At their core, heating elements are made from materials specifically chosen for their ability to resist the flow of electricity. This electrical resistance forces the energy from the current to be converted directly into heat. A common and advanced type, the PTC heating element, is constructed from specialized conductive ceramic materials that have a unique, self-regulating property.
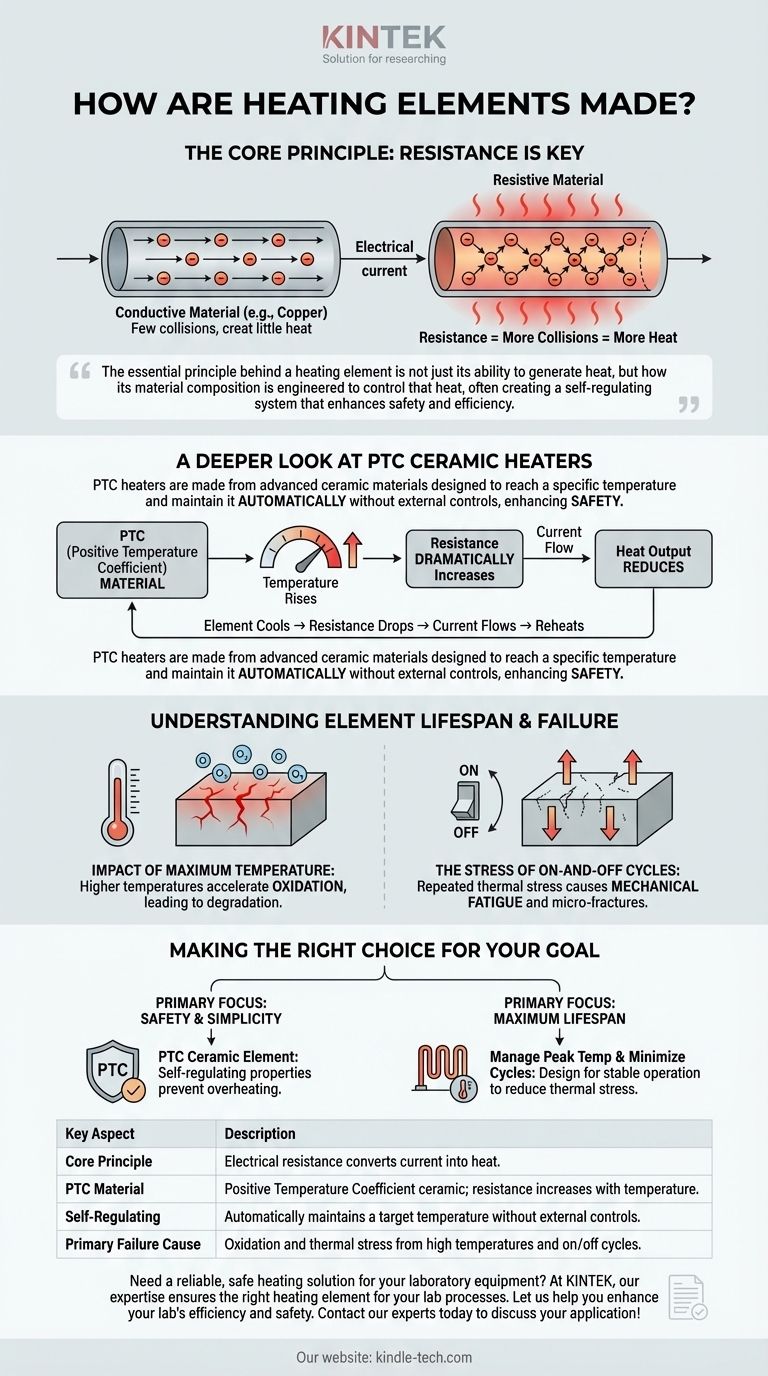
The essential principle behind a heating element is not just its ability to generate heat, but how its material composition is engineered to control that heat, often creating a self-regulating system that enhances safety and efficiency.
