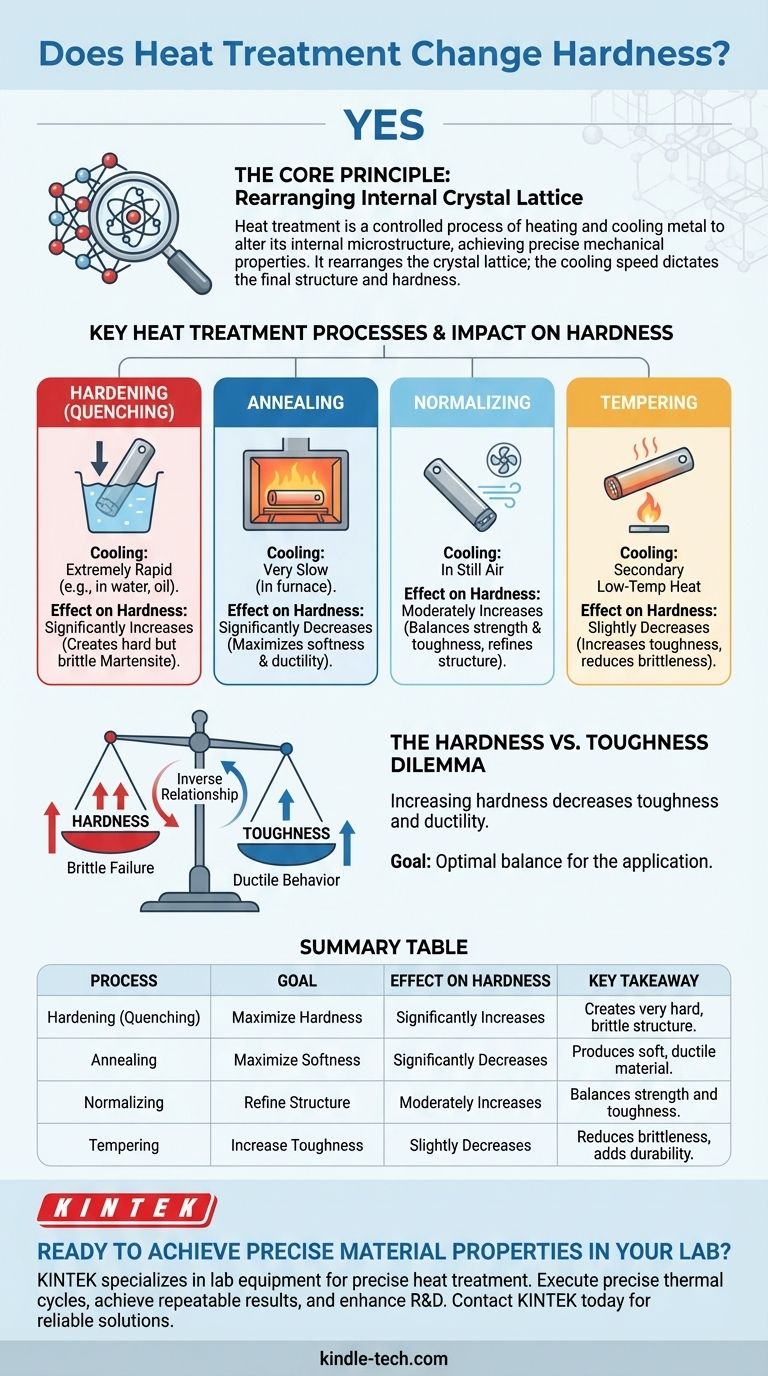
Yes, heat treatment is one of the most powerful methods for fundamentally changing the hardness of a material. It is a highly controlled process of heating and cooling a metal or alloy in its solid state to intentionally alter its internal microscopic structure. This manipulation allows engineers to achieve a precise set of mechanical properties, with hardness being a primary target.
The core principle to understand is that heat treatment doesn't just make a material hot; it rearranges its internal crystal lattice. The speed at which it's cooled from a high temperature dictates the final crystal structure, which in turn directly determines its hardness, toughness, and ductility.

The Mechanism: How Heat Alters Microstructure
To understand how heat treatment works, you must first understand that metals have a defined crystal structure. The goal of heat treatment is to manipulate this structure to achieve desired properties.
The Role of Crystal Lattices
Metals are composed of atoms arranged in a repeating, orderly pattern called a crystal lattice. The specific arrangement of this lattice and the size of the crystal "grains" dictate the material's mechanical properties, including its hardness.
The High-Temperature Transformation
For many steels, heating them above a critical temperature (a process called austenitizing) causes the crystal structure to change into a phase called austenite. In this state, carbon atoms—a key alloying element in steel—can dissolve evenly within the iron lattice, much like salt dissolves in water.
Cooling Rate: The Decisive Factor
The critical step is the cooling process. The rate of cooling from the austenite phase locks in a specific crystal structure, and this is what determines the final hardness.
