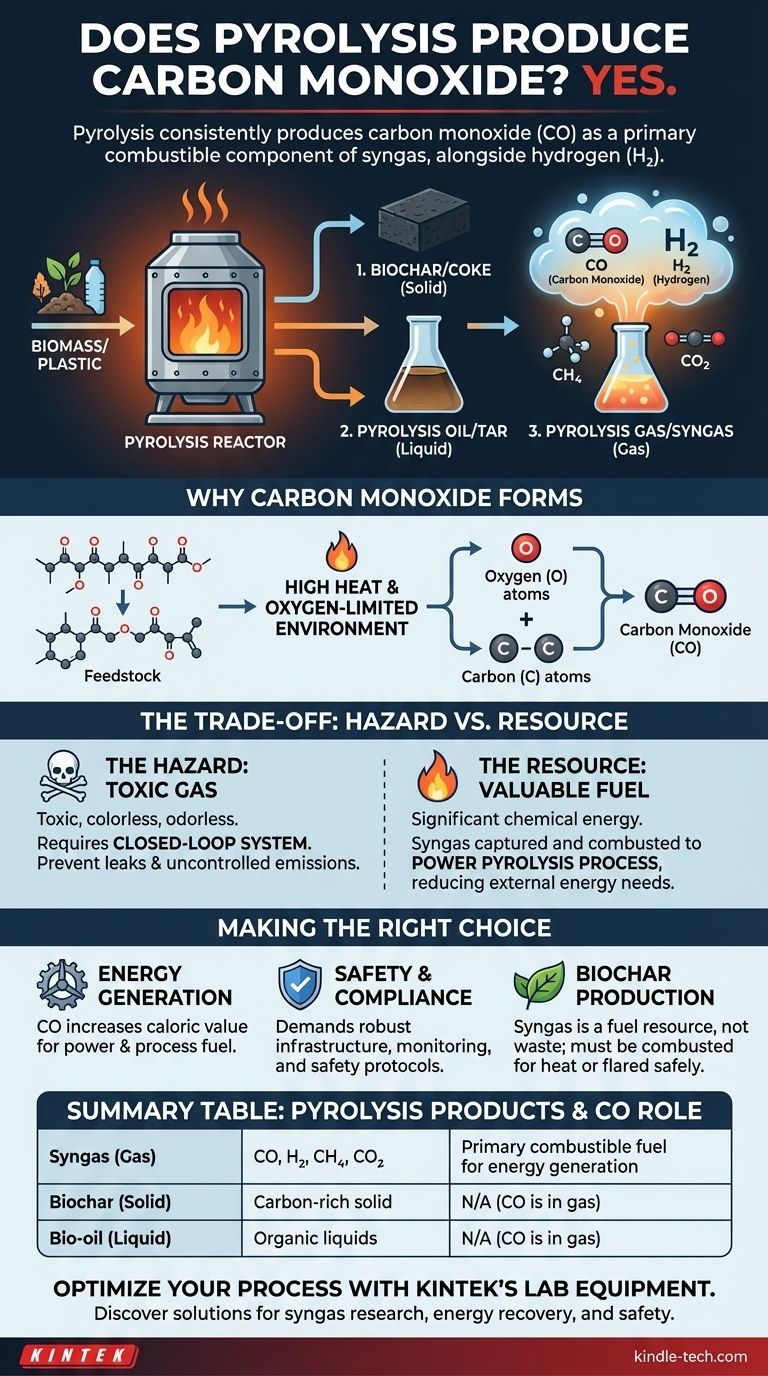
Yes, pyrolysis consistently produces carbon monoxide (CO). While often described simply as "pyrolysis gas" or "syngas," the gaseous output from this process is a mixture, and carbon monoxide is one of its primary combustible components, alongside hydrogen (H2). The exact amount varies, but its presence is a fundamental aspect of the chemical transformation.
