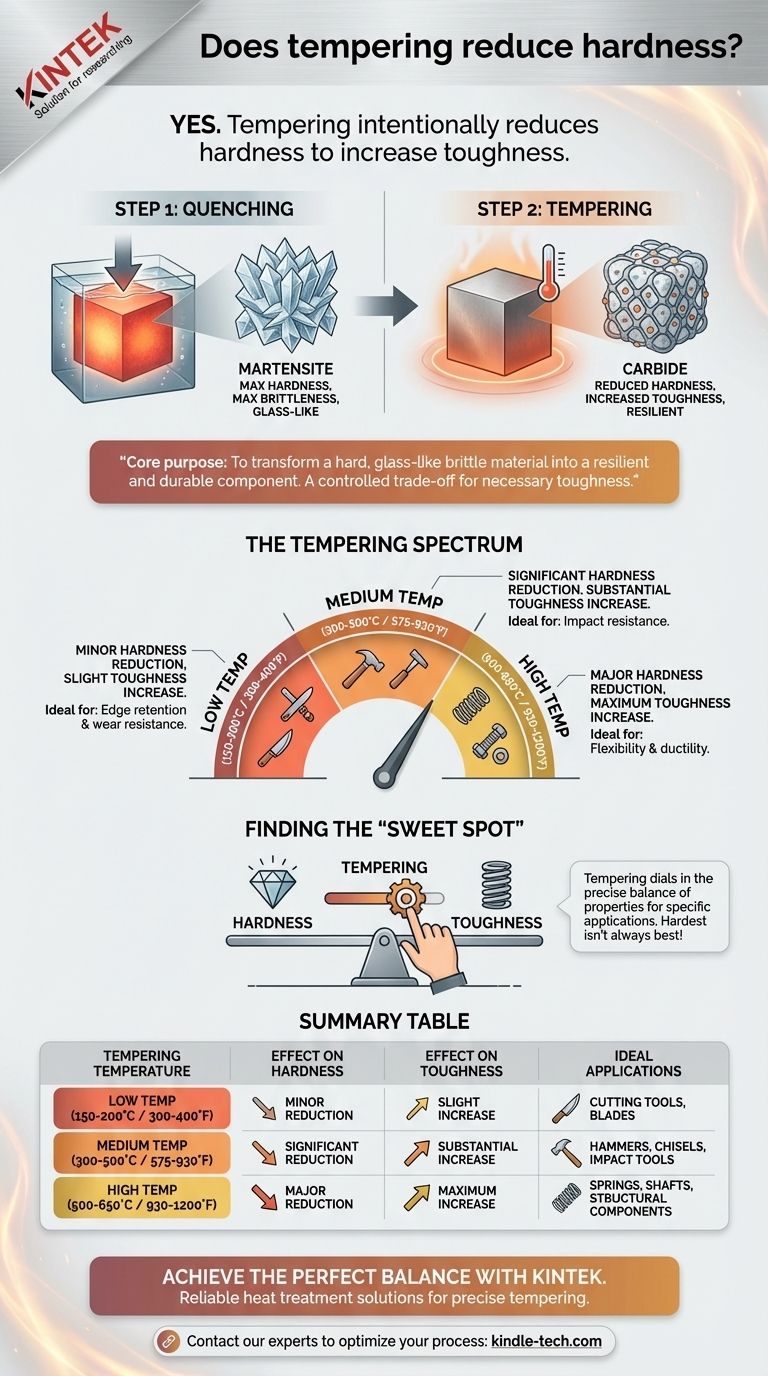
Yes, tempering intentionally reduces the hardness of a hardened material. This process is a critical step in heat treatment, performed after the initial hardening (quenching) phase. The reduction in hardness is not a flaw but a deliberate trade-off to decrease brittleness and significantly increase the material's toughness, making it suitable for practical applications.
The core purpose of tempering is not simply to lose hardness, but to transform a hard, glass-like brittle material into a resilient and durable component. It is a controlled process of trading a small amount of peak hardness for a large, necessary gain in toughness.

The Role of Tempering in Heat Treatment
To understand tempering, you must first understand the process it follows: quenching. Heat treatment is a two-step process designed to achieve a specific balance of mechanical properties.
Step 1: Quenching for Maximum Hardness
When steel is heated to a high temperature (austenitizing), its carbon atoms dissolve into the iron crystal structure. If the steel is then cooled very rapidly, or quenched, these carbon atoms are trapped.
