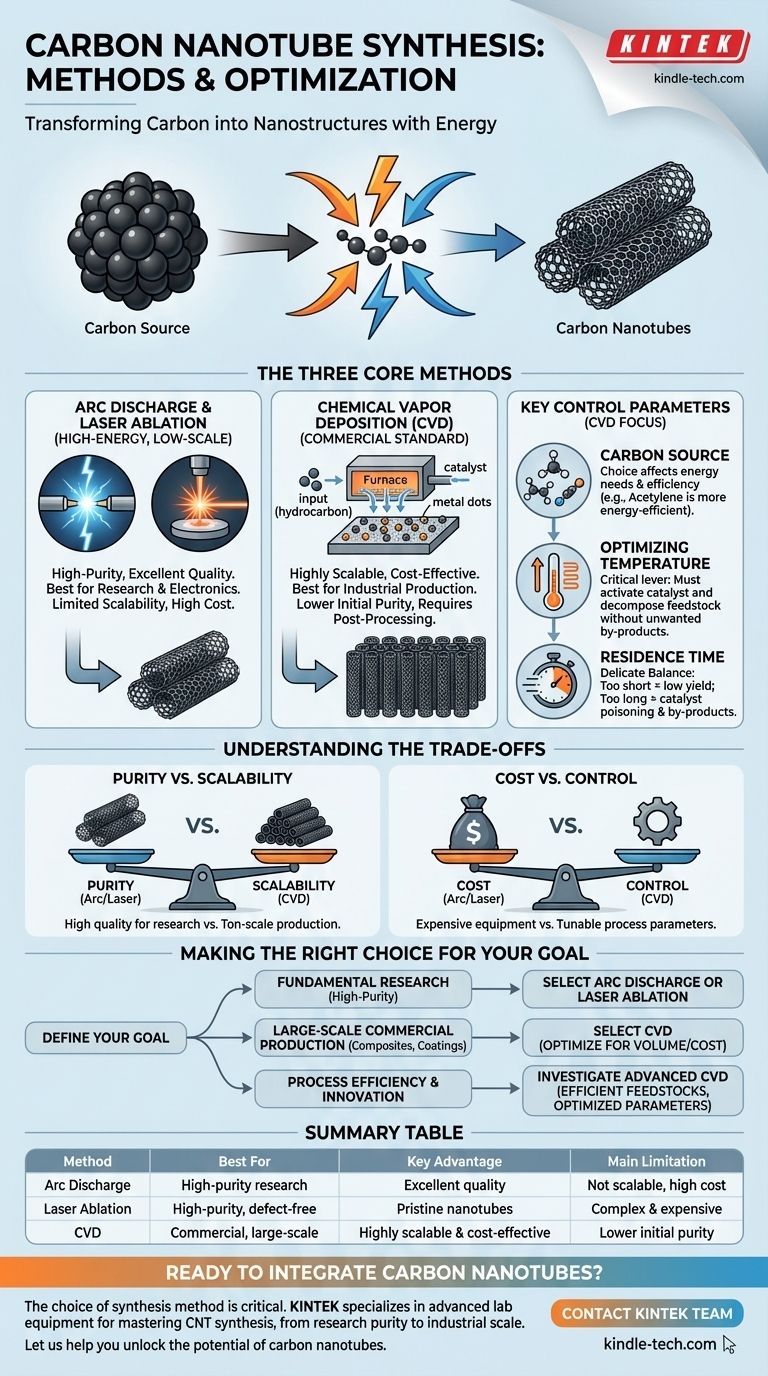
At its core, carbon nanotube (CNT) synthesis involves transforming a carbon-containing source into a cylindrical nanostructure using energy. The three principal methods are arc discharge, laser ablation, and chemical vapor deposition (CVD), with CVD being the dominant process for nearly all commercial applications due to its scalability and control.
The challenge is not simply making carbon nanotubes, but precisely controlling their growth to achieve the desired structure, purity, and volume for a specific application. The choice of synthesis method and its operating parameters is a strategic trade-off between quality, cost, and scale.

The Three Core Synthesis Methods
While several techniques exist, they fall into three main categories, each with distinct characteristics. The first two are high-energy methods best suited for small, high-purity batches, while the third is the workhorse of industrial production.
Arc Discharge
This was one of the earliest methods used. It involves creating a high-temperature electric arc (plasma) between two carbon electrodes in the presence of an inert gas. The intense heat vaporizes the carbon, which then condenses and self-assembles into nanotubes.
This method can produce high-quality, structurally-sound CNTs, but it is difficult to control and does not scale efficiently for large-volume production.