The key takeaway is that carbon monoxide is not an accidental byproduct of pyrolysis, but an inherent and valuable component of the syngas produced. Recognizing this dual nature—as both a useful fuel and a potential hazard—is critical for designing and operating any pyrolysis system safely and efficiently.

What is Pyrolysis Gas?
To understand why carbon monoxide is produced, we must first understand the outputs of the pyrolysis process itself.
The Three States of Matter
Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of materials at high temperatures in an oxygen-limited environment. This process breaks down complex organic materials, like biomass or plastic, into three main product streams:
- Solid: A carbon-rich solid known as biochar or coke.
- Liquid: A complex liquid mixture known as pyrolysis oil (bio-oil) or tar.
- Gas: A non-condensable gas mixture often called pyrolysis gas or syngas.
Deconstructing Syngas
The term "pyrolysis gas" is a general label for a mixture of different gases. A more precise term is synthesis gas, or syngas, which highlights its potential for use in energy generation or chemical synthesis.
The primary combustible components of this syngas are carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen (H2). It also contains other gases like methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2).
Why Carbon Monoxide Forms
Pyrolysis occurs in the near absence of external oxygen, but the feedstock itself (e.g., wood, agricultural waste) contains oxygen atoms within its molecular structure.
When the high heat of the pyrolysis reactor breaks down these large organic molecules, the trapped oxygen atoms are released. They then combine with available carbon atoms to form the stable gas molecule of carbon monoxide (CO).
Understanding the Trade-offs: Hazard vs. Resource
The presence of carbon monoxide in pyrolysis gas presents a classic engineering trade-off. It must be managed as both a significant safety risk and a valuable energy resource.
The Hazard: A Toxic Gas
Carbon monoxide is a well-documented toxic gas, posing a serious risk to human health. It is colorless, odorless, and can be lethal if inhaled.
Therefore, any industrial pyrolysis operation must be engineered as a closed-loop system. This ensures that the gas produced is properly contained, transported, and either used or safely flared, preventing any leaks into the atmosphere or workspaces.
The Resource: A Valuable Fuel
The very thing that makes CO dangerous in the open—its ability to react—also makes it a valuable fuel. The carbon monoxide within syngas is a significant source of chemical energy.
Most modern pyrolysis plants are designed to be self-sustaining by capturing this syngas. The gas is looped back to the heating chamber and combusted to generate the heat required to fuel the ongoing pyrolysis reaction, dramatically reducing the need for external energy inputs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding that CO is an integral part of pyrolysis gas allows you to design a system that aligns with your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is energy generation: The production of carbon monoxide is a direct benefit, as it contributes significantly to the caloric value of the syngas used to power turbines or fuel the process.
- If your primary focus is safety and environmental compliance: The presence of CO demands robust gas handling infrastructure, real-time monitoring, and clear safety protocols to prevent toxic exposure and uncontrolled emissions.
- If your primary focus is producing biochar: The syngas, rich in CO, is not a waste product but the fuel that makes your process energy-efficient. It must be managed by combusting it for heat or safely flaring it.
Ultimately, mastering the pyrolysis process means mastering the control and utilization of all its products, especially the valuable and hazardous gas it creates.
Summary Table:
| Pyrolysis Product | Key Components | Role of Carbon Monoxide (CO) |
|---|---|---|
| Syngas (Gas) | CO, H₂, CH₄, CO₂ | Primary combustible fuel for energy generation |
| Biochar (Solid) | Carbon-rich solid | N/A (CO is part of gas phase) |
| Bio-oil (Liquid) | Organic liquids | N/A (CO is part of gas phase) |
Optimize your pyrolysis process with KINTEK's reliable lab equipment and consumables. Whether you're researching syngas composition, scaling up energy recovery, or ensuring workplace safety, our specialized solutions help you manage carbon monoxide effectively and maximize efficiency. Contact our experts today to discuss your laboratory needs and discover how KINTEK can support your pyrolysis projects with precision and safety.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
People Also Ask
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy



