This creates a new, highly strained crystal structure called martensite. Martensite is extremely hard and wear-resistant, but it is also incredibly brittle and filled with internal stresses. This "as-quenched" state is often too fragile for most real-world uses.
Step 2: Tempering for Functional Toughness
Tempering is the process of reheating the quenched, hardened steel to a specific temperature below its critical point, holding it there for a period, and then letting it cool.
This reheating gives the trapped carbon atoms enough energy to move and precipitate out of the martensite structure, forming tiny particles of carbides. This process relieves the internal stresses, which reduces hardness and brittleness while dramatically increasing the material's toughness (its ability to absorb energy and deform without fracturing).
The Temperature-Hardness-Toughness Relationship
The final properties of the steel are determined almost entirely by the temperature used during the tempering cycle. The relationship is predictable and allows for precise control.
The Tempering Spectrum
Think of tempering temperature as a control dial. A lower temperature results in a smaller change, while a higher temperature results in a more dramatic transformation.
-
Low-Temperature Tempering (approx. 150-200°C / 300-400°F): This relieves stress with only a minor reduction in hardness. The result is a material that is still very hard and wear-resistant but is no longer dangerously brittle. This is ideal for cutting tools and blades.
-
Medium-Temperature Tempering (approx. 300-500°C / 575-930°F): This causes a more significant drop in hardness but provides a substantial increase in toughness and ductility. This is used for tools that must withstand impact, like hammers or chisels.
-
High-Temperature Tempering (approx. 500-650°C / 930-1200°F): This results in the lowest hardness but the greatest toughness and ductility. This is necessary for components that must flex and absorb major shocks, such as vehicle springs and structural steel.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Why "Hardest" Isn't "Best"
The central challenge in materials engineering is balancing competing properties. No single property is universally desirable, and this is especially true for hardness.
The Problem with As-Quenched Steel
A piece of steel directly after quenching can be compared to a piece of glass. It has exceptionally high compressive strength and can resist scratching (high hardness), but a sharp impact will cause it to shatter.
An un-tempered blade might hold a razor edge, but that edge would chip and break the moment it encountered any resistance. The material lacks the toughness to be useful.
Finding the Application's "Sweet Spot"
Tempering is the tool used to move away from the "glass-like" state and dial in the precise balance of properties an application demands.
An axe needs to sacrifice some edge retention (hardness) to gain the impact resistance (toughness) needed to chop wood without shattering. A spring needs to sacrifice nearly all its peak hardness to gain the flexibility required to compress and expand millions of times.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The tempering temperature you choose is a direct reflection of the component's intended function. Your goal is to achieve the optimal balance of properties for that specific task.
- If your primary focus is edge retention and wear resistance (e.g., knives, razors): Use a lower tempering temperature to retain maximum hardness while relieving just enough internal stress to prevent the edge from being brittle.
- If your primary focus is impact resistance (e.g., axes, demolition tools): Use a medium tempering temperature to trade more hardness for the significant toughness needed to withstand repeated, forceful blows.
- If your primary focus is flexibility and ductility (e.g., springs, fasteners, shafts): Use a higher tempering temperature to achieve maximum toughness and the ability to deform without fracturing, accepting a much lower final hardness.
Ultimately, tempering is what transforms steel from a simple, brittle material into a versatile and predictable engineering tool.
Summary Table:
| Tempering Temperature | Effect on Hardness | Effect on Toughness | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low (150-200°C / 300-400°F) | Minor Reduction | Slight Increase | Cutting Tools, Blades |
| Medium (300-500°C / 575-930°F) | Significant Reduction | Substantial Increase | Hammers, Chisels, Impact Tools |
| High (500-650°C / 930-1200°F) | Major Reduction | Maximum Increase | Springs, Shafts, Structural Components |
Achieve the Perfect Balance of Hardness and Toughness for Your Components
Tempering is a precise science that transforms brittle, hardened steel into a resilient and durable material. The right equipment is essential for achieving consistent, high-quality results.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable heat treatment solutions for laboratories and manufacturers. Our furnaces and ovens are designed to deliver the precise temperature control required for perfect tempering cycles, ensuring your materials meet exact specifications for hardness, toughness, and performance.
Ready to optimize your heat treatment process? Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's equipment can help you achieve superior material properties for your specific applications.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control
- What is quartz tube heating? Achieve Instant, Targeted Heat with Infrared Radiation
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What is the temperature of a quartz tube furnace? Master the Limits for Safe, High-Temp Operation



