Laser Ablation
Similar in principle to arc discharge, this method uses a high-power laser to vaporize a graphite target that is often mixed with a metal catalyst. The resulting carbon vapor cools and condenses to form high-purity CNTs.
Like arc discharge, laser ablation excels at producing pristine nanotubes for research but is too complex and expensive for most commercial-scale needs.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): The Commercial Standard
CVD is the most widely used method for producing CNTs in bulk. The process involves flowing a hydrocarbon gas (a carbon feedstock) over a substrate coated with catalyst particles at elevated temperatures.
The catalysts, typically metals like iron, nickel, or cobalt, break down the hydrocarbon molecules. The carbon atoms then diffuse and precipitate around the catalyst particles, "growing" the nanotube structure. This method's scalability and relative cost-effectiveness make it the go-to for industrial applications.
Mastering the Process: Key Control Parameters
Successful synthesis, particularly with CVD, depends on fine-tuning several critical variables. These parameters directly influence the quality, length, diameter, and growth rate of the final product.
The Role of the Carbon Source
The choice of hydrocarbon gas is crucial. Gases like methane and ethylene require significant thermal energy to break their chemical bonds before they can contribute to CNT growth.
In contrast, acetylene can act as a direct precursor without needing this extra thermal conversion step. This makes it a more energy-efficient feedstock for CNT synthesis.
Optimizing Temperature
Temperature is a critical lever in the CVD process. It must be high enough to activate the catalyst and decompose the carbon feedstock but controlled to prevent the formation of unwanted by-products like amorphous carbon.
The Criticality of Residence Time
Residence time is the duration the carbon feedstock spends in the hot reaction zone. This is a delicate balance.
If the time is too short, the carbon source doesn't have enough opportunity to accumulate and grow nanotubes, leading to low yield and wasted material.
If the time is too long, the feedstock can be depleted, and by-products can accumulate on the catalyst, poisoning it and halting further growth.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a synthesis method is fundamentally an exercise in managing trade-offs. There is no single "best" method; there is only the best method for a specific goal.
Purity vs. Scalability
The core conflict in CNT production is between purity and scale. Arc discharge and laser ablation produce exceptionally high-quality nanotubes with few defects, which is ideal for electronics or fundamental research.
However, these methods are not scalable. CVD is the only process that can produce CNTs by the ton, but this comes at the cost of purity, as residual catalyst particles often need to be removed in a post-processing step.
Cost vs. Control
The high energy requirements and complex equipment for laser ablation and arc discharge make them expensive.
CVD offers a much lower cost-per-gram, especially at scale. Furthermore, the parameters of a CVD process can be more easily manipulated to tune the final CNT properties, offering a degree of control that is difficult to achieve with other methods.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your end goal dictates the ideal synthesis strategy. The method and parameters must be selected to align with the required performance and economic constraints of your application.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research or high-purity samples: Arc discharge or laser ablation are your best options, providing superior structural quality despite their low yield and high cost.
- If your primary focus is large-scale commercial production for composites or coatings: CVD is the only commercially viable pathway, offering the necessary volume and cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency and innovation: Investigate advanced CVD techniques using more efficient feedstocks (like acetylene) or sustainable sources (like captured CO2) while meticulously optimizing residence time and temperature.
Understanding these synthesis principles is the key to unlocking the full potential of carbon nanotubes in your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Method | Best For | Key Advantage | Main Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arc Discharge | High-purity research samples | Excellent structural quality | Not scalable, high cost |
| Laser Ablation | High-purity, defect-free CNTs | Produces pristine nanotubes | Complex and expensive process |
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Commercial, large-scale production | Highly scalable and cost-effective | Lower initial purity (requires post-processing) |
Ready to integrate carbon nanotubes into your research or production line?
The choice of synthesis method is critical to achieving your goals for purity, volume, and cost. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables necessary for mastering CNT synthesis, from research-scale purity to industrial-scale production.
Our experts can help you select the right tools to optimize your process parameters, whether you're working with CVD reactors, catalyst materials, or gas delivery systems. Let us help you unlock the full potential of carbon nanotubes for your specific application.
Contact our team today to discuss your CNT synthesis needs and discover how KINTEK can support your innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the process capabilities of ICPCVD systems? Achieve Low-Damage Film Deposition at Ultra-Low Temperatures
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- Why is a Matching Network Indispensable in RF-PECVD for Siloxane Films? Ensure Stable Plasma and Uniform Deposition
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods
- Why does a PECVD vacuum system require both a rotary vane and turbo pump? Ensure High-Purity Coatings



















