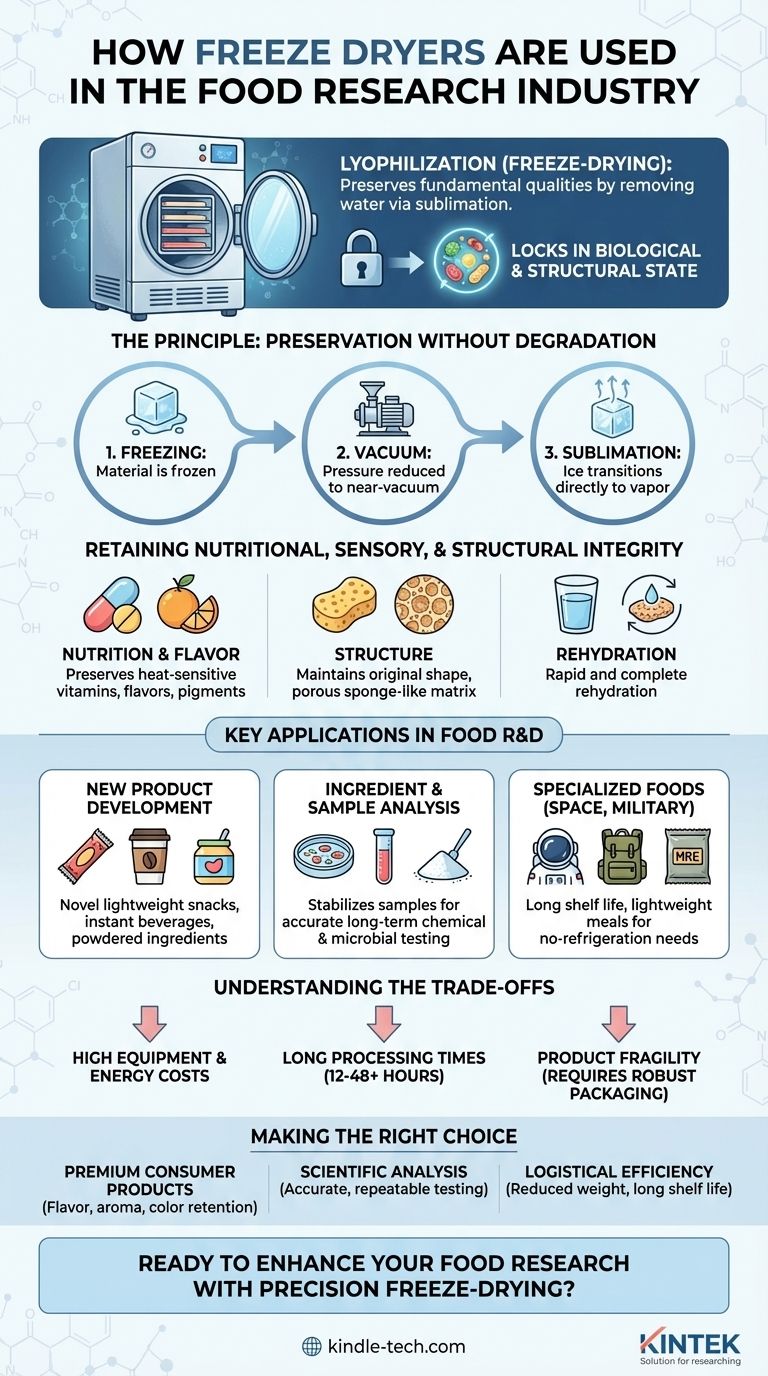
In the food research industry, freeze dryers serve as a critical tool for preserving the fundamental qualities of food products. Researchers use this technology, also known as lyophilization, to remove water from frozen materials via sublimation, creating high-quality, shelf-stable ingredients and finished goods that retain their original color, flavor, nutritional value, and texture far better than with heat-based drying methods.
At its core, freeze-drying is more than a simple preservation technique; it is a research instrument that "locks in" a food's biological and structural state. This allows for precise sample analysis and the development of innovative products that are impossible to achieve through conventional dehydration.

The Principle: Preservation Without Degradation
The value of freeze-drying in a research context stems from its gentle, non-destructive process. Unlike ovens or air dryers that use heat, which alters chemical compounds and damages cell structures, freeze-drying preserves the material's integrity.
How It Works: Sublimation
The process involves freezing the material and then reducing the surrounding pressure to a near-vacuum. This allows the frozen water to transition directly from a solid (ice) to a gas (vapor) without passing through a liquid phase.
