The most effective approach to selecting a lab freeze dryer is to work backward from your specific application. Instead of getting distracted by a long list of features, you must first define the thermal and physical properties of the samples you intend to dry. This application-first mindset ensures you invest in the capabilities you truly need and avoid overpaying for features that offer no value to your work.
The right freeze dryer is not the one with the most features, but the one whose core performance—condenser temperature, capacity, and vacuum control—is precisely matched to the demands of your samples and workflow.

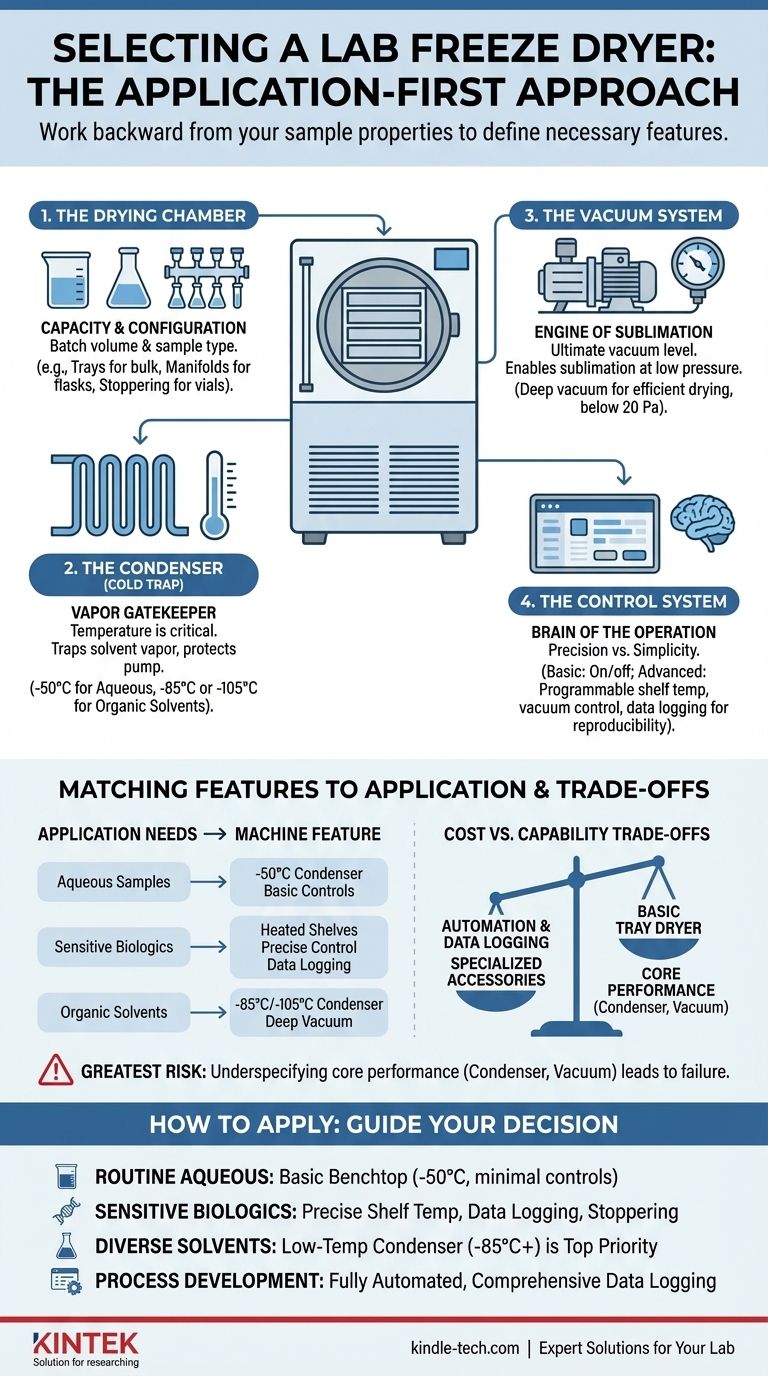
Deconstructing the Freeze Dryer: The Four Core Systems
To make an informed choice, you must understand how the machine works. A lab freeze dryer is an integrated system, and the performance of each part directly impacts the final result.
The Drying Chamber: Capacity and Configuration
This is where your samples are placed. The primary decision here is capacity, which is determined by the volume and number of samples you process in a typical batch.
Configurations range from simple tray-based chambers for bulk material to complex manifolds that hold individual flasks. Stoppering trays, which allow you to seal vials under vacuum, are a specialized but critical feature for pharmaceutical applications.
The Condenser (Cold Trap): The Vapor Gatekeeper
The condenser, also known as the cold trap, is arguably the most critical component. Its job is to freeze and trap the solvent vapor that sublimates from your sample.
If the condenser is not cold enough to trap the vapor, that vapor will travel into the vacuum pump, causing damage and compromising the entire process. Its performance dictates what types of samples you can safely dry.
