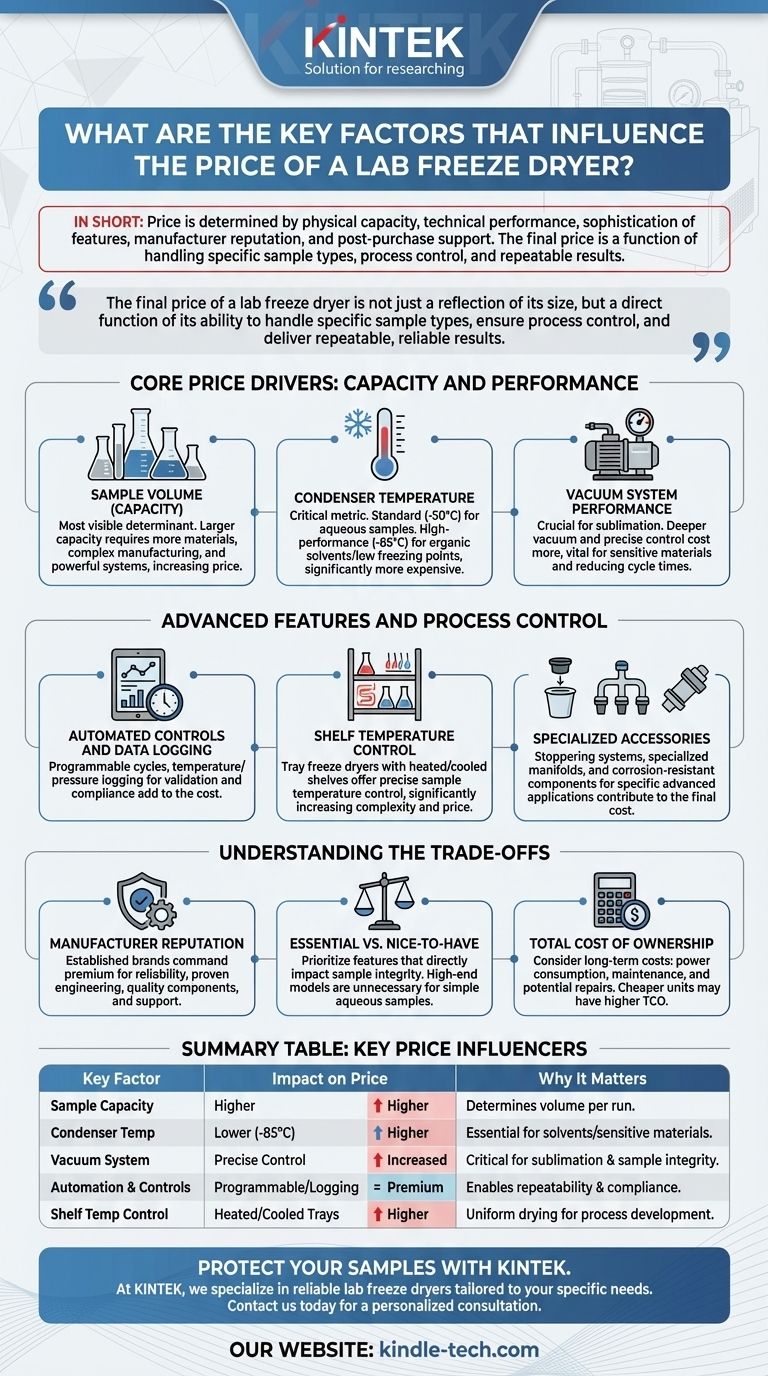
In short, the price of a lab freeze dryer is determined by its physical capacity, its technical performance capabilities, and the sophistication of its features. The manufacturer's reputation and the level of post-purchase support also command a premium, reflecting the value of reliability and quality engineering.
The final price of a lab freeze dryer is not just a reflection of its size, but a direct function of its ability to handle specific sample types, ensure process control, and deliver repeatable, reliable results.

Core Price Drivers: Capacity and Performance
The most fundamental factors influencing cost are the machine's physical size and its core performance specifications. These elements define the raw capability of the unit and are the primary cost drivers.
Sample Volume (Capacity)
Capacity is the most visible price determinant. It refers to the volume or surface area available for processing samples in a single run.
Larger capacity units require more materials, more complex manufacturing, and more powerful refrigeration and vacuum systems, all of which directly increase the price.
