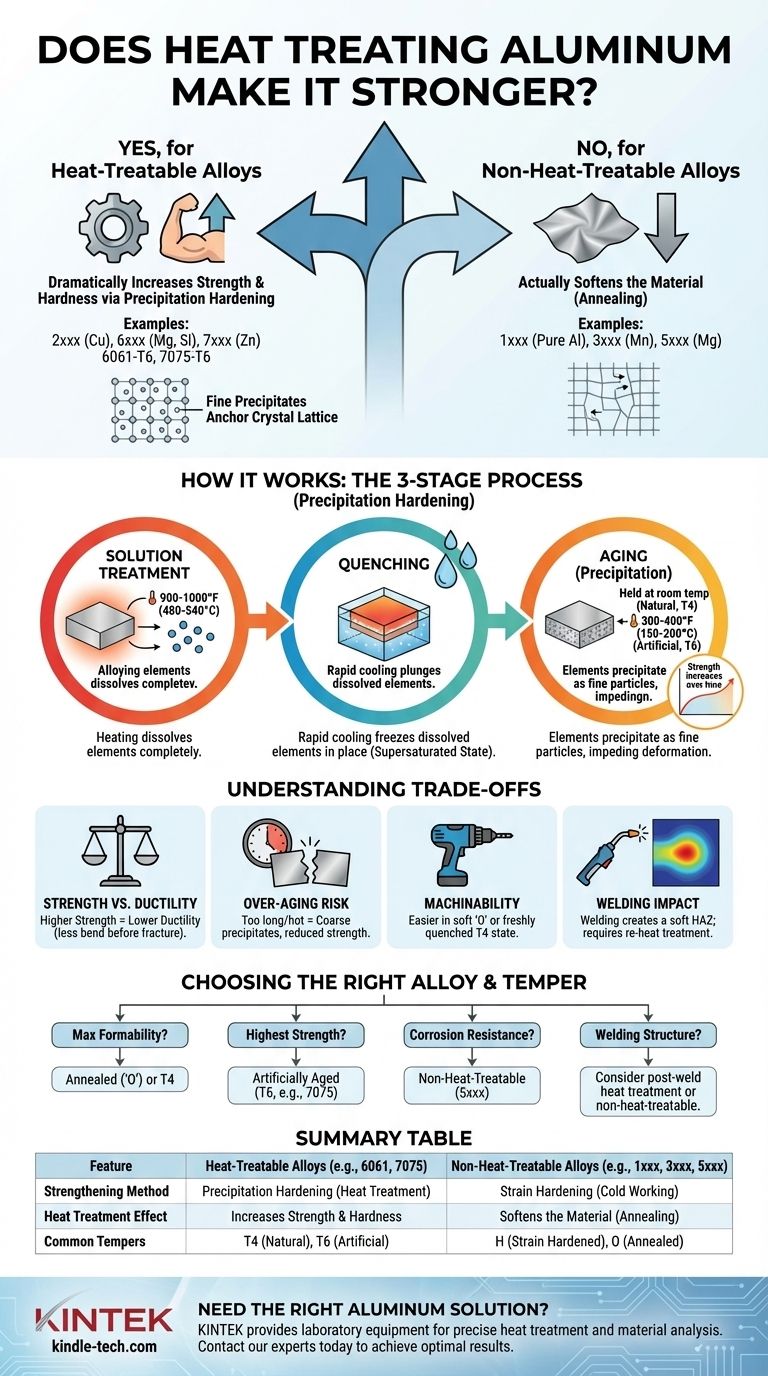
Yes, for specific types of aluminum, heat treatment is the primary method used to dramatically increase their strength and hardness. However, this process only works on "heat-treatable" alloys; applying it to "non-heat-treatable" alloys will actually soften them. The strengthening occurs through a precise, multi-stage process called precipitation hardening.
The core principle is not about simply heating the metal. It's about using heat to dissolve alloying elements into the aluminum's structure, trapping them there with rapid cooling, and then allowing them to form microscopic strengthening particles in a controlled manner.

How Heat Treatment Fundamentally Changes Aluminum
The strength of an aluminum alloy depends on how easily its internal crystal structure can be deformed. Heat treatment introduces microscopic obstacles within this structure, making it much harder for the crystals to slip past one another.
The Concept of Precipitation Hardening
Think of dissolving sugar in hot tea. When the tea is hot, you can dissolve a large amount of sugar. If you cool it down rapidly, the sugar stays dissolved for a time. This is a "supersaturated solution." Over time, tiny sugar crystals will begin to form, or precipitate, out of the liquid.
Precipitation hardening in aluminum works on a similar principle, but in a solid state. Alloying elements like copper, magnesium, or zinc act as the "sugar," and the aluminum is the "tea."
The Three Key Stages
The process, often referred to as a "temper," involves a strict sequence of heating and cooling cycles.
- Solution Treatment: The alloy is heated to a high temperature (around 900-1000°F or 480-540°C) and held there. This allows the alloying elements to dissolve completely into the aluminum, creating a uniform solid solution.
- Quenching: Immediately after solution treatment, the metal is rapidly cooled, typically in water. This sudden drop in temperature freezes the dissolved elements in place, creating a "supersaturated" and unstable state. The material is relatively soft at this point.