Key Heat Treatment Processes and Their Impact
Different combinations of heating temperatures, soak times, and cooling rates result in distinct processes, each with a different effect on hardness.
Hardening (Quenching): Maximizing Hardness
To make a steel as hard as possible, it is cooled extremely rapidly from its austenitic state. This process, known as quenching, is often done by plunging the hot metal into water, oil, or brine.
This rapid cooling traps the dissolved carbon atoms within the iron lattice, forcing the formation of a new, highly strained crystal structure called martensite. Martensite is extremely hard and very brittle.
Annealing: Maximizing Softness
Annealing is the opposite of hardening. After heating, the material is cooled as slowly as possible, often by leaving it inside a turned-off furnace.
This slow cooling gives the atoms ample time to rearrange into a soft, ductile, and stress-free crystal structure. Annealing is typically used to make a material easier to machine, stamp, or form.
Normalizing: Refining and Balancing
Normalizing involves heating the material and then letting it cool in still air. The cooling rate is faster than annealing but much slower than quenching.
This process creates a more uniform and fine-grained crystal structure, resulting in a material that is stronger and harder than an annealed one but more ductile than a quenched one. It provides a good balance of properties.
Tempering: Gaining Toughness by Reducing Hardness
A material that has been hardened via quenching is often too brittle for practical use. Tempering is a secondary, low-temperature heat treatment performed after quenching.
It slightly reduces the extreme hardness of martensite but dramatically increases the material's toughness, making it less susceptible to shattering under impact. The higher the tempering temperature, the more hardness is sacrificed for an increase in toughness.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Hardness vs. Toughness Dilemma
It is impossible to discuss hardness without also considering toughness. For most engineering applications, the goal is not maximum hardness but an optimal balance of properties.
The Inverse Relationship
In nearly all materials, hardness and toughness are inversely related. As you increase a material's hardness, you almost always decrease its toughness and ductility. A harder material is more resistant to scratching and wear, but it's also more likely to crack or shatter.
Why Brittleness Is a Critical Failure Mode
Think of the difference between a ceramic plate and a steel plate. The ceramic is very hard and scratch-resistant, but it shatters if you drop it (brittle failure). The steel plate may dent, but it won't break (ductile behavior). In a critical component like a vehicle axle, a brittle fracture would be catastrophic.
The Goal: Optimal Properties for the Application
The choice of heat treatment is always driven by the end-use of the component. A cutting tool needs extreme hardness to hold an edge, while a structural beam needs toughness to absorb energy without fracturing.
Choosing the Right Treatment for Your Application
Your final choice depends entirely on the performance you require from the component.
- If your primary focus is maximum wear and abrasion resistance (e.g., cutting tools, bearings): A quench-and-temper process is necessary to achieve high hardness and then relieve just enough brittleness to prevent chipping.
- If your primary focus is maximum machinability or formability (e.g., preparing a raw block of steel for CNC milling): Full annealing is the correct choice to make the material as soft and stress-free as possible.
- If your primary focus is a reliable balance of strength and toughness for a structural part (e.g., bolts, shafts, gears): Normalizing or a carefully controlled quench-and-temper process will provide the required performance without excessive brittleness.
By understanding these principles, you can select the precise heat treatment to engineer a material's properties for any required performance.
Summary Table:
| Process | Goal | Effect on Hardness | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardening (Quenching) | Maximize Hardness | Significantly Increases | Creates a very hard but brittle structure (martensite). |
| Annealing | Maximize Softness | Significantly Decreases | Produces a soft, ductile material for easy machining. |
| Normalizing | Refine Structure | Moderately Increases | Balances strength and toughness by cooling in air. |
| Tempering | Increase Toughness | Slightly Decreases | Reduces brittleness in hardened steel, essential for durability. |
Ready to Achieve Precise Material Properties in Your Lab?
Heat treatment is a science that requires precision equipment to control heating and cooling rates accurately. The right furnace is critical to achieving consistent, reliable results for your specific materials and applications.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing the reliable heat treatment solutions your laboratory needs. Whether you are developing new alloys, testing material performance, or processing components, our range of furnaces and expert support ensures you can:
- Execute precise thermal cycles for hardening, annealing, normalizing, and tempering.
- Achieve repeatable results with accurate temperature control and uniform heating.
- Enhance your R&D and quality control processes with robust and dependable equipment.
Let's discuss your heat treatment requirements. Contact KINTEK today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory's challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the three main heat treatments? Mastering Annealing, Hardening & Tempering
- Why do you heat treat in a vacuum? Achieve Perfect Surface Finish and Material Integrity
- How does heat treatment process work? Tailor Material Properties for Your Application
- What are the different types of heat treatment process for steel? Tailor Strength, Hardness & Toughness
- What is the process of vacuum quenching? Achieve Superior Hardness with a Pristine Surface Finish



















