon cycle.
The Process: Pyrolysis Stabilizes Carbon
Biochar is created through a process called pyrolysis. This involves heating biomass to high temperatures in a low-oxygen or oxygen-free environment.
Crucially, this is not burning. The lack of oxygen prevents combustion and instead transforms the unstable carbon in the biomass into a highly stable, crystalline-like structure. This resulting material is biochar, a form of elemental carbon that is highly resistant to decomposition.
The Purpose: Long-Term Storage in Soil
When this stable biochar is added to soil, it remains there for hundreds or even thousands of years. It resists the microbial breakdown that would have released its carbon back into the atmosphere.
This is how biochar contributes to carbon dioxide removal. It takes carbon from the fast, atmospheric cycle and locks it away in the slow, geological cycle, representing a net removal of CO2 from the atmosphere.
Combustion vs. Sequestration: Two Opposite Fates
The intended fate of biochar is sequestration. Burning it forces a completely different, and opposite, outcome.
What Happens When You Burn Biochar
Combustion is a chemical reaction that combines carbon with oxygen to release energy. When you burn biochar, you are forcefully oxidizing its stable carbon.
The carbon (C) in the biochar combines with oxygen (O2) from the air to create carbon dioxide (CO2), the same greenhouse gas the process was designed to capture.
Releasing Locked-Away Carbon
From a climate perspective, burning biochar is equivalent to digging up a fossil fuel and burning it. You are taking a stable, sequestered carbon source and converting it into an atmospheric greenhouse gas.
This action completely undoes the climate benefit achieved by its creation. The energy and resources used to produce the biochar are wasted, and the sequestered carbon is lost.
Understanding the Nuances
While burning the final biochar product is counterproductive, there are related processes involving combustion that can cause confusion.
Burning Pyrolysis Byproducts
The pyrolysis process that creates biochar also produces flammable gases (known as syngas) and bio-oil. These are often captured and burned on-site as a co-product.
This is a critical distinction. This energy is used to power the pyrolysis process itself, reducing or eliminating the need for external fossil fuels. You are burning the volatile byproducts, not the stable final product (the biochar).
The Overall Carbon Balance
A properly managed biochar system is carbon-negative. Even accounting for the energy used in production and the CO2 released from burning syngas, the amount of carbon permanently stored in the final biochar product results in a net removal of CO2 from the atmosphere.
This net benefit, however, is entirely dependent on the final biochar being added to the soil, not burned.
Making the Right Choice for the Goal
Your handling of biochar depends entirely on what you want to achieve.
- If your primary focus is carbon sequestration: The biochar must be incorporated into soil. This is the only way to achieve the long-term removal of carbon from the atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is renewable energy: Burning the original biomass directly or burning the syngas produced during pyrolysis are valid energy strategies, but the final biochar product should still be sequestered to maximize climate benefits.
The climate value of biochar lies in keeping its carbon locked away in the soil, not in releasing it through combustion.
Summary Table:
| Biochar Fate | Carbon Outcome | Climate Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Sequestration in Soil | Carbon is locked away for centuries | Carbon Negative (Net CO2 removal) |
| Combustion (Burning) | Carbon is oxidized and released as CO2 | Carbon Positive (Net CO2 release) |
Ready to achieve your carbon sequestration goals?
KINTEK specializes in the lab equipment and consumables needed for precise pyrolysis and biochar analysis. Whether you are a researcher developing new methods or a company scaling up production, our solutions help ensure the quality and stability of your biochar for effective, long-term carbon storage.
Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's role in climate solutions.
Get in touch with our experts →
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the two methods of control of corrosion? Master the Strategies for Metal Protection
- How does biochar improve water quality? An Engineered Solution for Contaminant Removal
- What is treatment through pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Valuable Resources with Thermal Decomposition
- What technical challenges do integrated membrane technologies address? Overcome Mass Transfer in Wastewater Treatment
- What apparatus is used for heating in a lab? A Guide to Choosing the Right Tool
- Is biomass electricity cheap? The True Cost of Dispatchable Renewable Power
- What is the temperature of activated carbon regeneration? Unlock the 1000°F Process for Reuse
- Can biomass be converted into fuel? Unlock Renewable Energy from Organic Matter



