- Aging (Precipitation): In the final stage, the trapped alloying elements begin to precipitate out of the solution, forming extremely fine, hard particles called precipitates. These particles anchor the metal's crystal lattice, impeding deformation and dramatically increasing its strength and hardness.
Natural vs. Artificial Aging
Aging can occur in two ways, resulting in different temper designations.
- Natural Aging (T4 Temper): This happens when the quenched material is left at room temperature for several days. The precipitates form slowly, resulting in a moderately strong but highly ductile material.
- Artificial Aging (T6 Temper): To achieve maximum strength, the material is placed in a low-temperature oven (around 300-400°F or 150-200°C) for several hours. This accelerates the precipitation process, creating a denser distribution of particles and resulting in significantly higher strength and hardness.
Not All Aluminum is Created Equal
The ability to be strengthened by heat is determined entirely by the alloy's chemical composition. Aluminum alloys are separated into two distinct families based on this property.
Heat-Treatable Alloys
These alloys contain elements like copper (2xxx series), magnesium and silicon (6xxx series), and zinc (7xxx series), which have changing solubility in aluminum as the temperature changes.
Common examples include 6061-T6, a versatile and widely used alloy, and 7075-T6, which offers one of the highest strength-to-weight ratios and is common in aerospace applications.
Non-Heat-Treatable Alloys
These alloys gain their strength through a different mechanism called strain hardening (or work hardening), which involves physically deforming the metal by rolling or drawing it.
This family includes pure aluminum (1xxx series), manganese alloys (3xxx series), and magnesium alloys (5xxx series). Heating these alloys removes the effects of strain hardening, a process known as annealing, which makes them softer, not stronger.
Understanding the Trade-offs of Heat Treatment
While heat treatment significantly boosts strength, it comes with important considerations that impact design and fabrication.
Strength vs. Ductility
There is an inverse relationship between strength and ductility. As an alloy is aged to a higher strength level (like T6), it becomes less ductile, meaning it will stretch or bend less before it fractures.
The Risk of Over-Aging
If the material is held at the aging temperature for too long or at too high a temperature, the fine precipitates will coarsen and grow too large. This "over-aged" condition actually reduces the material's strength and hardness.
Machinability and Formability
Aluminum is significantly easier to machine or form in its soft, annealed state ('O' temper) or its freshly quenched state (before aging). Many complex parts are formed in a T4 condition and then artificially aged to T6 for final strength.
The Impact of Welding
Welding a heat-treated part introduces intense, localized heat. This over-ages or anneals the material in the heat-affected zone (HAZ) next to the weld, creating a soft spot that can be a critical point of failure. Restoring full strength requires a complete re-heat-treatment of the entire part.
Choosing the Right State for Your Application
Selecting the correct alloy and temper is critical to meeting the performance requirements of your project.
- If your primary focus is maximum formability: Use the material in its soft, annealed ('O') state or a freshly quenched T4 temper.
- If your primary focus is the highest possible strength and hardness: Specify a heat-treatable alloy in a fully artificially aged temper, such as 6061-T6 or 7075-T6.
- If your primary focus is corrosion resistance and moderate strength: A non-heat-treatable alloy from the 5xxx series is often the superior choice, especially for marine environments.
- If you are welding a structural component: Understand that welding will compromise the strength of a heat-treated alloy unless the entire assembly can be heat-treated again after fabrication.
Ultimately, understanding the metallurgy behind heat treatment empowers you to select the right material and ensure it performs as expected.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Heat-Treatable Alloys (e.g., 6061, 7075) | Non-Heat-Treatable Alloys (e.g., 1xxx, 3xxx, 5xxx) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Strengthening Method | Precipitation Hardening (Heat Treatment) | Strain Hardening (Cold Working) |
| Effect of Heat Treatment | Increases Strength & Hardness | Softens the Material (Annealing) |
| Common Tempers | T4 (Naturally Aged), T6 (Artificially Aged) | H (Strain Hardened), O (Annealed) |
| Key Alloying Elements | Copper, Magnesium, Silicon, Zinc | Manganese, Magnesium |
Need the Right Aluminum Alloy for Your Project?
Selecting the correct aluminum temper is critical for performance, whether you require maximum strength (T6), high formability (T4/O), or superior corrosion resistance. KINTEK specializes in providing the laboratory equipment and consumables needed for precise heat treatment processes and material analysis.
Let us help you achieve optimal results. Our expertise ensures you get the right materials and support for your specific application, from aerospace components to custom fabrications.
Contact our experts today to discuss your aluminum needs and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of the wiped film evaporator? Purify Heat-Sensitive Compounds Efficiently
- How are diamonds used for industrial purposes? Unlock Extreme Performance with Diamond Tools
- What are some challenges of using waste biomass for energy? Navigating Logistics, Cost, and Efficiency Hurdles
- What is the basic instrument for IR spectrometry? FT-IR Spectrometers for Modern Chemical Analysis
- What is the principle of XRF thickness measurement? Unlock Non-Destructive Coating Analysis
- How do magnets enhance the sputtering rate in magnetron sputtering process and improve the thin film quality? Boost Deposition Speed & Film Quality
- What is the thermal property of graphite? Mastering Extreme Heat Management
- How much temperature can graphite withstand? Unlock its true potential up to 3000°C



