This avoidance of liquid water is crucial, as it prevents the migration and degradation of sensitive compounds and protects the physical structure of the food.
Retaining Nutritional and Sensory Integrity
Heat can destroy heat-sensitive vitamins, alter flavor compounds, and degrade natural pigments. By operating at low temperatures, freeze-drying is the premier method for preserving these essential qualities.
This allows researchers to create products, like instant coffee or powdered spices, that deliver an experience remarkably close to the original fresh ingredient.
Maintaining Structural Form
Because the water is removed from an already-frozen structure, the process leaves behind a porous, sponge-like matrix. This preserves the food's original shape and size.
This unique structure is responsible for the crisp, light texture of freeze-dried snacks (like astronaut ice cream) and enables extremely rapid and complete rehydration for products like instant meals.
Key Applications in Food R&D
Freeze-drying is not a single-use tool but a versatile platform that enables multiple research and development pathways.
New Product Development
The most common application is in the creation of novel consumer goods. Researchers use freeze dryers to formulate lightweight snacks, instant beverages, powdered ingredients for supplements, and convenient baby food.
The technology allows for experimentation with textures and formats that would otherwise be unachievable, opening doors for market innovation.
Ingredient and Sample Analysis
For pure research, freeze-drying is an essential step in sample preparation. By lyophilizing a food sample, a scientist can halt all biological and chemical activity instantly.
This creates a stable, dry powder that can be stored for long periods without refrigeration before being analyzed for its chemical composition, microbial content, or other properties. It ensures that the test results reflect the sample's original state, not one degraded by time.
Creating Foods for Specialized Needs
The combination of long shelf life and low weight makes freeze-dried foods ideal for specific logistical challenges.
Applications include developing nutrient-dense, lightweight meals for astronauts, hikers, and military personnel, where storage space and refrigeration are non-existent.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, freeze-drying is not the solution for every application. A clear understanding of its limitations is crucial for any R&D professional.
High Equipment and Energy Costs
Freeze dryers are complex machines that are significantly more expensive to acquire and operate than conventional ovens. The process of maintaining a deep freeze and a strong vacuum is highly energy-intensive.
Long Processing Times
A typical freeze-drying cycle can last anywhere from 12 to 48 hours, or even longer, depending on the product and equipment. This low throughput makes it a less viable option for high-volume, low-margin products.
Product Fragility
The porous structure that provides a pleasing texture and rapid rehydration also makes the final product very brittle. Freeze-dried foods often require specialized, robust packaging to prevent them from being crushed into powder during shipping and handling.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding whether to use a freeze dryer depends entirely on your project's priorities and constraints.
- If your primary focus is premium consumer products: Use freeze-drying to maximize the retention of flavor, aroma, and color for a superior final result that commands a higher price point.
- If your primary focus is scientific analysis or quality control: Use freeze-drying as the gold standard for stabilizing samples and preserving their original chemical composition for accurate, repeatable testing.
- If your primary focus is logistical efficiency for specialized applications: Use freeze-drying to dramatically reduce product weight and achieve a multi-year shelf life without the need for refrigeration.
Ultimately, freeze-drying empowers researchers to preserve the very essence of a food, whether for precise scientific measurement or for creating an exceptional product experience.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| New Product Development | Creates lightweight snacks, instant beverages, and ingredients with superior sensory qualities. |
| Ingredient & Sample Analysis | Stabilizes samples for accurate, long-term chemical and microbial testing. |
| Specialized Foods (e.g., Space, Military) | Achieves long shelf life and minimal weight without refrigeration. |
| Trade-offs | High equipment/energy costs, long processing times, and product fragility. |
Ready to enhance your food research with precision freeze-drying? KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment, including freeze dryers, to support your R&D in creating innovative products and ensuring accurate sample analysis. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory's needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulsating Vacuum Desktop Steam Sterilizer
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What are the key factors that influence the price of a lab freeze dryer? A Guide to Capacity, Performance & Features
- How can budgetary constraints be managed when purchasing a lab freeze dryer? A Strategic Guide to Cost-Effective Investment
- How does capacity affect the price of a lab freeze dryer? Find the Right Fit for Your Lab
- What is the significance of freeze dryers in biotechnology? Preserving Life-Saving Samples for Research
- What factors should guide the final decision when choosing a lab freeze dryer? Match Your Science to the Right Specs



