The Core Principle: Resistance is Key
How Resistance Generates Heat
A heating element functions based on a fundamental law of physics. When an electric current is passed through a material, the electrons in the current collide with the atoms of that material.
In a highly conductive material like copper, electrons flow easily with few collisions. In a resistive material, however, many collisions occur, converting the electrical energy into thermal energy—or heat.
The Critical Role of Material Choice
The choice of material dictates the element's performance. Different materials offer different levels of resistance and behave differently as they heat up.
Advanced elements use materials like conductive ceramics, which are engineered to change their resistance based on their temperature. This allows for precise and inherent control over heat output.
A Deeper Look at PTC Ceramic Heaters
What is a PTC Material?
PTC stands for Positive Temperature Coefficient. This means the material's electrical resistance increases as its temperature rises.
PTC heaters are made from these advanced ceramic materials. They are designed to reach a specific temperature and then maintain it automatically.
The Self-Regulating Mechanism
As current flows through the PTC ceramic, it heats up rapidly. As it approaches its designed temperature threshold, its resistance dramatically increases.
This rise in resistance restricts the flow of current, which in turn reduces the amount of heat being generated. If the element cools, its resistance drops, allowing more current to flow and reheating it.
The Benefit of Built-in Control
This self-regulating behavior is a key advantage. It enables the heating element to create, maintain, and monitor its own heat without the need for complex external sensors or controls. This makes the entire system simpler, more reliable, and inherently safer from overheating.
Understanding Element Lifespan and Failure
The Impact of Maximum Temperature
The single most critical factor affecting the life of any heating element is the temperature of its hottest point.
Higher temperatures accelerate oxidation, a process where the element's material chemically reacts with oxygen in the air, leading to degradation and eventual failure.
The Stress of On-and-Off Cycles
The ratio of intermittent to continuous operation also plays a crucial role. Each time an element heats up and cools down, it expands and contracts.
This repeated thermal stress can cause mechanical fatigue over time, leading to micro-fractures and ultimately compromising the element's integrity. A continuously operating element held at a stable temperature often experiences less mechanical stress than one that is frequently cycled on and off.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The construction of a heating element is a direct reflection of its intended use. Understanding these principles allows you to select the right technology.
- If your primary focus is safety and simplicity: A PTC ceramic element is an ideal choice because its self-regulating properties prevent overheating without external controls.
- If your primary focus is maximum lifespan: You must design the system to manage the peak operating temperature and, if possible, minimize rapid on-off cycles to reduce thermal stress.
Ultimately, the effectiveness and longevity of a heating element are determined by its core material properties and the operational stresses it endures.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Electrical resistance converts current into heat. |
| PTC Material | Positive Temperature Coefficient ceramic; resistance increases with temperature. |
| Self-Regulating | Automatically maintains a target temperature without external controls. |
| Primary Failure Cause | Oxidation and thermal stress from high temperatures and on/off cycles. |
Need a reliable, safe heating solution for your laboratory equipment?
At KINTEK, we understand that the right heating element is critical for the performance and safety of your lab processes. Our expertise in lab equipment and consumables ensures you get a solution tailored to your specific needs, whether you require the inherent safety of a PTC ceramic heater or a design optimized for maximum lifespan.
Let us help you enhance your lab's efficiency and safety. Contact our experts today to discuss your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Aluminum Oxide Al2O3 Heat Sink for Insulation
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Flat Corrugated Heat Sink for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- High Temperature Wear-Resistant Alumina Al2O3 Plate for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- What kind of metal is used in heating elements? A Guide to Materials for Every Temperature & Atmosphere
- What is a silicon carbide heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat for Industrial Processes
- What is SiC melting point? Discover the Extreme Thermal Stability of Silicon Carbide
- What is the maximum temperature for a SiC heating element? Unlock the Key to Longevity and Performance
- What is SiC elements? The Ultimate High-Temperature Heating Solution



