The Vacuum System: The Engine of Sublimation
The vacuum pump removes air from the system, reducing the pressure inside the chamber. This low-pressure environment is what allows the frozen solvent in your sample to turn directly into a gas (sublimation) at a low temperature.
The key specification is the ultimate vacuum level the pump can achieve. A deeper vacuum is essential for efficient drying and for samples that require very low temperatures.
The Control System: The Brain of the Operation
The control system integrates the other components. Basic systems may offer simple on/off control for the refrigeration and vacuum.
Advanced systems provide precise, programmable control over shelf temperature, vacuum levels, and process duration. These are essential for developing and repeating complex drying protocols, especially for sensitive materials.
Matching Performance Features to Your Application
With an understanding of the core systems, you can now translate your sample requirements into specific machine features.
Condenser Temperature: Protecting Your Pump
The required condenser temperature is determined by the freezing point of your solvent. For purely aqueous samples, a standard -50°C condenser is sufficient.
However, if your samples contain organic solvents (like acetonitrile or ethanol), you need a lower temperature to trap their vapors effectively. For these applications, a -85°C or even -105°C condenser is non-negotiable.
Shelf Temperature Control: Precision vs. Simplicity
Some freeze dryers simply have unheated shelves that rely on ambient energy for sublimation. This is adequate for robust, non-sensitive materials.
For sensitive biologics or pharmaceuticals, you need heated shelves. This feature allows you to precisely control the rate of sublimation, shortening drying times and protecting the sample's integrity. The uniformity of temperature across the shelf is also a critical factor for batch consistency.
Vacuum Level: Reaching the Sublimation Point
The required vacuum level is linked to your sample's eutectic point (the temperature at which it will melt). To prevent melting, the system pressure must be kept below the vapor pressure of ice at that temperature.
A high-performance vacuum pump capable of reaching low pressures (e.g., below 20 Pa) provides a wider operating margin and ensures successful lyophilization for a broader range of products.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Cost vs. Capability
Every feature decision involves a trade-off, most often between capability and budget. Understanding these compromises is key to making a sound investment.
The Price of Automation and Data Logging
Automatic controls and data logging significantly increase a unit's cost. However, for process development, quality control (QC), or cGMP environments, they are indispensable.
These features provide the reproducibility and documentation required to validate a process. For basic, exploratory research, they may be an unnecessary expense.
The Impact of Specialized Accessories
Specialized accessories like manifolds, stoppering systems, or flask attachments expand a freeze dryer's versatility but also add to the initial cost.
Evaluate whether you need this flexibility from the start. A simple tray dryer is far more cost-effective if you only ever plan to dry bulk material.
The Risk of Underspecifying Your Machine
While avoiding overspending is wise, the greatest risk is buying a machine that cannot meet your core scientific needs. A freeze dryer with a condenser that's too warm for your solvents will fail to work and will quickly destroy its vacuum pump.
It is always better to invest in the core performance specifications (condenser temperature, vacuum) than in user-interface conveniences.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Use your primary goal to guide your final decision.
- If your primary focus is routine drying of aqueous samples: A basic benchtop unit with a -50°C condenser and minimal controls is a cost-effective and reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is sensitive biologics or pharmaceuticals: Prioritize a unit with precise shelf temperature control, data logging, and potentially a stoppering mechanism for vial sealing.
- If your primary focus is diverse research involving organic solvents: A low-temperature condenser (-85°C or colder) is the most critical feature and should be your top priority.
- If your primary focus is process development or scale-up: Invest in a system with fully automated controls and comprehensive data logging to ensure process reproducibility and optimization.
Ultimately, defining your application with absolute clarity is the only way to select a freeze dryer that will be a productive asset for years to come.
Summary Table:
| Core System | Key Feature to Consider | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Condenser | Temperature (-50°C, -85°C, -105°C) | Determines solvent compatibility and protects the vacuum pump. |
| Drying Chamber | Capacity and configuration (trays, manifolds, stoppering) | Defines batch size and sample handling flexibility. |
| Vacuum System | Ultimate vacuum level (e.g., below 20 Pa) | Ensures efficient sublimation for a wide range of samples. |
| Control System | Programmability and data logging | Essential for reproducibility in sensitive or regulated work. |
Ready to find the perfect freeze dryer for your lab?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment, including freeze dryers tailored to your specific application—whether you're processing aqueous samples, sensitive biologics, or working with organic solvents. Our experts will help you select a system with the right condenser temperature, capacity, and controls to ensure efficient, reliable results.
Contact us today for a personalized consultation and let KINTEK be your partner in enhancing your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- What is the critical temperature in freeze drying? The Key to Successful Lyophilization
- What is a Laboratory Freeze Dryer and what is its primary function? Achieve Perfect Preservation of Sensitive Materials
- In which fields is the laboratory freeze dryer commonly used? Essential for Biopharma, Food Science & Research
- What are the advantages of using a laboratory freeze dryer? Achieve Unmatched Sample Preservation
- How does freeze drying extend the shelf life of pharmaceutical products? Preserve Potency and Stability for Years



