Condenser Temperature
The cold trap (or condenser) temperature is a critical performance metric. Standard units typically reach -50°C, which is sufficient for aqueous samples.
High-performance models capable of reaching -85°C or lower are significantly more expensive. This capability is essential for samples containing organic solvents or materials with very low freezing points, as it ensures efficient trapping of vapors.
Vacuum System Performance
The vacuum pump and control system are crucial for the sublimation process. A system that can achieve a deeper vacuum level and maintain precise control throughout the cycle costs more.
This level of control is vital for sensitive biological materials and for optimizing the drying process, ensuring sample integrity and reducing cycle times.
Advanced Features and Process Control
Beyond core performance, the level of automation, control, and specialized accessories adds significant cost. These features move a freeze dryer from a basic appliance to a sophisticated scientific instrument.
Automated Controls and Data Logging
Freeze dryers with programmable, automated cycles for freezing, primary drying, and secondary drying are more expensive than manually operated units.
The ability to log temperature and pressure data is critical for process validation, troubleshooting, and meeting regulatory requirements, adding to the unit's cost.
Shelf Temperature Control
Simple manifold freeze dryers, where flasks are attached externally, are the most basic option.
Tray freeze dryers with shelves that can be heated and cooled offer precise control over the sample temperature. This feature is essential for process development and ensuring product uniformity, but it significantly increases complexity and price.
Specialized Accessories
Features like a stoppering system (for sealing vials under vacuum), specialized manifolds, or corrosion-resistant components for acidic samples all contribute to the final cost. Each addition is engineered for a specific, advanced application.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a freeze dryer involves balancing your immediate needs with your budget and future goals. A higher price often corresponds to greater capability and reliability, but not all features are necessary for every application.
Manufacturer Reputation
Established manufacturers with a long history of reliability and innovation command higher prices. You are paying a premium for proven engineering, quality components, and accessible technical support, which can prevent costly downtime.
"Essential" vs. "Nice-to-Have"
It is critical to distinguish between features that are essential for your work and those that are merely convenient.
If you only work with simple aqueous samples in flasks, a high-end tray dryer with a -85°C condenser is an unnecessary and significant expense. Prioritize the features that directly impact the integrity of your specific samples.
Total Cost of Ownership
The initial purchase price is only part of the equation. Consider long-term costs such as power consumption, regular maintenance for the vacuum pump and refrigeration system, and potential repair costs. A cheaper unit may have a higher total cost of ownership over its lifespan.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your specific application is the ultimate guide to selecting the right freeze dryer and justifying its cost.
- If your primary focus is basic academic research with aqueous samples: A reliable benchtop manifold unit with a -50°C condenser often provides the best value.
- If you are working with organic solvents or low-eutectic point samples: Investing in a unit with a -85°C condenser is non-negotiable to ensure sample protection and process efficiency.
- If you are involved in process development or require cGMP documentation: A tray freeze dryer with programmable shelf temperature control and comprehensive data logging is essential, justifying the higher cost.
Ultimately, a freeze dryer is a long-term investment in protecting your valuable samples and ensuring the integrity of your results.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Impact on Price | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Sample Capacity | Higher capacity = Higher price | Determines the volume of samples processed per run. |
| Condenser Temperature | Lower temperatures (e.g., -85°C) = Higher cost | Essential for solvents or sensitive materials. |
| Vacuum System | Precise control = Increased price | Critical for sublimation control and sample integrity. |
| Automation & Controls | Programmable cycles & data logging = Premium cost | Enables repeatability, validation, and compliance. |
| Shelf Temperature Control | Tray dryers with heating/cooling = Higher price | Provides uniform drying for process development. |
Protect your samples and optimize your freeze-drying process with the right equipment. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing reliable lab freeze dryers tailored to your specific needs—whether you're handling aqueous samples, organic solvents, or require cGMP-compliant documentation. Our experts will help you select a unit that balances performance, features, and long-term value. Contact us today for a personalized consultation and see how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your laboratory's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- What is the recommended approach to selecting features for a lab freeze dryer? Match Core Performance to Your Application
- What is the critical temperature in freeze drying? The Key to Successful Lyophilization
- What is a Laboratory Freeze Dryer and what is its primary function? Achieve Perfect Preservation of Sensitive Materials
- What are the overall benefits of freeze drying technology across industries? Achieve Unparalleled Product Preservation
- What are the main components of a laboratory freeze dryer? A Guide to the 5 Essential Systems



















